We have considered. They found out what they are and estimated the main advantages and disadvantages of these or those types of metal pipes. And today, as I promised, we'll talk about plastic (polymer) pipes. Hello.
Polymer pipes made of polyethylene (PE), polyvinylchloride (PVC) and polypropylene (PP), etc. have been widely used in sewerage and water supply systems recently. To begin with, let's see what is characteristic of all plastic pipes and highlight their main pluses and minuses .
Common advantages of plastic pipes:
Strength;
Durability;
Plasticity and ability to stretch up to 7% while maintaining their qualities;
Excellent dielectric properties (protection from stray currents is not required);
Low thermal conductivity;
Resistance to corrosion;
Slight friction losses (small surface roughness);
Absence of bacteria, decay, decay, calcareous deposits on the walls;
Good sound insulation properties (low noise level);
Easy transport (light weight);
Ease of installation.
Common disadvantages:
Inability to fire water supply systems;
Loss of strength from time and loads;
Do not tolerate visible sunlight;
For various types of plastic pipes, certain assembly and welding devices are required;
Oxygen permeability.
I think we need to clarify what is oxygen permeability. The term seems to be understandable, but still. Under oxygen permeability in this case we mean the diffusion through the walls of a pipe of a small amount of oxygen contained in the air. And what's wrong with that, you say? In the case of a pipeline to feed water to the tap, it's okay that there's a piece of oxygen in the water, no. But in the case if we are dealing with a coolant (antifreeze, water), then the oxygen that gets into it will disable either the boiler or heating appliances, which is not gud. That is, in this case, such pipes will not work for us.
At present, pipes of polyethylene, cross-linked polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene, polybutene and fiberglass are widely represented on the market of plastic pipes.
The service life of plastic pipes is at least 50 years.
Polyethylene pipes (PE or PE)
Pluses:
Low cost;
Light weight;
Ease of installation;
Low thermal conductivity;
Resistance to the effects of various chemical compounds.
Disadvantages:
Flexibility is lower than that of other polymers.
Pipes made of polyethylene are used for internal and external pressure pipelines (sewerage, water supply, drains).
There are 2 types of polyethylene:
1) high pressure polyethylene LDPE (or LDPE - low density polyethylene);
2) low density polyethylene HDPE (or PVP - high density polyethylene).
Pipes made of PVD have less mechanical strength than HDPE pipes, so they have thicker walls and a correspondingly larger mass. This gives a certain advantage to the LDPE pipes: they absorb the noise of the medium transported much better.
Pipes from PVP are widely used for cold water supply systems. These pipes are characterized by very high strength. Frozen inside a high-density polyethylene pipe, water will not damage it, and the pipe, when thawed, will perfectly maintain its operational properties.
Pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene
As a result of various types of processing of polyethylene in order to give it additional strength and resistance to temperature effects between its molecules, cross bonds (the so-called stitching, or bridges). The processing process is called cross-linking, and the material formed after such processing is cross-linked with polyethylene. Cross-linked polyethylene has a characteristic labeling - PE-X (PE-C). There are four types of PE-X, depending on the type of crosslinking: PE-Xa, PE-Xb, PE-Xc and PE-Xd. They differ in the proportion of crosslinked molecules and, consequently, strength. So, of all the above varieties, cross-linked polyethylene with the abbreviation RE-XA has the highest percentage of cross-linking.
Due to high oxygen permeability, XLPE pipes are mainly used for hot and cold water supply. For warm floors and heating systems, pipes with an internal or external diffusion barrier, preventing the penetration of oxygen, are specially designed. The inner barrier is achieved with ethylene vinyl alcohol, and the outer barrier is achieved using an aluminum foil layer having a thickness of 0.1 to 0.15 mm. In addition, due to the use of aluminum foil, a significant reduction in the value of thermal expansion is achieved (these pipes are also called stabilized ).
For the installation of PE-X pipelines, mechanical connectors are used in the form of threaded and press fittings, as well as clamping sleeves of various designs. The installation of RE-X pipes with threaded fittings, in my opinion, is akin to masochism in its pure form: first, it is quite laborious, and secondly, it requires maintenance and control in the process of operation. The tightening of the crimp nuts gradually weakens, which can lead to depressurization of the joint.
Diameters of PE-X pipes presented in the modern market have a small range - 12-32 mm. This is a functional and economic explanation: with a larger diameter, accordingly, a greater wall thickness will also result, resulting in a decrease in the elasticity of such pipes, and the connectors for such pipes will cost considerably more. Do we need it?
Polypropylene pipes (PP or PP)
Polypropylene pipes are rapidly gaining ground in the Russian market. Pressure polypropylene pipes are produced with a diameter of 16 - 250 mm and are used for cold, hot water, heating and sewage systems. Polypropylene pipes and fittings are connected by the method of high-temperature socket fusion.
Like PE-X pipes, PP pipes are presented in the market in the form of both single-layer and multi-layer structures (with a layer of fibrous plastic or aluminum foil). Multilayer pipes are called stabilized. In their labeling there is either the word "stability" or its derivatives. Such pipes less oxygen and have greater stability of shape (have a smaller linear expansion).
Pluses:
Pipes made of polypropylene are hygienic, non-toxic and do not impart foreign smells and tastes to drinking water;
Durability: service life for cold water - more than 50 years, for hot - more than 25 years;
Absence of corrosion;
Small cost in comparison with metal pipes;
Ability to extinguish vibration and noise;
Easy welding and easy installation;
Resistant to pressure and temperature changes;
Low coefficient of hydraulic resistance;
Low level of heat losses.
Disadvantages:
For installation, additional equipment is required;
The service life drops sharply under the influence of ultraviolet rays.
There are several types of pipes from different types of polypropylene:
PP-H (PP-type 1 or PP-G) are made of homopolymer and are mainly used for cold water supply systems;
PP-B (PP-type 2 or PP-B) are produced from the block copolymer. They are stronger and better tolerate negative temperatures (down to -40 ° C). They are used both for cold water supply systems and for floor heating systems;
PP-R (PP-type 3 or PP-P) - they are made of a random copolymer with high strength, tightness, elasticity, resistance to high temperatures, practicality and ease of installation and welding. Polypropylene of the third type is also resistant to contact with various media passed through polypropylene pipes in the liquid or gaseous state. Random-copolymer pipes are used in systems of hot and cold water supply, water and underfloor heating.
There are 3 main types of PP-R polypropylene pipes that differ in operating pressure:
PN 10 - are intended for use in cold water supply systems operating at a pressure of 1 MPa;
PN 20 - are used for cold and hot water supply pipelines operating at a pressure of 2 MPa at a temperature of 20 ° C; 0.6 MPa - at a temperature of 75 ° C;
PN 25 - reinforced, multilayer, stabilized pipes; They are used both for hot and cold water supply pipelines and for heating with a pressure of 2.5 MPa at a temperature of 20 ° C; 1.0 MPa at a temperature of 90 ° C.
Polybutene pipes (PB or PB)
Polybutenein many respects similar to polyethylene and polypropylene, but it is able to withstand both lower and higher temperatures and has increased flexibility. It can either be connected with threaded or press fittings, or can be welded in a thermal way.
Pipes from polyvinylchloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride is a thermoplastic material. It is obtained by polymerization of vinyl chloride.
Pluses:
Cheapness compared to other plastics;
The thermal elongation is almost half that of polypropylene;
Natural oxygen permeability;
High strength;
Chemical resistance;
Resistance to abrasion.
Disadvantages:
Stiffness is higher than that of other plastics;
The use of glued joints during installation (polydiffus gluing method) complicates, lengthens and increases the cost of the installation process;
Flammability;
Increased toxicity.
There are 2 types of polyvinyl chloride:
PVC-U (NPVC) - unplasticized polyvinyl chloride;
PVC-C (CPVC) is chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (has a higher plasticity than PVC-U).
Application: in cold water supply systems, non-pressure drainage (internal and external) and drainage. Since polyvinyl chloride is destroyed under thermal influence with the liberation of chlorine, pipes from of this material Do not use in hot water systems. At elevated operating temperatures, chlorinated PVC is used.
Pipes from fiberglass
The basis of the walls of fiberglass pipes is fiberglass, the filler is a polyester or epoxy resin. With the use of these materials, it became possible to obtain strength characteristics comparable to steel pipes, while the fiberglass pipes are about four times lighter. Despite the fact that such pipes have been produced in our country for more than 20 years, they have not been widely used. The reason is both in the absence of a reliable and fast way of joining pipes and fittings, and in the insufficient assortment of fasteners and fittings.
Products made of polymers have become firmly established in everyday life. The field of application of plastic pipes is very extensive. They are used in the construction of major highways, delivering water, oil and gas. Without them, the construction of a private house can not be avoided, such as the laying of sewers, water pipes, installation of drains.
Plumbing from plastic pipesThere are varieties of plastic pipes, because in the production of a different polymer is used.
Varieties of products
The main types of plastic pipes are conventionally divided into the following:
- from polyvinyl chloride;
- polypropylene;
- polyethylene products;
- from a metal polymer.
Let us consider in detail the types of plastic pipes.
Polyvinylchloride models
This type of material is characterized by a high level of fire resistance - it does not burn in the air. Low frost resistance - up to -15 degrees and low melting point - at 100 it "melts", and at 260 melts. Nevertheless, the material is resistant to bending (100 MPa) and tensile (80 MPa).
Plastic pipesTechnical characteristics of products:
- to withstand pressures of up to 120 atmospheres, due to excellent indicators of ring stiffness.
- Low threshold of resistance to negative temperatures. Because the highway needs to be insulated.
- Resistance to deformation: when heated to an acceptable level, the product lengthens only by 5% of its original size. But at a temperature of +78, the shape is lost.
- Smooth outer and inner surface. Due to this characteristic of the product at a minimum clogged.
- Light transmittance of the material and ability to resist exposure to ultraviolet.
Does not change the properties of water transported through the water. For communications, delivery of both drinking and industrial water is possible.
A high percentage of slip allows the use of plastic pipes for laying a long sewage system.
Polypropylene products
The properties of this type of pipe depend on the source material. The most demanded products are made of polypropylene with the ability to withstand high temperatures. This material belongs to the category of thermoplastics, it is resistant to the action of solvents. The temperature range ranges from 10 to +90 degrees. When the water freezes, the pipeline does not burst because of the elasticity of the material. In addition, during processing, no harm is caused to the surrounding nature.
Advantages of models from polypropylene:
- Availability of the price.
- Simplicity of installation in comparison with metal pipes. For fixing, it is sometimes sufficient to use a plastic pipe clamp.
- Elasticity of the material, which makes it possible to use it in various systems (including for the installation of warm floors).
- Chemical inertness, which allows you to deliver drinking water without changing the characteristics of the composition.
- Resistance to corrosive processes. Long life without reducing the internal diameter due to clogging. Absence of condensation on the surface.
- Resistance to pressure and temperature changes.
- High levels of sound insulation limit noise when water flows through the system.
- Easy maintenance - the surface of the outer plastic pipes does not require painting.
The ability to withstand the effects of high temperatures, can be used in a heating system.
Application of plastic pipes for greenhousesPolyethylene products
From the school chemistry course it is known that polyethylene repels water. In the production process, the inner surface of the pipe becomes smooth, which prevents clogging and siltation of the system.
Products from this material produce two types:
- plastic pipe of non-pressure type;
- pressure pipe.
Advantages of water supply:
- Long-term operation (from 50 to 300 years).
- Resistance to corrosive processes and chemical fluids.
- Absence of consequences of hydraulic shocks.
- It is undemanding in maintenance (painting, lubrication).
- Excellent thermal insulation properties.
- Availability of the price.
Another type are pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene. The products are manufactured by the method of cold pressing. Polyethylene pipes of this kind are durable, do not be afraid of the effects of ultraviolet rays. Suitable for transporting hot water up to +95 degrees.
Pipes from metal polymers
Products of this type are distinguished by high indexes of ring stiffness, heat resistance, inertness with respect to aggressive substances. This is achieved through the combination of metal and plastic.
The construction of the metal-plastic pipe is as follows:
- extruder extrudes inner shell (cross-linked polyethylene);
- a layer of aluminum foil is mounted on top;
- the top layer is glued.
Advantages of the products:
- The use of cross-linked polyethylene has made it possible to achieve greater strength than standard polymer pipes.
- In a state withstand pressure up to 10 bar at a temperature of +95 degrees.
- Slippery internal surface prevents the formation of lime scale and clogging.
- It has antibacterial qualities, which prevents the appearance of mold.
- Ecological cleanliness of the material.
- Low thermal conductivity prevents heat loss during transportation.
- The flexibility of the material allows the installation of a pipeline of any configuration.
Given the technical characteristics, manufacturers give a guarantee for 10 years of service. In practice, the service life is 50 years.
Manufacture of polymer pipes
The production of plastic pipes is different, but mainly enterprises use the extrusion process.
The production process is as follows:
- Granulated.
- In the process, the pellets melt and move into the extrusion die.
- Under the influence of pressure from molten plastic, the product is molded.
- The workpiece is moved to a vacuum calibration chamber, where the diameter is specified and partially cooled.
- In the last compartment, the product is finally cooled, and the workpiece is cut to the required length.
SEE VIDEO
Accurate observance of technological processes is carried out by a logic controller. The extruder system works smoothly and smoothly.
Due to performance characteristics, when laying a water pipe, it is more expedient to use polymer pipes than metal ones. The use of plastics allowed to reduce the cost of production, without worsening the quality indicators.
Two types of pipes, made of non-metallic materials, have recently become the most widespread. It:
- polypropylene pipes;
- metal plastic pipes.
Let's consider two main types of plastic pipes.
Metal-plastic
These pipes consist of three layers of dissimilar materials.- The inner layer is made of cross-linked polyethylene. This is the name of a modified polyethylene with a closed spatial molecular structure. This material has a low roughness, and high heat resistance.
- The second (middle) layer is aluminum foil up to 0.5 mm thick.
- The outer, the most durable and thick layer, is made of polyethylene.
The main feature of the metal-plastic pipe is its ability to bend without critical discontinuities and deformations with a radius of 3 diameters without using special bending methods. And if you bend it with a special spring - you can achieve even smaller bending diameters.
Technical characteristics of a metal-plastic pipe are the best (in comparison with another plastic):
- long operating temperature - up to 95 degrees;
- the maximum short-term temperature is up to 110 deg. (can last for several hours);
- working pressure - up to 10 atmospheres;
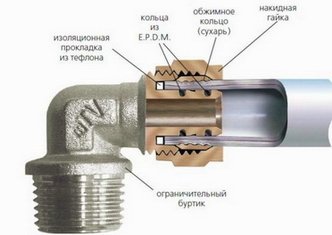
The metal-plastic pipe is available in fixed diameters ranging from 16 to 40 mm (outside diameter) and is sold in coils with a length of 100 meters, which makes it possible to lay long pipelines without connections. This is necessary, for example, in warm floor systems, to create a single circuit without connections.
There are two methods for joining metal-plastic pipes with fittings:
- with the help of crimping
- collet.

The unreliability of the collet joint is due primarily to the temperature deformation of the pipe, which makes the connection weak and requires a tightening.
Therefore, collet connections on metal-plastic pipes should be in open, easily accessible places.
For heating systems, of course, it is better to use compression joints. Also, the increased cost of fittings made of bronze and other metals, limits the popularity of metal-plastic pipes.
Polypropylene
In fact, these pipes can be made from several polypropylene derivatives, for example, from polypropylene-rand material, which, in comparison with conventional polypropylene, has increased ductility, better temperature stability at lower values, lower cost. Advantages of pipes consist in simplicity of installation and connections, at the cheapest fittings made of the same polypropylene. Also, these pipes have increased thermal insulation, relatively low weight and a significant service life (more than 50 years) subject to compliance with technical standards.Characteristics for polypropylene pipes are as follows:
- long operating temperature - up to 75 degrees. (with the appropriate wall thickness);
- the maximum short-term temperature is up to 95 ° C. (may be in the course of several hours);
- working pressure - up to 20 atmospheres (with maximum wall thickness).
There is also, so-called, reinforced polypropylene with a layer of aluminum foil, with the best indicators for heat safety.

Pipes are produced with different wall thickness, for working pressures - 10, 16 and 20 atm. That makes it possible to use them for their intended purpose without unnecessary overpayment.
The diameters of the pipes produced are in the range from 16 to 125 mm (outer diameter). 
Polypropylene pipes are connected by the method of polyfusion welding, or, more simply, by heating. The connection can be of the type of a coupling or a butt joint. For pipes with a diameter above 63mm - only a butt. For welding, a simple and cheap heater is used, and the process of connection does not require the performer special qualification. Fittings and pipes are heated simultaneously, inserted in special shapes, and then connected by molten edges (melting point of about 260 deg.), After which they cool down quickly, forming an indissoluble connection equivalent to the strength characteristics of the pipe itself.
Limitations in the use of plastics
A significant service life of 50 years is a guarantee given by the manufacturer to pipes under normal operating conditions. Namely - working pressure and temperature should not exceed the values of pipes specified in the technical documentation. So you should pay attention first of all to the real characteristics of the systems in which the pipes will be used, and to correlate them with technical characteristics pipelines.By the way, building codes and regulations, the restrictions in heating and water supply systems on the operating pressure and temperature are regulated. So if these real values do not go beyond SNiP, then the pipelines corresponding to the operating conditions of the brand will serve regularly and for a long time.
But there is another warning. SNiPom it is forbidden to heat water over 90 degrees. C in systems where plastic pipelines are used. Therefore, it is better to use plastic pipes in a system where there is a limitation of the maximum temperature of the heat carrier, for example, in individual heating, where the water temperature is limited by the boiler settings, and where such situations are not possible. Alternatively, a thermostatic safety system must be installed in the DHW hot water supply circuit, carrying out a cold water supply to the supplied hot water, and thus protecting the system from overheating.
The pressure is somewhat simpler - the constraints are laid at the level of about 6 atm., Which does not exceed the operating parameters of the pipelines.
Features of operation
When installing and operating the pipeline, one important feature of polypropylene pipes, which is often forgotten, must be taken into account. Namely, polypropylene has a significant coefficient of thermal expansion. The meter section of the pipe when heated not 1 degree is elongated by 0.15 mm. This means that when heated to 60 degrees. (quite normal operating mode), on each meter the pipeline will be extended by 9 millimeters. If the pipe is not allowed to expand, then due to internal stresses it will simply burst. Therefore, it is necessary to mount and place the pipeline, especially of a long length, taking into account these qualities. The breakdown of polypropylene pipes operating in a heating system or hot water supply in the overwhelming majority of cases is not due to overheating and exit for normal operation, but to disruptions during laying.What would be safe from such a negative development of events, in the pipelines make the temperature compensators. In a household, a pipeline with a length of more than 1 meter can not be enclosed in tight confined spaces. Also, there are special designs for polypropylene pipes, in which a layer of aluminum foil is included - something like metal-plastic pipelines. This dramatically reduces the coefficient of temperature expansion - up to 0.025mm / deg.C m, but naturally such pipes will be more expensive.
With metal-plastic pipes in this respect, the situation is somewhat simpler. One meter of metal-plastic is elongated when heated by one degree only but 0.02 mm. This is not so critical, and these pipes are much more plastic, so the metal-plastic pipelines can be used in confined spaces of warm floors. Expansion is dangerous only for joints of pipes with fittings. Therefore, to hide and isolate the fittings of metal-plastic pipes, as it was said before, it is impossible.
After installing the pipeline, do not forget about the simple rules of thermal insulation. This helps to save heat and money. In unheated rooms and on the street, the hot water or heating piping should be properly insulated. The same applies to the cold water pipeline, - heat insulation will prevent heating, as well as fogging pipes.
It should also be taken into account that the construction standards require testing of the newly installed pipeline. Those. after completion of the soldering, one hour is waited, and the tube is filled with a carrier. The test conditions are as follows: pressure - 15 atmospheres, testing time - 1 hour. In this case, the pressure drop in the system is not allowed more than 0.2 atm.
Which plastic pipes to choose.
When selecting and purchasing plastic pipes, read the manufacturer's instructions on the pipe. At normal manufacturers there is a lot of useful information, namely:
- the size of the pipe;
- pipe material. The materials have their own abbreviation. For metal-plastic - PEX-AL-PEX. For polypropylenes - PPH - homopolymers, PPB - block copolymers, PPR-C - random copolymer;
- compliance of the product with the requirements of the standard (DIN);
- working pressure and pipe temperature;
- date and place of manufacture, as well as the name of the company. At the moment plastic pipes are made in Germany, Russia, Czechoslovakia and Turkey.
When purchasing, ask the seller for a certificate of quality. Normal manufacturers supply their products with similar accompanying documents. Checking the certificate, you need to make sure that the validity period has not expired, and the name of the organization is correct. Also in the trading organization you need to take checks to buy and save them. Pipe - the equipment responsible. And in the event of its breakdown and flooding the apartment (!), Only checks for the purchase of poor-quality products will help resolve property disputes.
Add to bookmarks
Application and types of plastic pipes
To date, plastic pipes have a wide enough scope, they are very in demand for various internal engineering systems, namely sewerage, water supply, heating, ventilation, gas pipeline. A number of properties that favorably distinguish them from other species make these products of plastic practically indispensable. So, unlike metal, they do not undergo corrosion, resistance in time does not increase, and their loss of pressure on friction is 30% less. In addition, such pipes are frost-resistant and retain plasticity at a reduced temperature. They have low weight, good throughput, low thermal conductivity. They also have excellent dielectrics and are easy to assemble. The only downside is the low resistance to crushing.
Manufacture of plastic pipes
Plastics are produced from propylene (PP) or ethylene (PVC, PE) carbons that are part of oil and gas. During processing, these low-molecular substances are amenable to polymerization, resulting in the formation of new substances, the number of bonds between the molecules of which increases. Depending on the type of bond formed (linear or spatial) and on the structure of molecules, the plastic is divided into thermosets and thermosets.
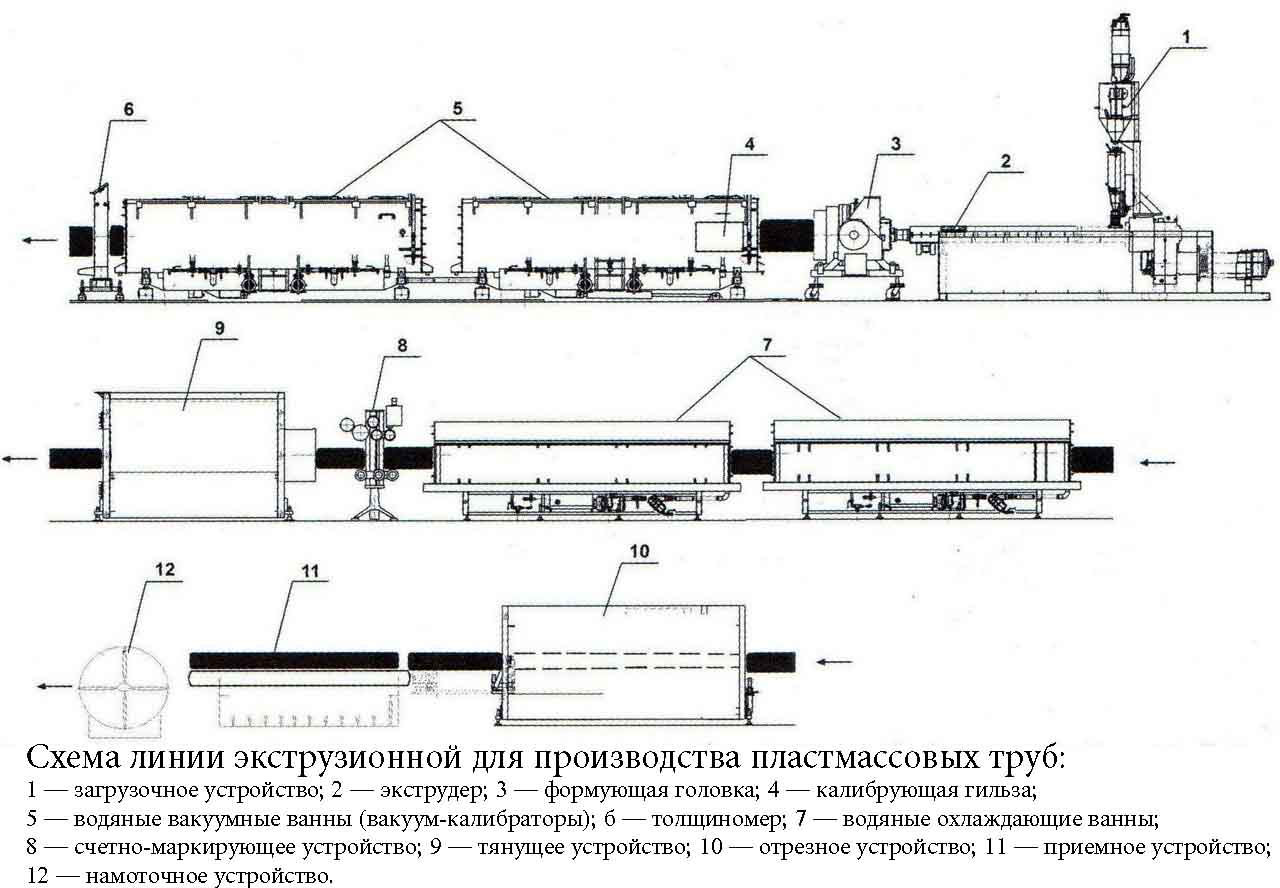
There are several methods of manufacturing plastic pipes, but the main one is the extrusion method.
Thermoplastics (thermoplastic plastics) are formed from homogeneous linear molecules. When heated, they soften, and upon cooling, the former structure is restored again. Due to the low softening temperature (from + 60 ° C), the application area of the thermoplastic is somewhat limited. Reaktoplasty (thermosetting plastics) differ from the thermoplastic composite composition, they do not have a chemically homogeneous structure, and during processing there is an additional "technological hardening", as a result of which additional three-dimensional bonds are created by the molecules. Reaktoplasty is more resistant to high temperatures, but after exceeding the temperature threshold, they are destroyed. Thermoplasts are also less fragile and retain their internal bonds even when completely melted.
There are several methods of manufacturing plastic pipes, but the main one is the extrusion method. In the first production stage, the plastic in the form of granules is fed to the extruder hopper, after which they are melted and transferred to the extrusion die. The form of the future product is already formed there. This happens under the influence of high internal pressure. In the next step, the workpiece enters the vacuum calibration chamber, where the diameter is calibrated directly and cooling begins. In the next chamber, the pipe is completely cooled, after which it is cut into separate parts. The production process at all stages is monitored by a logical controller responsible for manufacturing high-quality products.
Plastic pipes and their types
For the manufacture of plastic pipes, materials such as polyvinylchloride, polypropylene, polyethylene are most often used.
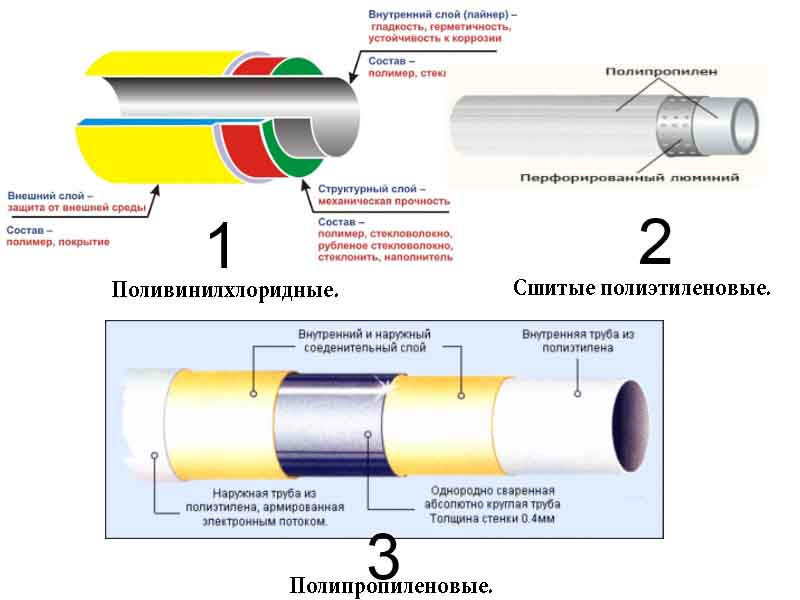
The scheme of the structure of layers of plastic pipes
The most popular are plastic pipes made of polyvinylchloride (PVC). They are able to keep the shape at relatively high heating (+ 80-85 ° C), easily weldable, can dissolve in some solvents, have the lowest coefficient of linear expansion at operating temperature + 60 ° C. They are used in sewerage and water supply systems, in food industry and other technological systems. Installation of PVC pipes is usually carried out by cold welding. They are laid out both in an external and hidden way.
Pipes made of polypropylene (PP) are used for the construction of pipelines for hot and cold water supply, as well as for installing air ducts. They can function at a working fluid temperature of up to + 95 ° C for several decades. Their installation is carried out by diffusion welding, which can be done in just a few minutes, and the design itself has a high seal.

Example of the use of plastic pipes in the plant irrigation system
Polyethylene (PE) pipes are suitable for use at low temperature. They are often used in the creation of external pipelines intended for transportation of drinking and household water, and in addition, a variety of gaseous and liquid substances that do not cause chemical reactions in contact with polyethylene. PE retains its characteristics even at a temperature of -20 ° C, but it should be remembered that the temperature of the transported substances should not exceed +40 ° C., having a diameter of less than 63 mm, is carried out using electrically welded couplings, polypropylene and c. Pipes with a diameter exceeding 63 mm are connected by the butt-welding method, and pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene by the method of permanent jointing or cold pressing, as it is also called.
Metal-plastic pipes, which differ from other types with their three-layer construction, are often used. Between the two layers of plastic is a layer of aluminum foil. It serves as a protection from penetration of oxygen and is necessary to reduce the parameters of thermal linear expansion. is carried out due to compression and press fittings. Such pipes are applicable in pressure and heating systems, since they can be operated at a working medium temperature of up to 95 ° C.

Compared with steel, cast iron and copper pipes, polymer pipes pollute the atmosphere very little during production, require a relatively small amount of electricity, while laying in the ground almost do not pollute the soil.
Application of plastic pipes for sewerage
Due to objective reasons, many types of pipes today are laid out of plastic, rather than metal. Steel is not an exception and sewer. Plastic pipe from PVC due to its resistance to the corrosive effects of substances in the drainage waters, has long consolidated its leadership position in this direction. Among other things, such sewerage is easy to operate, it can easily be disassembled and clean the clogged pipe. And to avoid clogging, leakage and depressurization, you need to choose perfectly smooth products, without burrs, blisters and cracks. Otherwise, it will be possible to face many unpleasant consequences in the course of operation.
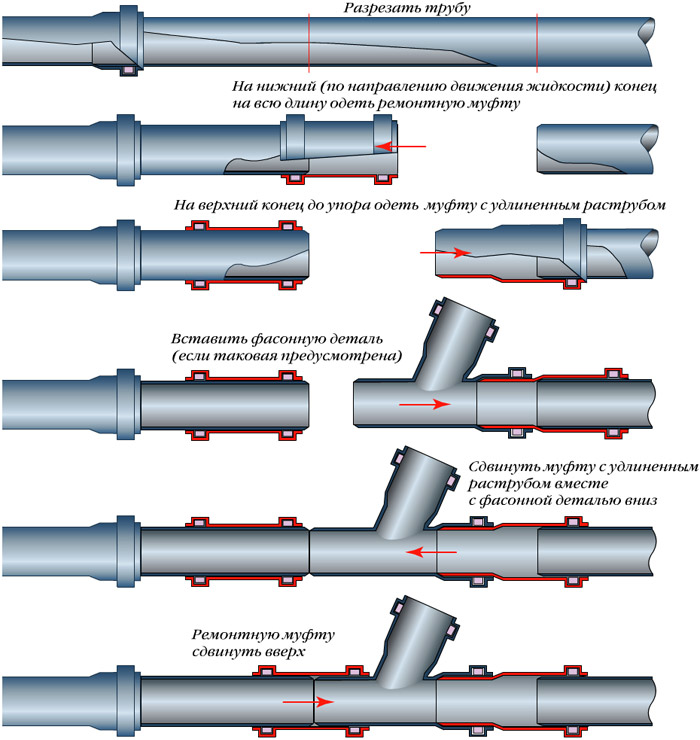
The installation of plastic pipes is quite simple. You just need to insert one tube into the socket of the other, where there is a rubber sealing ring, allowing them to connect without leaks.
Sewer pipes have a different diameter, which should be chosen based on the load. It can be high and low. For example, for multi-family houses, cottages, public facilities, it is recommended to choose a large diameter, designed for increased load. In hotels, hospitals, educational institutions, pipes with a diameter of 200 mm are used, at industrial enterprises - 300 mm. If large loads are not provided for sewerage, a diameter of 50 mm will suffice.
The installation of plastic pipes is quite simple. You just need to insert one tube into the socket of the other, where there is a rubber sealing ring, allowing them to connect without leaks. You do not need to cover anything, mint. If the pipe does not enter the bell, you can warm up its end over the lamp or plate hob. It is important not to overheat and melt the plastic, otherwise the pipe will simply become unusable.
In apartments the plastic pipe is usually mounted in this order:

For general sewerage (faeces and water) at the optimum flow rate (from 0.7 to 1 m / s) the slope is made at the rate of 1-2 cm per m.
- siphon under the sink in the kitchen;
- branch (knee) - a short pipe bent at an angle of 90 °;
- pipe diameter of 50 mm;
- Y-fitting (oblique tee) for connecting the bath;
- again a pipe with a diameter of 50 mm;
- T-fitting (straight tee) for connecting the washbasin;
- pipe 50 mm in diameter, leading up to the entrance to the sewer riser.
When laying the sewage system for private houses, two factors must be taken into account: slope and depth. The slope will depend on the ability of the pipeline to self-clean and the flow rate. For the general sewerage (faeces and water) at the optimum flow rate (from 0.7 to 1 m / s), the slope is made at the rate of 1-2 cm per m. The recommended depth is 70-90 cm at the house, followed by a deepening along the slope, not less than 1 m to the outlet.
Plumbing from plastic pipes
Plastic pipelines are often used for installation of water pipes. The pipes involved in this can be of different types, namely:
- Polyethylene (PE), withstanding operating pressure from 6 to 10 kgf / cm 2 and having the lowest operating temperature (-20 ° C). They are suitable for both indoor and outdoor water supply.
- Cross-linked polyethylene (PEH), which have higher strength and improved temperature characteristics.
- Pipes made of polyvinylchloride (PVC), having high operational properties and a fairly low cost.
- Metal-plastic pipes (PEH-AL-PEH), capable of withstanding pressure up to 10 bar, and their operating temperature is + 95 ° C.

Trenchless laying of plastic pipes for water supply
The main thing when installing plastic pipes is to use short nodes with high rigidity as little as possible, leaving the system as flexible as possible. The minimum number of connections reduces the risk of leakage. Mount the plastic piping to the walls and ceiling is with the help of mobile supports. When they are connected to metal parts, it is necessary to use combined split fittings with metal inserts. On the straight section of the water pipe, more than 3 m in length, it is necessary to install ring compensators, ready-made or welded. If it occurs in the ground, it is important to avoid mechanical impact on them.
At the initial stage of installation, measure and cut off a part of the pipe of the required length, and peel off the butt from the burrs and crumbs. Then mark the depth of the inlet fitting, while not allowing the fitting to move to the stop. In order to avoid distortion, at the junctions of the pipe and fitting, labels are also applied, after which they are put on the heated nozzle of the soldering iron. It is important that both parts are heated simultaneously, and fit as tightly as possible, without turning along the center line. Trub will need 20-30 seconds to fully freeze. The same scheme connects the other constituent elements.
Heating, gas pipeline and ventilation
For a heating system, plastic pipes are chosen for a variety of reasons. First, they serve up to 50 years and can not be corroded. Secondly, due to their smooth internal surface, they do not produce noise during the flow of water through them. In addition, they do not form calcareous deposits. Also plastic pipes have a low thermal conductivity, the water in them cools much more slowly than in metal ones. And they are resistant to pressure and temperature changes.
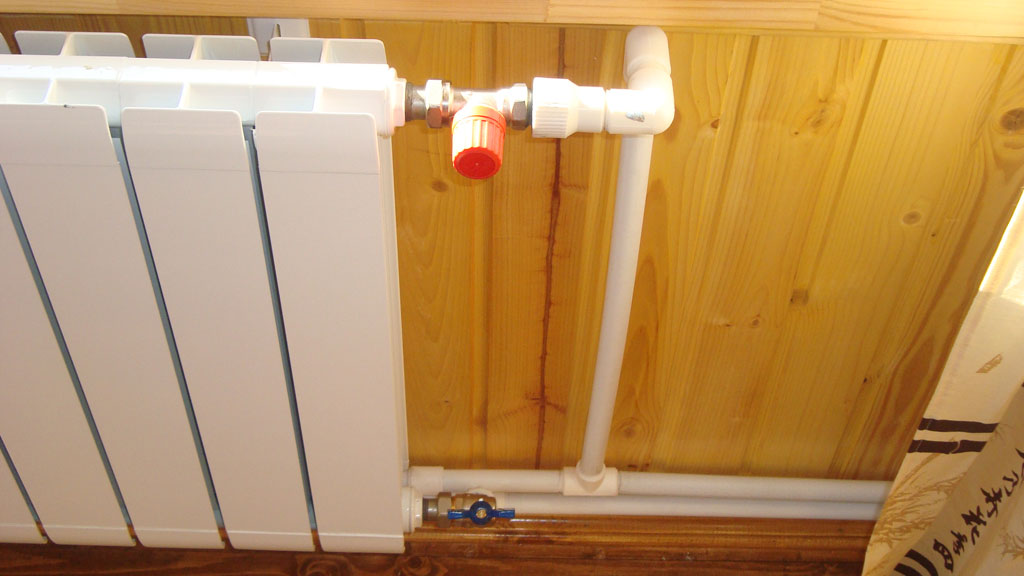

For the heating system suitable metal-plastic pipes, PVC, polyethylene and polypropylene.
For the heating system suitable metal-plastic pipes, PVC, polyethylene and polypropylene. It should be noted that the latter are slightly different from all other types of plastic pipes. So, over time, they can change their shape, because they have high fluidity. And they are deformed even under the influence of their own weight, so you need to increase the number of fasteners or use them only for internal wiring.
As in a number of other cases, they are connected without welding, but only by soldering or fittings. In the case of installing a hidden heating system with use, attention should be paid to the fact that the linear expansion of the pipe section, whose length is 5 m, is 4-5 mm. To avoid damaging the finish of the walls, sufficient number compensators on the pipeline.
If only pipes made of steel were used for laying the gas pipeline 10 years ago, today polyethylene ones are used. They have high resistance to the negative effects of environmental factors and various chemical compounds. The ductility of such pipes is combined with strength, which makes their laying convenient and possible even in regions with harsh climatic conditions. Plastic pipes do not require additional protection before their laying in the ground, because they are already protected from electrochemical damage.
It is necessary to know that plastic pipes are used only for underground installation, and the entry into the house and the distribution of the gas pipeline directly inside the premises is carried out only by steel. In addition, use is prohibited in areas where the air temperature drops to -45 ° C, and seismicity exceeds 6 points. They can not be built inside buildings, in an urban area for transporting high-pressure gas (I and II categories).
Another area of application of plastic pipes is ventilation. This is due to the fact that they provide high reliability of engineering systems and guarantee a high service life. For installation next to the ventilation outlet, a pipe is installed, from which other pipes extend, with a diameter of 160 mm. Sometimes, in order to avoid the appearance of unpleasant smells, plastic pipes are equipped with additional fans, which ensure the maximum speed of air transport. It is advisable to use plastic ventilation pipelines in places of large population, for example, in cafes, restaurants, gyms, fitness clubs.
Pipelines from plastic are widely used. They and connecting parts to them (fittings) are made of high-density polyethylene (LDPE), low-density polyethylene (HDPE), polypropylene (PP) and unplasticized PVC (PVC), sometimes called viniplast.
The industry produces pipes of various diameters in lengths up to 12 m. Polyethylene pipes up to 160 mm in diameter are supplied in coils or coils.
Plastic pipes differ a number of advantages compared with pipes from other materials.
This is a low thermal conductivity, so that less condensate forms on the pipes, they do not so "sweat" in warm rooms. With the same consumption of material, the insulation of plastic pipes is more effective.
This is the best throughput (than steel and cast iron pipes) because of the small friction of the fluid on the smooth surface of the plastic.
This - high dielectric properties, excluding the appearance of wandering currents, destroying metal pipes.
This is light weight, easy machining and welding.
True, pipes made of PVC are less welded, but without difficulty they are glued together. Pipes made of polyethylene are frost-resistant and retain plasticity at low temperatures. If the liquid in them freezes, the pipes will only swell. After the thawing of the liquid, the pipes will narrow again.
However, plastic pipes have a number of serious drawbacks. They are extremely sensitive to mechanical damage. They should be protected from the formation of deep scratches and scratches, which significantly reduce their mechanical strength. As the temperature rises, their strength decreases. Therefore, the temperature of the liquid in the pipe is strictly limited.
Plastic pipes can not be used in hot water and heating systems. In sewer plastic pipes, the temperature of the liquid of permanent effluents should not exceed 60 ° C for LDPE and HDPE, 50 ° C for PVC and 70 ° C for the most heat-resistant of materials - PP. Therefore, when draining boiling water dilute it cold water. This particularly applies to plastic parts in metal sinks and sinks, exhausts, siphons, etc.
To all the problems, the coefficient of linear expansion of plastics is 7 ... 15 times higher than that of steel.
Pipes made of PVC and PP become brittle at low temperatures. All plastic pipes are susceptible to fire. Do not put open flames to them and do not lean them against hot objects. When processing pipes with flames, have a water near them or a wet rag.
The sun adversely affects the pipes. The aging of plastic under the influence of ultraviolet radiation is expressed in an increase in brittleness and a deterioration in the appearance of the outer surface of the pipes. This, in particular, can be noticed by those in whom in the rooms above the windows are hung plastic tubular cornices for curtains.
Polyethylene pipes made of PVD and HDPE are often used for pressurized water pipes [Polyethylene LDPE, obtained at high pressure and temperature, otherwise known as low density polyethylene and denoted by PNP, and HDPE "produced" at low pressure and temperature - high-density polyethylene and designated PVP .].
Polyethylene LDPE is softer and more plastic than HDPE. To slow down the aging process, soot is added to the polyethylene (from here water pipes, siphons and a black knee).
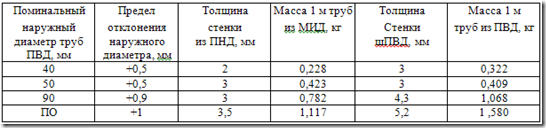
Polyethylene pipes, depending on the permissible water pressure (at a temperature of +20 ° C) are available with different wall thicknesses: lungs A - 0.25 MPa, medium lungs - 0.4 MPa, medium C - 0.6 MPa, heavy T - by 1 MPa. The characteristics of the pipes are given in Table 1.
Table 1.Characteristics of HDPE pipes according to GOST 18599-83, mm
Pipes made of HDPE are produced in lengths from 5 to 12 m with a multiplicity of 0.5 m. Limit deviation of the length from the nominal + 50 mm. The color of the pipes is black. Pipes from PVD are produced with a diameter of up to 160 mm. The walls of these pipes have a larger thickness and correspondingly a larger mass (per 1 m of length) compared to HDPE pipes.
The conditional designation of pipes consists of the name of the material, the diameter of the pipe, the type of pipe, the indication of the purpose of the pipe (for drinking and drinking, it is denoted by the word "drinking", in other cases - "technical"). Pipes marked "technical" for drinking water pipes are not used.
Examples of the symbol:"HDPE 63 LL drinking GOST 18599-83" This should be understood as follows: a pipe made of low pressure polyethylene, with an external diameter of 63 mm, medium-light type, for household and drinking systems. "LDPE 110 T technical GOST 18599-83" is deciphered as follows: a pipe made of high pressure polyethylene, external diameter DN mm, heavy type, for pipes not used for domestic and drinking purposes.
The marking is applied to the surface of the pipe with a heated metal stamp with an interval of approximately 4 m and includes the company's trademark and pipe designation. A label from plywood, cardboard or any other material is attached to each bay, package or block-tube package. On the label, indelible paint is applied transport marking, which indicates the main, additional and information inscriptions. Directly marking of pipes may be supplemented by the date of manufacture, the number of the shift, the line, the code of the apparatchik. Pipes with a diameter of 10 and 12 mm are sometimes not marked.
Pipes made of polyethylene sewage and fittings to them - fittings, are designed for internal sewage systems of houses with a maximum temperature of sewage of 60 ° C and short-term (up to 1 min) - 95 ° C. The main parameters and dimensions of the pipes are given in Table 2.
Table 2.Sewer pipes from HDPE and PVD according to GOST 22689. 2 - 89
An example of the conventional designation of a sewage pipe (TK) with an external diameter of 110 mm, length 6000 mm, of HDPE:
"TK 110-6000-PND GOST 22689.2-89"
The marking of each pipe is made on its surface with an interval of no more than 4 m and contains: the name or trademark of the manufacturer and the symbol. The pipes are produced by straight lengths of 2.0; 3.0; 5.5; 6.0 and 8.0. It is not allowed to weld pipes or fittings made of PVD with pipes or fittings made of HDPE. This will weaken the seam. Estimated service life of pipes and fittings is 25 years.
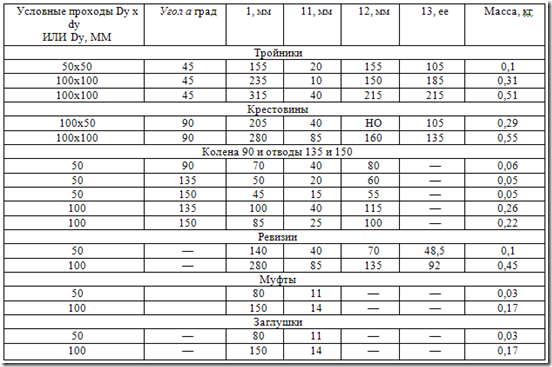
Data on the dimensions and shape of fittings to sewage pipes (Fig. 1) are given in Table 3.
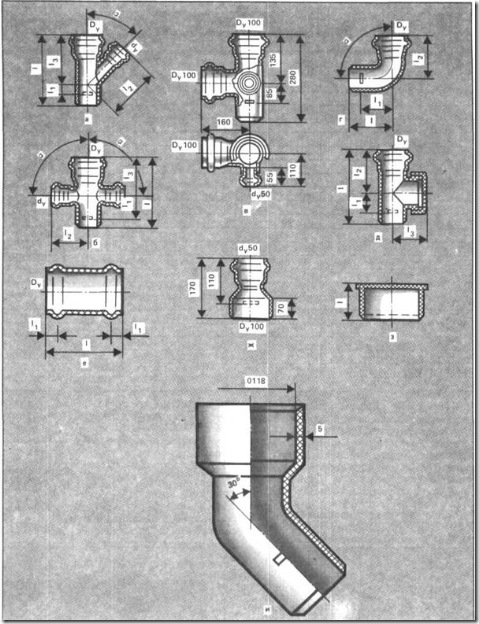
Fig.1. Fittings for plastic sewer pipes: a - tee, b - cross, c - double-spike, g-corner, d - revision, e - clutch, g - clutch, j - plug, and - branch with socket for connection to the toilet
Table 3.Fittings for sewer pipes
Of the total mass of produced plastic pipes, about 20% are corrugated (GT), They have a number of advantages over smooth plastic tubes. Thanks to the "accordion" (Fig. 2), the need for bending is eliminated. The number of fittings is sharply reduced, like the number of pipes. For the corrugated pipes are conducted at the shortest distance. Weight of GT is many times less than smooth-walled. When there is no pressure in the latter, the GT can replace them. For draining, watering and heating of greenhouses the most convenient GT (Table 4).
Table 4.Drainage corrugated pipes made of PVP according to TU 6-19-224-83
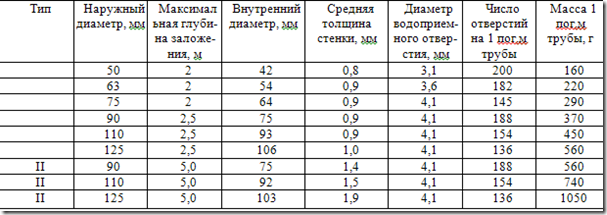
Drainage corrugated pipes made of PVC according to TU 33-291-84 are produced with the same external diameters, but type I - up to an external diameter of 90 mm and with a depth of laying up to 2 m; type II - external diameter of the PO and 125 mm at a depth of laying up to 2.5 m; Type III - with external diameters of 90, 110 and 125 mm with a depth of laying up to 5 m. In addition, the average thickness of the walls of PVC pipes is smaller than that of air defense pipes.
The fittings for corrugated pipes include couplings, adapters, plugs. One type of coupling is shown in Fig. 2.6.

Fig.2. Plastic corrugated pipe: a - drainage pipe, b - coupling
Pipe connectors
Pipe joints are detachable and one-piece. Consider first detachable connections.
The main view of a split connection of non-pressure sewer pipes - Spigot with seal rubber ring (Fig. 3). The bell has an annular groove for the rubber ring, the pipes without the funnels are connected by fittings (see Fig. 1). The industry produces fittings with sockets to plastic sewer pipes.
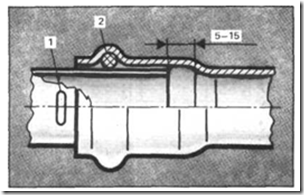
Fig. 3. Fig. Connector socket with rubber sealing ring: 1 - mark, 2 - ring
Here is the sequence of assembly of the bell seal with the rubber ring. At the end of the pipe, a chamfer at an angle of about 15 ° is removed from the outside, Make it a drill file or a knife. The outer surface of the pipe on the connection length and the inside of the fitting is cleaned of dirt. Rubber ring is inserted into the groove of the fitting. The end of the pipe is lubricated with any fat or soap solution and injected with rotation into the fitting. If after assembly the pipe easily turns, means, the ring in its "box", in the groove. The pipe should protrude beyond the ring for at least 10 ... 15 mm. This ensures that the seal is shortened when the temperature drops. The most effective reduction of the ring is 40%, which is ensured by the appropriate selection of the diameters of the socket and the pipe. The value of the immersion of the pipe in the socket is controlled by the label (Fig. 3). To the bottom of the bell, the pipe to be inserted must not reach 10 ... 15 mm to compensate for the temperature expansion.
Transitional fittings join pipes of different diameters, both at an angle and in a rectilinear arrangement. Smooth non-pressure plastic pipes are connected and without a rubber ring. The principle of connection, as in cast-iron pipes. But the plastic pipes are more "soft", so after the annular gap is laid on 2/3 of the depth of the tarred pile or the fat-impregnated string of hemp rope, the remaining 1/3 of the asbestos-cement or special putty is closed. The cement mixture due to the deformability of the pipes will crumble, although the socket flanks near the fastening to the walls can be covered with a cement mixture and a rubber ring (Fig. 4).

Fig.4. Split connection of polyethylene pipe with cast iron sewer: 1 - polyethylene pipe, 2 - cement mortar. 3 - sealing rubber ring, 4 - cast-iron pipe
Flange connections also belong to plug-in connectors. They are of three kinds. The first type includes connections with free flanges. To do this, thickenings in the form of sockets or collars form at the ends of the pipes. After the emergence of the bell or shoulder on one side of the pipe, a pair of flanges are put on the sleeve and thickenings are formed on the other side of the pipe. This is done with each pipe in the thread. When assembling between flanges, a soft rubber gasket with holes is laid and the flanges are tightened with bolts. The tightening of the nuts is made evenly and crosswise (Fig. 5, a).
In the second type, the flanges of the viniplast are welded to the viniplast tubes (Fig. 5.6). It is important to observe the strict perpendicularity of the plane in which the flange is located to the axis of the pipe or fitting. Do not forget about alignment. The rubber gasket does not always compensate for significant misalignments also because the tightening of the nuts is contraindicated, since it causes the destruction of welding.
The minimum length of each bolt is chosen so that after the tightening of the flanges it protrudes from under the nut by 6 ... 12 mm. The internal diameter of the rubber gasket is cut out with an excess of the internal diameter of the pipe by 3 ... 6 mm. The outside diameter of the gasket is limited by the bolts. The tightness of the nuts is determined by thinning the rubber gasket. It lies in the range of 10 ... 25%. The configuration of the collar is shown in Fig. 5a, and dimensions in Table 5, for free flanges - in Fig. 5, in and in Table 6.
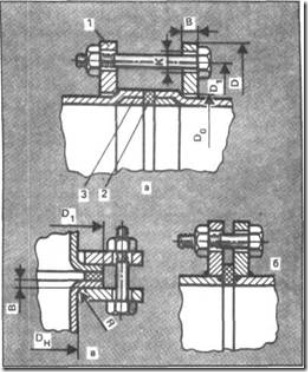
Fig. 5. Split flange connections of plastic pipes: a - flange flanges, delayed flanging of pipe ends; b - viniplast flanges welded to viniplast tubes, c - flare flanges, retained by pipe sockets, 1 - flange, 2 - rubber gasket, 3 - plastic tube cut off from molding.
Table 5.Dimensions of collars, mm

Table 6.Dimensions of free flanges for straight thickened collars, mm

Notes: 1. The denominator gives the outer diameters of the flanges for pressure pipelines. 2. The non-indicated internal DO diameters take a few millimeters more than the outer diameter of the pipe.
In tables 5,6, pipes of large diameters and connections to them are not accidental. These pipes are applicable, say, for the installation of a sewer of a backlash-closet, polyethylene - for a water tank, etc.
The third type of detachable flange connection is one in which a metal intermediate biconical sleeve is installed (Fig. 6). This sleeve and the corresponding tapered grooves on the flanges produce the flanging of the joined plastic pipes. For a quality seal on the bushing, before clamping, you can pull a flat rubber ring, cut off, say, from a suitable car camera. This type also includes a detachable flange connection, as if an intermediate single-cone bushing. It is used (Fig. 7), when it is necessary to combine a plastic pipe with a flanged stop valve, for example, a valve type. When the pipe to be joined is metal, and even with a flange, a single-cone bushing is welded to this flange. The second flange usually rotates freely on the plastic pipe before tightening. The seal will become more reliable if a rubber gasket is placed between the bushing and the pipe, and in the hole for the pipe on the flange, remove the large chamfer, say 8 * 45 ° or lathe to pierce the cone.
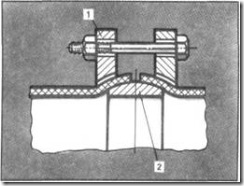
Fig.6. Detachable connection polyethylene pipes: 1 - flange clamping with inner conical part, 2 - double-cone metal bushing
Threaded joints are widely used for plastic pipes. They are molded in a hot condition. Threaded cylindrical threads (GOST 6357-81), thrust reinforced 45 ° (GOST 13535-68), round (ST SEV 3293-81), etc. are used.
For plastic pressure pipes, the maximum thread diameter is G-1 / 2.-A. That is, the pipes have an average outer diameter of 25 mm. A standard connection is also made to these pipes. It consists of a polyethylene (PNP) tube and two union nuts made of plastic or brass (Fig. 8). Flexible piping allows you to connect not coaxially located pipes, both plastic and steel. It is usually installed in comfortable toilets between the flushing cistern and the water supply pipe.
Among the many fittings produced for polyethylene sewer pipes are available with threaded sockets and with clamps for threaded nuts (tables 7 and 8) (Fig. 9).

Fig.7 Plug-in connection of polyethylene pipe to steel pipe: 1 - steel pipe, 2 - flange with outer conical part, 3 - clamping flange with inner conical part, 4 - plastic pipe

Fig. 8. Flexible connection to plastic and steel pipes with 1 / 2V thread: 1 - union nut, 2 - polyethylene tube, 3 - rubber gasket
When co-axial connection of non-pressure plastic pipes and pipes of other materials, two options are possible. First, when the outer diameters of pipes are the same, the second - different. If one of the pipes is cast-iron, then one plastic rubber ring will slide into its socket (Fig. 4). The annular gap is finally cemented with a cement mixture. Rubber rings can be replaced with resin strands, which are tightly crocheted. You can try to connect in the ring the right diameter, for example, rubber tires for baby carriages, rubber hoses or seals for doors of refrigerators, etc.

Fig. 9. Plug-in connection of plastic pipes: 1 - pipe with thread on the socket, 2 - rubber gasket, 3 - plastic union nut, 4 - tube with boutique and centering end
To connect the plastic and asbestos-cement pipes (the second variant) a coupling is used (Fig. 10). Transitional branch pipes and collars are also used here (Figure 1).

Fig. 10. Connection of plastic and asbestos-cement pipe: 1 - plate, 2 - plastic pipe, 3 - asbestos-cement pipe, 4 - rubber gasket! 5 - yoke
It is very important to prepare the bed for the pipes in such a way so as not to disturb their alignment during operation. This condition is also decisive for connecting pipes of different diameters, that is, for the second variant. Rubber rings still allow a small departure from the alignment of the pipes, but the cement will begin to crumble and, as a result, flow. Therefore, at large construction sockets are sealed with UT-37A sealant.
Table 7.External thread of sockets, according to GOST 22689.2-89, mm
Non-detachable pipe joints
These include welding for LDPE, HDPE, PP, PVC, and gluing for PVC. To the pipes of the first three kinds of plastics are used for joining butt welding. It reliably holds pipes with a wall thickness of at least 4 mm. Pipes of any thickness are connected to the socket.
Before butt welding, the ends of the pipes are cleaned with a file and coaxially positioned, fastened in any way. Between the ends of the pipes a heating device 4 is inserted (Fig. 11). Its temperature is adjusted to approximately 200 ° C. When fusing the ends, the device is removed and the pipes are joined under pressure. This pressure must not be weakened until the joint solidifies.
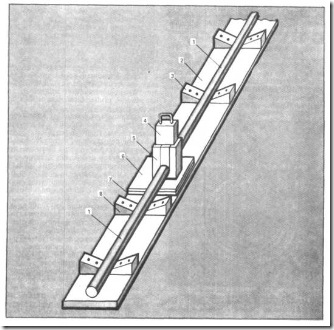
Fig.11. Device for butt welding of plastic pipes: 1 - pipe, 2 - wooden board, 3 - nail, 4 - heating device, 5 - metal guides, 6 - metal sheet, 7 - asbestos board, 8 - wooden rail
A heating device is a disc with a nichrome helix embedded in a chain. The thermostat maintains the desired temperature. The device can replace a large metal washer. It is heated in the flames of a fire, a furnace, a furnace furnace, a gas stove oven, etc. The main condition is uniform heating, this will ensure equal fusion of the ends and a quality connection.
Table 8.Nuts are acc. To GOST 22689. 2-89
Check the temperature of the washer is not difficult. Swipe a piece of pipe along a heated washer. If the dash evaporates within 5 ... 8 s, the temperature for welding is normal.
The joint is more durable when welding into the bell. To create a socket on the lathe, a metal certificate (fig. 12) is cut out according to the dimensions of the diameters of the pipes to be joined. Polish the surface of the mandrel even on the machine. The diameter of its forming part 3 is equal to the outer diameter of the pipe.
Before forming, the pipe end is heated to a temperature of 130 ... 140 ° С. To do this, use a bath with a liquid medium, for example with glycerin, or a furnace with air heating.
At home, this can be done in the oven of a gas or electric stove. Prepare a sheet of roofing steel in size slightly larger than the door plate. In the sheet, cut a circular hole that would be larger than the outer diameter of the pipe by the thickness of the asbestos sheet.
Cover with asbestos one side of the steel sheet. In asbestos, cut a hole equal to that found in the steel sheet.
Heat the oven to 150 ° C. Open the door and lock it on the door of steel and asbestos. In the opening of the door, insert the end of the pipe, wrapped in asbestos. The length of the heated section of the pipe (not wrapped with asbestos) should exceed the desired length of the bell by 20 ... 30%. Eliminate the tube softening time by experiment. Remember that the thermal conductivity of the plastic is very low and that the tube should be slowly rotated.
To heat the ends of pipes, you can use a homemade electric heater. From nichrome or nikilinovoy wire wind spiral with a diameter of turns of 6 ... 12 mm. Depending on the material and the diameter of the wire, calculate its length.
On an asbestos-cement pipe with an internal diameter of 18 ... 35 mm larger than the outer diameter of the plastic pipe, wind the spiral. Install it on the metal stand.
Warm the plastic pipe inside the asbestos cement. For this, the plastic pipes must rest on adjustable supports.
The asbestos-cement pipe can be replaced by a metal tube wrapped with several layers of asbestos board. The softening time of the end of the plastic pipe is selected by experiment.
In such an electric heater, two ends of different plastic pipes can be heated at once.
After softening the end, the tube is positioned so that it is convenient to insert the mandrel (Fig. 12) to the support band. Remove the mandrel after complete cooling.
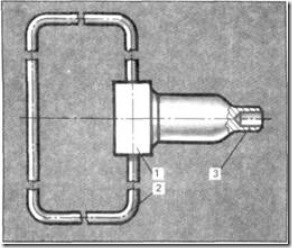
Fig. 12. Metal mandrel for the formation of the socket in the plastic pipe: 1 - body, 2 - handle, 3 - guide and forming part
For reliable connection by welding pipes having at one end of the socket, certain conditions must be observed, as in butt welding. The additional requirement is that the pipe must be firmly inserted into the socket before heating. The device for heating 4 (Fig. 13) has a protrusion called a mandrel, and the hollow is a sleeve. The device must be free, but without significant swinging to enter the pipes. It can be preheated with a blowtorch, a gas oven oven burner, etc. Before heating on the end without a bell, a stopper is put on. As the last, a clamp is used or the tube is tightly wrapped with a metal wire. The stopper does not allow the pipe end to rest against the bottom of the cartridge case, as this causes the part of the hole to melt.
The heated device is quickly transferred to the pipes and the mandrel is inserted into the socket, and the tube is inserted into the sleeve. When pipes on the pipes, at the butt end of the mandrel and sleeve, the annular melted protrusion appears, push the pipes apart. Take out the device and instantly put the pipe into the socket until it stops. From this point on, the connection does not move until completely cooled. That's when the alignment and inertia of the supports are important.
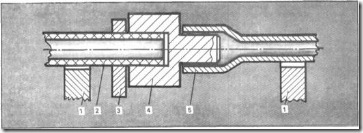
Fig.13. Device for welding into the socket of plastic pipes: 1 - base centering pipe; 2 - pipe with melted end, 3 - stop, 4 - heating device, 5 - inside pipe socket
The tool is turned on the lathe in accordance with the dimensions of the pipes to be joined. The more fundamental the thickness and diameter of the bridge between the mandrel and sleeve, the device holds the heat longer. From metals for the adaptation choose cast iron, bronze, brass. In time, scale is removed. All this will affect the strength of welding.
Instead of the bell, use a piece of pipe with a suitable internal diameter (the material at the pipes is the same). Wrap a piece at the junction of the pipes so that the overlap is not less than 3/4 or the whole diameter of the pipe. Then put two stops. One will prevent the shift of the segment, which is more correctly called the clutch, the second - to restrict the movement of the pipe. Weld the pipe to the coupling - get the bell. Then they act according to the previously stated method.
The industry produces electric couplings in which electric spirals are mounted. Connect the findings of such a coupling to the current source. Heating is completed by fusing and setting the clutch and pipe after the current is cut off. The spiral remains in the coupling.
Pipes from PVC are welded much worse than pipes from PVP and PNP. Therefore, to join the pipes from PVC buttock is not enough just to reflow the ends it is necessary to apply filler material.
At the ends of pipes having a thickness of at least 3 ... 5 mm, a chamfer is removed. Between the coaxially set and converging ends, a gap of no more than 1 mm is achieved. The annular groove is ouked and degreased. In it, insert a ring from the filler rod. Welding is carried out with the help of gas or electric devices that give hot air, and welding is carried out by them.
The electrical device resembles an electric soldering iron. After starting the air, the electric spiral is powered. The air is heated to 200 ... 260 ° С. The temperature is checked with a thermometer or a piece of plastic placed about 10 mm from the nozzle. After a few seconds, a stain should appear on the plastic, a smooth surface will swell slightly. The air temperature is controlled by the air supply from the compressor. The presence of small droplets of oil from the compressor on the heated surfaces will worsen the strength of the seam. To eliminate this, put an oil filter.
A special gas burner for welding plastics is a coil through which air is passed and which is heated by gas.
Applied and conventional burners, fed from gas cylinders used in everyday life. Using them, try not to touch the flame with plastic, and if it flashes up and conceives, a wet rag is applied.
When welding, hot air or flame is directed to the filler material, then to the groove. As soon as softening occurs, the landing rod is "smeared" into the groove. And immediately dock the second pipe.
Pipes from PVC are perfectly glued. The connection is stronger than the welding joint. For gluing use fittings made of PVC or sockets.
There is also a simplified method of forming the bell. At the end of one of the pipes, remove the outer chamfer. The other end of the pipe, which is already joined, is heated and pushed to the first. After cooling the pipe, undo it.
This technique is also applicable when a socket is formed for flange connection of PVC pipes (Fig. 5, a).
Before gluing, the outer surface of the pipe at the end and the inner surface of the socket are treated with a sanding pad. The appearance of the roughness is cleaned with a hair brush and degreased. The pipe is pushed into the socket. If the pipe swings, then the glue GIPK-127 is applied. It consists of polyvinyl chloride resin, silicon oxide and PVC-tetrahydrofuran solvent. In terms of consistency, this composition should resemble a clerical glue. Glue ГИПК-127 is applied by a hair brush with a thin layer on 2/3 of depth of a funnel and on the end of a pipe. The first layer is dried until it ceases to stick to the finger. Apply a second coat. After it has dried, the pipe is injected into the socket and all are allowed to freeze for a day.
For pipes with an external diameter of up to 90 mm, adhesive from perchlorovinyl resin (14 ... 16%) and methylene chloride (86 ... 84%) is used with a minimum gap. For pipes over 90 mm in diameter, glue made of perchlorovinyl resin (14 ... 16%), methylene chloride (76 ... 72%), cyclohexane (10 ... 12%) is used. The same composition is suitable for pipes of any diameter when the temperature exceeds 20 ° C.
Adhesive connection is made and with the help of a sliding sleeve or a suitable piece of pipe made of the same material. There are two options. The first, when the ends of pipes and the inner surface of the coupling or segment are blown, the second one, when the sleeve or the segment is heated without a lubricant, and move on the ends of the pipes covered with glue.
Preparing the glue, note that the solvents of perchlorovinyl resin are weak (methylene chloride, dichloroethane, trichloroethane, acetone) and strong (trihydrofuran, cyclohexanone). With a glue on weak solvents for sampling the gap, the pipes can be calibrated in a specially cut shell. The ends of PVC pipes are heated to 11.0 ... 130 ° C and introduced into the sleeve, which for the speed of operation is cooled by a stream of water or a wet rag.
Pipes connected by glue are ready for installation in 24 hours.
Bending of pipes
Bending of pipes is carried out on the same devices as for steel pipes. If the ratio of the wall thickness to the average outside diameter is more than 1:10 and the radius of bending along the axis of at least 4 ... 5 outer pipe diameters allowed to bend without filler, heating is mandatory.
Bending causes crushing of the pipe walls. The resulting corrugations cause resistance to the flowing liquid, and they accumulate debris that water carries with it. Bending with filler eliminates the appearance of corrugations. The filler is usually replaced with a rubber hose, selected so that it fits snugly into the pipe. For the hose to move more easily through the pipe, it is moistened with water or with liquid fat. The hose is stuffed with sand. The ends of the hose with sand are tied or crushed by a clamp. When bending the pipe, do not stand against the ends of the hose.
The bending points are heated by special gas or electric burners. In their absence, a normal burner with an open flame is used, constantly moving the burner along the heating section and not touching the fire of its surface.
Softening of the material occurs already at 120 ... 130 ° С. The PVC pipe is bent and the rounding is fixed, cooling it with water. Polyethylene and polypropylene pipes are cooled in the open air.
Mechanical restoration
Pipes are cut with a hacksaw or a circular saw with a thickness of 2..3 mm, a pitch of teeth - 3 ... 4 mm and a wiring of teeth 0.5 ... 0.6 mm on the side. Pipes made of PVC are cut at a speed of 600 ... 800 rpm (disk diameter 250 ... 350 mm), made of PVP, PNP and PP - 1800 ... 2200 rpm (the diameter of the disc is 350 ... 500 mm ).
The holes in the pipes are drilled with a drill or a drilling machine. Drills for metal and wood are suitable. Considering the round surface of the rub, before the drilling starts, "hook" the pipe with a hot nail. When drilling on a machine, the feed is manually, slowly, carefully.
It is desirable to process PVC pipes from +17 ... + 22 ° С. Lesser temperatures will cause the formation of cracks, larger - flattening. In polyethylene pipes, the spread of operating temperatures lies in the range from -10 to + 40 ° C.
Stackingexternal networkwater supplyfrom polyethylene pipes
To an individual house can be carried out-laying a water pipe with a diameter of 20 or 25 mm. The depth of the deposit is located below the freezing boundary of the ground. But in any climatic zones this depth should exceed 1 m if the pipes are not covered with concrete blocks, brick, etc.
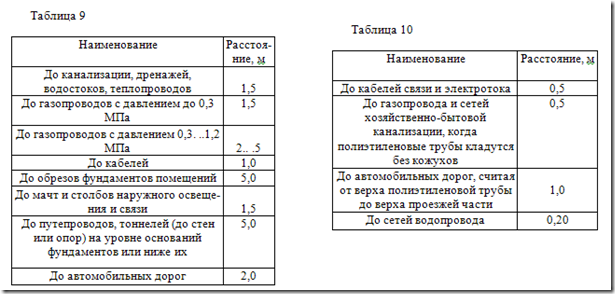
Minimum distances of polyethylene pipes in the horizontal plane-
from other underground networks and ground communications are shown in Table 9.
In the vertical plane, the minimum distances of the polyethylene pipes to the intersecting communications are indicated in Table 10.
The swarm is trenched, the ground is thrown to one side, pipes are laid on the other side of the trench. The bottom of the trench is leveled. If the soil is rocky, pour the sand with a layer 8 ... 25 cm thick. When the distance from the top of the pipe to the soil surface is less than 1 m (due to complex relief or other reasons), the trench and especially its bottom are reduced to a minimum size. Slope of the pipeline in the direction of the lowest point is kept within 0.003 ... 0.005.
The ready pipeline before pressing is necessarily pressed, and they do it in the cold time of day.
Fastening of plastic pipes
Structurally, the fastening elements are the same as for steel and cast iron pipes. But there is a specificity, which is due to the weak mechanical strength of plastic pipes. Electric and gas welding work is not allowed near them. The pipes should not contain inorganic oils and solvents.

Fig.14. Fastening of plastic pipes and fittings; a - valve, 6 - flange connections, c - polyethylene staples, d - clamp, glued to the pipe, e, g - clamping metal staples, з - movable support
Metal fastenings should not have burrs and sharp corners. Between this fastening and the pipe, rubber or felt pads must be placed, which are glued with BF-2, Moment, epoxy or glued to the pipe with twine. For these purposes, a special cushion tape with a width of 27 mm and a thickness of 1.5 mm with a rim of 2.5 mm is made of PVD.
Fixed fastenings (Fig. 14) compensate for vertical loads in risers. Attachments are placed under the sockets or glue the pipe directly to the clamps. In the riser, the fasteners are positioned after 1 ... 1.5 m. The larger the diameter of the pipe, the more often the fasteners.
From polyethylene, it is possible to make fixing brackets by yourself (Fig. 14).
Through interfloor overlappings, walls, pipe foundations are preferably carried out in metal sleeves so that the edges of the sleeves do not damage the pipe walls. For this, thick-walled (not microporous) rubber is placed under the pipe at the edges of the sleeve. The gaps between the pipe and the sleeve are crocheted. The sleeve should not impede the movement of the pipe, so its inner diameter must exceed the outer diameter of the pipe by 10 ... 20 mm. The sleeves themselves are made of metal tubes, choosing the length so that the sleeve 15 ... 30 mm goes outside the wall, floor, etc.
Movable supports are often used for horizontally or obliquely conducted pipes. These supports do not interfere with the temperature elongation of the pipes. The suspension (Fig. 14, h) is the most successful construction of such supports.
When plastic and metal pipelines intersect in the same plane (see Table 9), then the envelope loop is made on a metal pipe.
Pipelines of hot water supply, heating, chimneys near plastic pipes (with a shortening of the minimum distance) are insulated with asbestos or other non-flammable materials with low thermal conductivity. Plastic pipes are always mounted at the very bottom of the vertical plane, in which there are also other hot pipelines.
Shut-off valves (valves, mixers, taps) should not hang on plastic pipes. They are fixed on the brackets (Fig. 14, a, b).
