The VVG power cable is the most demanded and inexpensive conductor of electric current, used practically for all electrical work.
Technical characteristics of the wire depend on its type, marking, the number of cores, cross-section and other parameters included in it.
The VVG wires are manufactured in accordance with GOST 16442-80
Design features
VVG wires are divided by the number of cores. Their 5 species - one - five-core.
1 and 2 category is used for laying a single-phase alternating current network. Wire single-strand is laid parallel in two rows, two-wire - in one row. If one core is connected to the phase, the other wire is connected to 0. In this case, the neutral wire is mostly blue or blue.
Four- and five-core cables are installed in three-phase networks. In the first case, 3 cores are phases, and the fourth is zero. In the other, a ground conductor has been added.
Section
The cross-section for all conductive veins varies between 1.5 and 50 mm2. If they are folded, the cross-section of the wire will be obtained.
- In a single-core VVG cable, the conductor cross-section varies from 1.5 to 240 mm2.
- In a two-four-wire wire the maximum size is 95 mm².
- In the five-core it reaches 50 mm2.
When the cross section of the main veins is increased, the cross-section of the cores of grounding and zero conductors decreases.
All these parameters are indicated in the label of the power wire. Let us give an example.
The VVG 4x cable has the following transcript: 4-wire four-wire. The figure "10" indicates the cross-section in mm².
The most common VVG models are those in which veins with different cross-sections, four- or five-core, are laid.
Design
Modern VVG wires are of different size, type and material.
Conductors consist of 3 main components: conductors, insulation, protective shell. The composition of the individual wires depends on the intended use. As a rule, it is mostly the power aluminum wire VVG used. The design and material depend on 3 main factors:
- Working voltage (network load) and power, from which the thickness of insulation is determined.
- Maximum electric current and resistivity, on which the size of the conductor core and the cross section of the conductor depends.
- Environmental conditions (temperature, laying under the ground or on it, humidity, chemical composition of the environment or the amount of sunlight, etc.) that determine the composition and shape of the outer sheath of the wire.
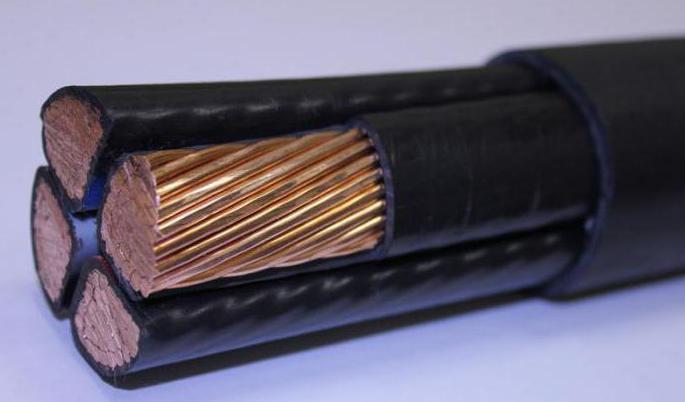
In power VVG wires, stranded aluminum or copper conductors are used, but in small power wires, solid wires can be used.
If the VVG wire is viewed in a section, it can be seen that there are certain differences between the models withstanding the power of 6-10 kV and 0.66-1.0 kV. They are basically the same all the same: insulation of copper wires of different colors (white phase, yellow-green ground, zero blue).
- Metallic and electrically conductive screen.
- Interlayer.
- The shell.
The outer diameter of the cable itself depends on the number of layers of insulation and the number of wires present.

Where is the VVG power cable used?
Power copper cable VVG is used for fixed installation in power networks, where the voltage is up to 1000 W and the frequency is 50 Hz. The VVG conducts wiring along the route. If the installation is carried out outdoors, additional protection from direct sunlight (cable tray, HDPE pipe, etc.) will be required, because the ultraviolet life of the VVG cable significantly reduces. When laying in the ground, additional measures of protection against mechanical damage to the shell are necessary. It should be remembered that in buildings and structures in accordance with the requirements of fire safety VVG paving is prohibited.
Where is the VVGG power wire used?
Non-combustible copper cable ВВГнг is used for stationary laying in electric networks, voltage of which is up to 1000 W and frequency of 50 Hz.
The cable VVGng can be installed in buildings and structures and outdoors. Wiring should be protected from direct sun rays, because ultraviolet can shorten the life. When laying in the ground, it is necessary to use additional means to prevent various mechanical damages.
Where is the VVGG-LS power cable used?
Cable VVG ng-LS It is used for stationary laying in a network with alternating voltage up to 1000 W and frequency of 50 Hz. It is installed in the power supply network in different buildings and structures, it is used for group laying in cable structures, boxes and trays. According to new fire safety requirements, the VVGng-LS wire should not be used in socially significant objects (kindergartens, schools, etc.).

terms of Use
Manufacturers specify certain conditions under which VVG wires can be laid and operated.
- Installation can be performed at an air temperature of at least -15 ° C.
- Operate in the limit -50 C +50 C.
- In non-standard cases, the temperature regime can rise to +70 C., in case of emergencies (short-term), even up to +80 C.
- The permissible humidity is not more than 98%.
- Warranty operating period - up to 30 years. As practice has shown, with proper operation this term can be twice as high.
- Installation can be carried out by air. If the stacking height exceeds 4300 m above sea level, special trestles will have to be used for laying.
- In production, where there is increased corrosive activity, installation must be carried out in special boxes.
Conclusion
The choice of an VVG wire, the characteristics of which are described above, should depend on the power consumption and the current passing through it. So, for lighting can be used VVG cable 2 × 1.5, for the outlet VVG 3X2.5 (with grounding). To connect household appliances, it is recommended to have a separate line. For example, for an air-conditioning unit VVG 4X2.5 or 3 × 2.5.
To the house is best to bring a five-core cable 5 × 10 or 5 × 6.

VVG wire: price
Buy VVGProvod almost any electrical shop. Its cost in most cases is quite low. The average price is 8 rubles per square meter.
The sale can be carried out wholesale and retail. Manufacturers individually offer discounts and ways of delivery. Before buying, be sure to check the certificate of compliance and passport. Remember that the choice of quality material directly depends on the availability of such documents.
Without electricity, it is almost impossible to live today. More and more we are dependent on the availability of electricity, therefore the power network accompanies us everywhere - at enterprises, in public institutions, in houses and apartments, in cottages. Literally everywhere, where a person spends at least some more or less long period of time. And most often for laying the wiring is used VVG cable and its modifications.
Cable VVG: field of application
When laying / replacing wiring, other works on the part of electricians in private houses and apartments, the VVG cable is most often used. This is due to a wide range of applications and a relatively low price. It can be used in electrical networks with voltages no higher than 1000 V and a frequency of 50 Hz (special types up to 100 Hz). That is, it is suitable for single-phase and three-phase networks. It can be mounted indoors and outdoors. When outer liner needs additional protection. It is laid in pipes HDPE, cable trays, etc.
It is not recommended to use its gaskets in the ground, since it does not have armor, which quickly breaks down. If desired, it can be laid in the ground, but in an additional protective shell (corrugated pipe) and / or in the cable duct.
The field of application largely depends on the modification: the type of material from which the sheaths of the cores and the cable itself are made. About this in more detail we will talk a little further.
Explanation and modifications
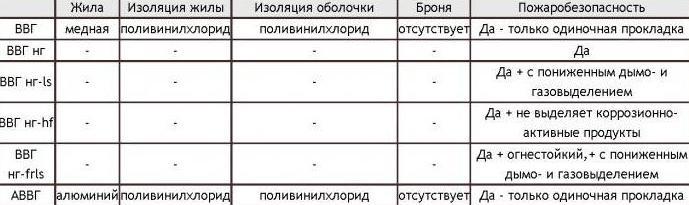
To understand the difference between different types of this cable, you need to know the name decoding. Then it is already possible to decide which species will suit you more.
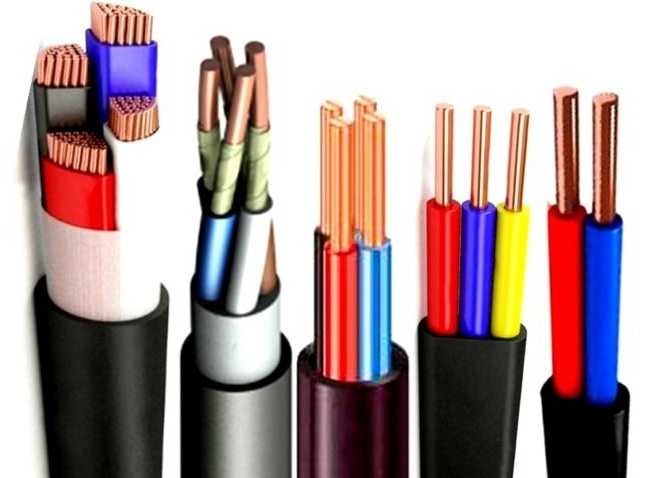

Normal VVG
Explanation of the main abbreviation - VVG - is simple:
- absence in front of the letter A indicates that the veins are copper;
- the first letter "B" denotes the insulation material of the veins - PVC (polyvinylchloride);
- the second letter "B" - the insulation material of the cable - also PVC;
- "G" - speaks about the lack of additional protection (armor or other protective shells).
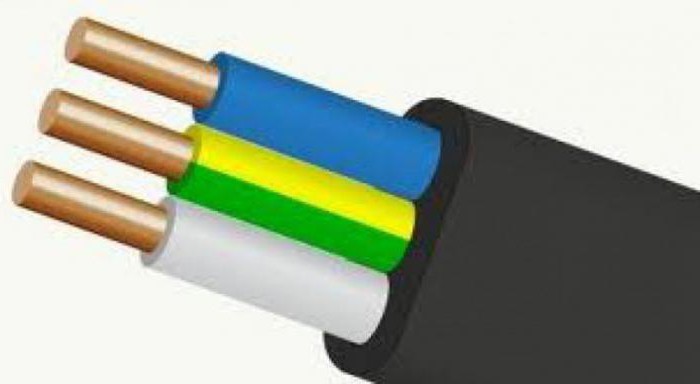
That is, the VVG cable - consists of several copper cores and PVC insulation. Each of the wires has its own color (read the color markings). The conductors are twisted in one plane, protected by a PVC sheath. Conductors can be multi-core or single-core (in the abbreviation is added coolant).
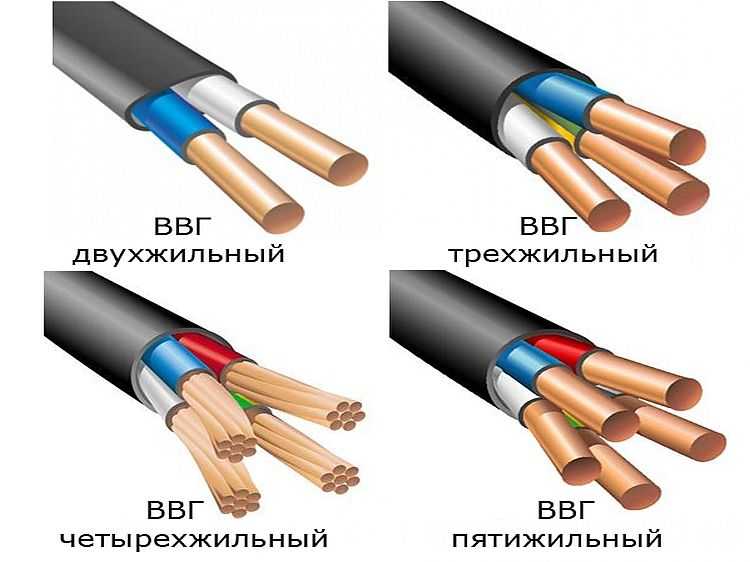
Frequent houses use single-core cables more often. They can have 2, 3, 4 or 5 veins. The cable can be round or flat section, with zero residential (blue) and / or with a residential earth (yellow-green color).
Non-flammable VVGng
In fire-hazardous premises ( wooden houses, bathhouses, etc.) and public buildings (children's and medical institutions, in particular) need cables that do not support burning. In such cases, you can use products with low combustibility - VVGng. The additional letters "ng" just indicate that the shell does not support combustion.
There are several other types of cable VVGng:
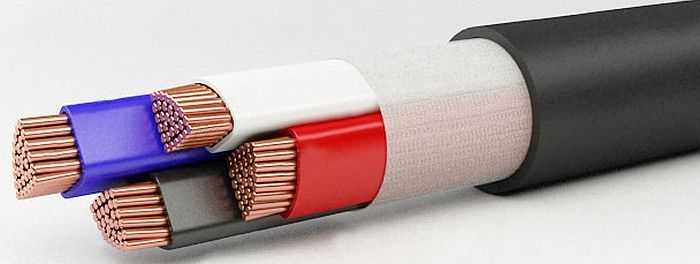
So, what is the difference between a conventional VVG cable from VVGng and its varieties? A conventional VVG conductor does not support combustion with a single gasket. Products with the prefix "ng" does not burn even when grouped - in a bundle with other conductors. The remaining "additions" to the name simply improve the characteristics.
Forms of release
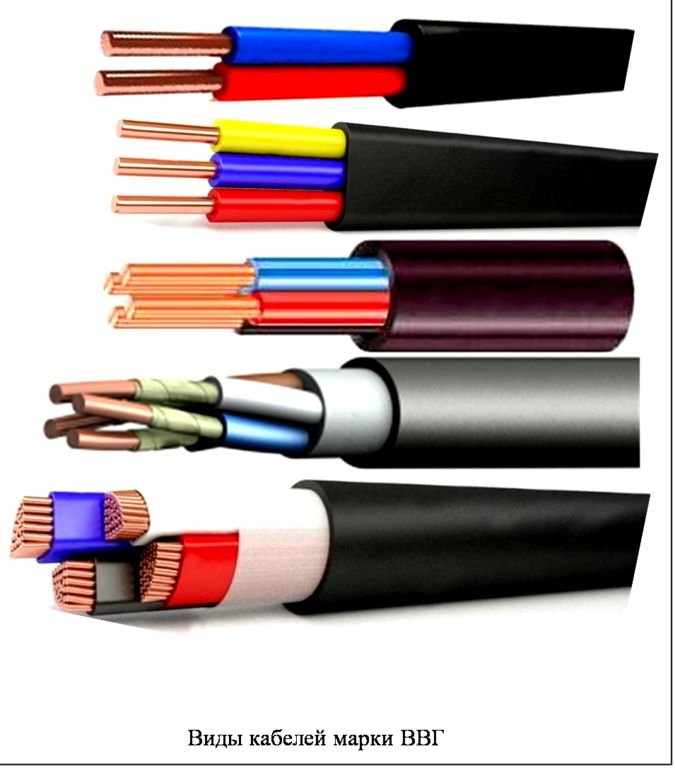
Depending on the number and shape of the cores, the VVG cable can be round, flat, triangular or pentagonal (see photo below).
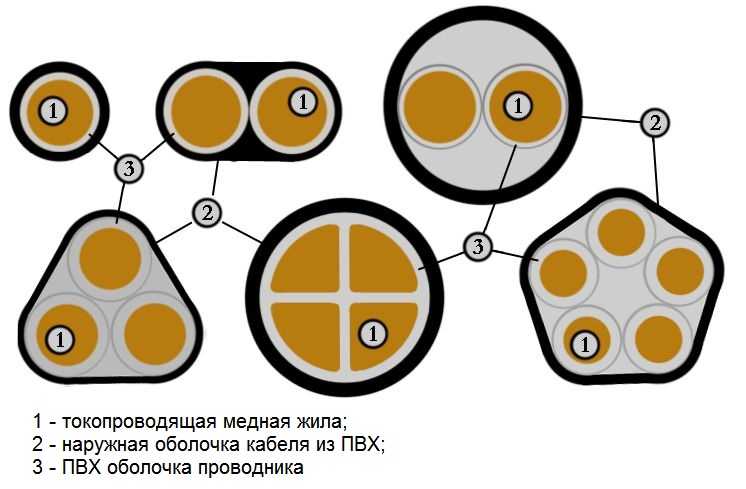
The shells are made of polyvinyl chloride of various modifications. The gaps between the cores are filled with the same plastic material. In some embodiments, a tourniquet of the same material is used. With a small cross-section of the conductors - up to 25 mm2 - it is allowed to release without filling.
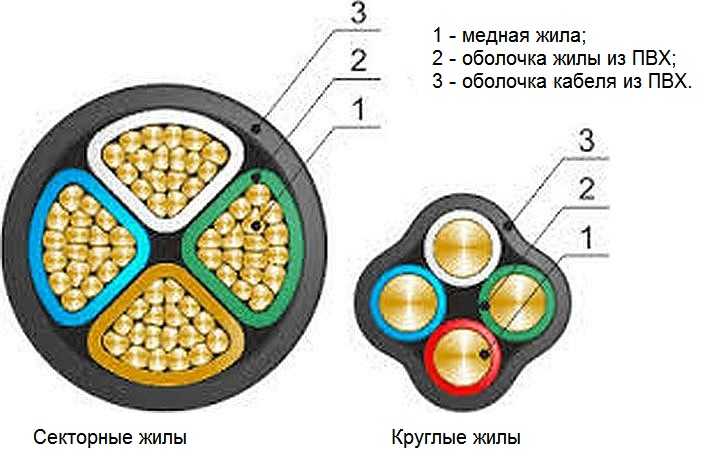
The wires in the cable are round or sectional. Sectional are usually stranded, round - single-core. In any case, their cross section must match the declared parameters (as verified, read).
Technical characteristics of cable VVG
The peculiarities of using different types of cable VVG were described above, but now we are talking about the technical parameters of the conductors of this brand.

It must be said that specifications cable VVG depend not only on the specific type, but also on the manufacturer. Therefore, before buying, see the cable certificate (you can ask the seller). Above are the parameters common to all brands of VVG cables.
Not surprisingly, these conductors are very popular - with good technical indicators they are relatively small, can be used almost everywhere - both in enterprises and offices, and in homes and apartments.
Section and number of cores
Cross-section of cores of VVG cable of any brand can be from 1.5 mm 2 to 240 mm 2. For sale, conductors with cores of up to 35 mm 2 are usually found, the rest, larger sizes must be ordered.
As already mentioned, there are VVG cables with 2, 3, 4 and 5 wires. The number of veins is registered immediately after the abbreviation: VVG 2 x 3.5; VVGng 4 x 4, etc. The first digit is the number of cores, the second is the cross section of the conductor.
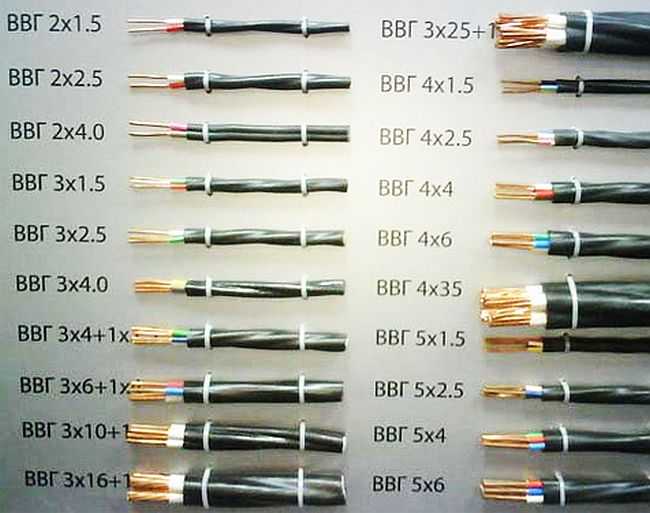

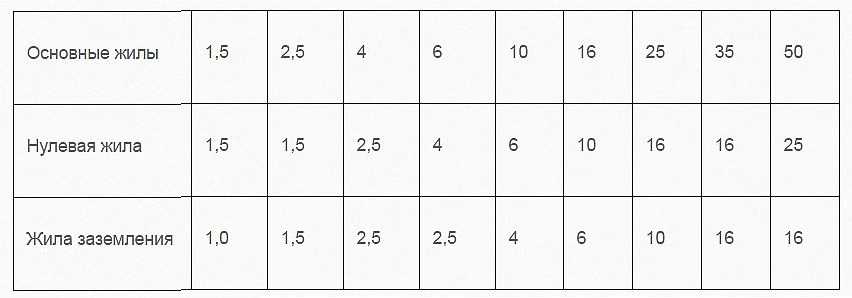
There may be cables VVG with conductors "neutral" and "grounding". And there are options in which the protective wires go the same section, there are - with a smaller diameter (to save copper and lower cost). Most often the smaller size is made by the "earth" conductor, in some cases a little less is done and "neutral". If the protective conductor has a smaller diameter, it is designated as +1. For example, VVGng 4 x 4.0 + 1 (read as 4 wires with a cross section of 4 mm 2 and 1 for a step smaller than 2.5 mm 2). Such variants of VVG cable are also standardized, their parameters are given in the table below.
Continuous current
When selecting the cable cross-section, a more correct method is to use the maximum current. In connection with this, this characteristic is normalized as a long-time permissible current. It depends on the number and cross-section of the veins, as well as on the method of laying - open or closed.
| Conductor cross-section | Continuously permissible current | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| with two main cores | with three main cores | with four main cores | |
| 1.5 mm2 | 24 A | 21 A | 19 A |
| 2.5 mm2 | 33 A | 28 A | 26 A |
| 4 mm2 | 44 A | 37 A | 34 A |
| 6 mm | 56 A | 49 A | 45 A |
| 10 mm | 76 A | 66 A | 61 A |
| 16 mm | 101 A | 87 A | 81 A |
| 25 mm | 134 A | 115 A | 107 A |
| 35 mm | 208 A | 177 A | 165 A |
Two versions of VVG cables are available - with a rated voltage of 0.66 kW and 1 kW.
For power transmission over distances, along with air lines, power cables are widely used. As for electricity supply to consumers in buildings of industrial enterprises, as well as electrical wiring in residential houses, isolated wires and cable lines are used for this purpose. One of the most successful types of such wires, which has been widely used in electrical networks, is the VVG cable.
In general, the power cable is an electrical conductor of a large cross section with one or more cores. Each such vein is covered with a layer of insulation, in addition, they are all enclosed in a protective shell. In some models, protective screens or armor can be used to increase their performance.
During operation, power cables pass very high currents through themselves, so the isolation of their individual live conductors from each other and from the external environment is performed in compliance with the highest reliability requirements.
Transmission and distribution of electricity in low-power households is carried out using copper and aluminum electrical wires, which are much inferior to power cables in reliability and power, but are more compact, convenient to use and cheap.
Characteristics of cables VVG
The description of such products is advisable to begin with the decoding of their abbreviation. Consider it on the example of an VVG 2x4 cable. Explanation of the VVG cable:
- the first letter "B" corresponds to PVC insulation of cable cores,
- second "B" - PVC sheath insulation,
- the letter "G" means the absence of protective covers,
- and the numbers 2x4 - respectively the number of veins and their cross-section.
The maximum temperature at which prolonged use of VVG wires is permissible is +50 C0, the minimum temperature is -50 C0. At the same time, the maximum possible temperature of their heating during overload can reach +80 C0, and in the case of a short-circuit current flowing for no more than 4 s, it is allowed to increase to +160 C0.
We continue to get acquainted with the technical characteristics of the VVG cable, it has several (from one to five) individual copper conductors, which are covered with insulation. If the number of such strands is greater than 2, then all of them can have the same diameter, or one of the cores, intended for zero or grounding wires, may have a somewhat smaller cross-section.
As a material of isolation, in the manufacture of VVG cables, polyvinyl chloride compound or, in short, PVC, is used. This material is a kind of plastic that has high dielectric properties, resistance to aggressive chemicals and low combustibility. There are models of cables, the insulation of which is made of PVC plastic, with improved properties:
- Reduced flammability (VVGng).
- Reduced smoke and gas evolution.
The cores can be produced in one-piece (single-wire) and multi-wire versions. In addition, VVG cables with round and sector (segment) sections of copper cores are distinguished.
The cross-section of each individual core depends on their purpose and the power of the consumers being fed. The VVG cable line provides models whose cross-sections vary from 1.5 to 240 mm2. Depending on the diameter and number of veins, the weight of the VVG cable also varies.
Depending on the functional purpose, the required cross-section and the location of the gasket, VVG cables of various diameters, made in different options: flat, non-flammable, etc.
There are such variants of their marking:
- VVG. A universal option.
- AVVG. With aluminum conductors.
- VVGng. Incombustible.
- VVG-P and VVGng-P. Flat and, accordingly, nonflammable flat.
- VVGz. Filled. It is meant that between the insulated cores there is an additional dielectric filler.
When laying any cable line, there is a need for bends and turns of current-carrying wires. In order to ensure the maximum reliability and durability of such an electrical network, it is necessary to adhere to clearly defined requirements for the maximum bending radius of its conductors. For the brand VVG this parameter is from 7.5 to 15 of its diameters.
Scope of application
The VVG power cable of any cross-section is designed for use in 660 and 1000 V electrical networks with a frequency of 50 Hz. The main purpose of such cable lines is the supply of powerful consumers of electricity in enterprises and industrial facilities, but they can also be successfully used for the installation of domestic electrical wiring (for example, VVG 2X4 and VVG 3X2.5).
Insulation of these products does not allow their laying in places with aggressive environmental impact. These options include:
- In the ground without the use of special boxes.
- In the reservoirs. Although the insulation characteristics of such wires allow them to be laid in places with high humidity, they are not intended for use in water.
- Under the layer of plaster. Since the external insulation of VVG power cables is made of PVC plastic and does not have an additional protective layer, if it is necessary to lay them under plaster, it is better to use the BBG-ng brand.
Despite all the positive qualities of PVC insulation, its essential disadvantage is its poor frost resistance. Therefore, the laying of such lines can not be carried out at temperatures below -15 ° C.
Advantages of VVG cables

Due to their excellent technical characteristics, VVG power cables have the following advantages:
- Providing high quality of transmitted electricity. The main task of any power transmission system is to preserve the electric power quality indicators as much as possible. To do this, the conductors of such a system should have such technical characteristics as low reactive and reactive resistance, as well as high quality of insulation. To date, copper is one of the best materials for use in such systems.
- Non-combustibility. Allows the use of wires of this type in rooms with increased fire hazard.
- High tensile strength of the insulation. It makes it possible not only to protect the electric network from short-circuits in the event of unintended mechanical actions on the wires, but also to ensure the convenience of wiring and the operation of electrical appliances. In addition, products of the BBG brand are characterized by increased resistance to mechanical vibrations.
- High dielectric properties of PVC insulation. This makes it possible to produce reliable and powerful cables of relatively small diameter. According to the regulatory documents, each VVG copper power cable is tested by an increased voltage, the value of which, depending on the rated voltage of the cable, is 3 or 3.5 kV.
- Resistance to moisture. Although such products are not designed for laying in water, however their insulation is sufficiently resistant to the influence of a moist environment. This allows the use of cables of this type in places with high humidity (reaching 98%), which include bathrooms, bathrooms, kitchens, shower cabins, etc.
- High reliability. The VVG power cable, laid in protective systems, such as special cable boxes, corrugated pipes or cable lines, is extremely reliable.
- Long service life. According to the technical specifications, the minimum life of this cable is 30 years.
- Wide range of models. A wide choice of copper and aluminum conductor cross-sections allows to select with a high accuracy the required cable diameter for supplying electrical installations of a certain power. This makes it possible to save money considerably when designing and installing electrical wiring. In addition, the ability to use VVG-P cables (flat) allows you to achieve maximum convenience when performing installation work.
- Convenient color and digital marking of conductors. The phase wire has white, red or brown insulation, the neutral wire is blue, and the ground wire is yellow with a green stripe.
Selection of cable VVG for electrical wiring of the apartment
To power the shield at the entrance to the apartment, as a rule, the power cable VVG 3X6, (can also be 3X10 and 3X16) is used.
Unlike wires ПВС and ШВВП, often used for installation of electric wires, copper cable ВВГ 2Х4 corresponds to higher requirements as it is intended for operation also in the industry. In other words, for VVG 2X4, with an equal cross section, the larger the maximum permissible current, the higher the insulation quality, it much less supports combustion. In addition, each such product undergoes production tests, which can not be said about most of their household counterparts. As for the choice of the type and cross-section of the cable for powering electrical appliances located in the apartment itself, everything here depends, first of all, on their technical characteristics. One of the most common, is the brand VVG 2X4.
Power calculation table
When choosing a cable, you need to know what permissible load each section of the wire. Fold the power of all consumers on the selected power line, take a stock of at least 30% and select the required cable cross-section in accordance with the table.
| Conductor cross-section, sq. Mm | Copper wires | |||
| 220 V | 380 V | |||
| current, A | power, kWt | current, A | power, kWt | |
| 1,5 | 19 | 4,1 | 16 | 10,5 |
| 2,5 | 27 | 5,9 | 25 | 16,5 |
| 4 | 38 | 8,3 | 30 | 19,8 |
| 6 | 46 | 10,1 | 40 | 26,4 |
| 10 | 70 | 15,4 | 50 | 33 |
| 16 | 85 | 18,7 | 75 | 49,5 |
| 25 | 115 | 25,3 | 90 | 59,4 |
| 35 | 135 | 29,7 | 115 | 75,9 |
| 50 | 175 | 38,5 | 145 | 95,7 |
| 70 | 215 | 47,3 | 180 | 118,8 |
| 95 | 260 | 57,2 | 220 | 145,2 |
| 120 | 300 | 66 | 260 | 171,6 |
The disadvantage of VVG cables is their relatively high price, so it is advisable to use them to connect powerful consumers of electricity, for example, electric stoves, cooking surfaces or running water heaters.
Electrotechnical equipment is now on the market in a wide range. Among such products, the VVGng wire is very popular.
Those who decided to implement the wiring of low-voltage internal and external power grids, experienced masters recommend using just this current-carrying equipment. Information on the VVGGG wire and its technical characteristics is presented in this article.
What is the product?
The VVGGG wire is a type of VVG power cable that allows power to be connected to indoor equipment, as well as to external cable structures and electrical appliances. Structurally, the VVG cable (GOST 16442-80) is represented by one or more current-conducting veins, each of which is equipped with its own insulation coating. In the power cable, the strands are twisted together and contain a common insulating jacket.

Abbreviation
The first letter in the electrical current-carrying system indicates the material from which the vein is made. If it were aluminum, then the abbreviation on this wire would start with the letter "A". Since it is absent in the VVG marks, it means that the veins of all products are copper.
The letter "B" indicates the material from which the insulating coating is made: vinyl (polyvinyl chloride). Since "B" stands in abbreviation twice, this means that the VVGng wire (GOST 53762-2010) is equipped with double vinyl insulation. Polyvinylchloride is used to make the wire winding and the outer insulation layer.
The presence of the symbol "G" in the designation indicates that the cable does not contain armor. Due to this, the wire has sufficient flexibility, but at the same time is not protected from external mechanical influences.
What is the difference between VVGng and VVG wire?
With a single laying of electrical current-carrying products, their ignition does not occur. When co-laying VVGng with other wires, in order to prevent the burning of the cable, it is treated with a special anti-inflammable solution. This is evidenced by the designation "NG". For basic VVG cable, conventional PVC insulation is provided, therefore, self-extinguishing and flame retardant properties are not characteristic for it.
Types of wires
- VVG. Basic model with conventional polyvinyl chloride insulation. The wire can be ignited when combined.
- VVGng. The insulating layer is equipped with special halogen chemical elements, preventing the ignition of the cable.
- VVGng Is. The wire is equipped with an insulating sheath of halogen-free PVC. With the help of this type of VVG cable, distribution and transmission of electrical energy to equipment related to a similar voltage class is carried out. Due to its technical characteristics, it is primarily used in places with a particularly high probability of ignition. The wire in the marking is additionally supplemented with the designation (Low Smoke).
- VVGng-frls. The insulation layer of this wire is also made of halogen-free materials. The cable has fireproof properties. When smoldering the plastic insulation of this wire, a small amount of smoke is released.
Cores
This element is the basis of any conductive electrical product. The VVGGG wire may contain one or more copper conductors. Their number varies from 1 to 5. About how much in the cable lived, you can judge by its marking. The very first digit indicates their number. For example, the wire ВВГнг 3х 2,5 is equipped with three copper veins. Structurally, each of them can be a separate copper wire, or several, twisted together.

This can also be determined by marking. The designation "M" stands on those cables that contain stranded copper wires. Conversely, "0" is available on products with a single-wire core.
The form
Depending on how the wires are laid in the wire, the VVGGG products can be:
- Round. This form has cables that contain veins with small cross sections. Round-shaped wires are marked with the letter "K".
- Segmental, or sectoral. Each of the veins is given the shape of a certain part of the sector of the circle. Such wires are designated by the symbol "C".
- Flat. In such wires, veins are laid along one plane. This shape is typical for wires with a small cross-section.
Section
In the electrical products VVGng this parameter varies from 1.5 mm square. up to 50 mm square. The number of sections is indicated by the second digit. For example, in wire ВВГнг 3 х2 5 veins have a cross section of 2.5 mm square. Nevertheless, there are also wires, the cross section of which can be 400 mm. sq. m. However, such cables are made by special order. If a parameter of 4 mm square is specified, this does not mean that all five wires of the VVGG wire have exactly this section. 2.5 sq. M. mm is considered to be their optimal value, since the zero conductor and the ground conductor have a smaller cross-section.
The best conductivity is possessed by that equipment, in which the cross section is larger. Conductivity is measured as the conductor resistance per thousand meters of length. For example, a cable with a cross section of 1.5 mm square. has a resistance of up to 12 ohms, and an article with a cross section of 50 mm square. - 0.39 Ohm.
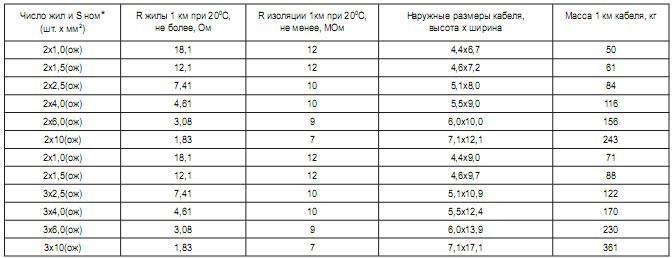
The wire can be operated if its resistance is in the range of 7-12 ohms for a length of thousand meters. The resistance value is measured at a temperature not exceeding 20 degrees.
Insulation coating
The thickness of the insulation depends on the wire parameters, such as its nominal cross-section and the voltage to which it is designed. With a cross-section of 16 mm. sq. m. and the voltage is not more than 660V, the thickness of the insulation coating is 0.9 mm. If this wire is operated at a voltage of 2.5 kV, the insulation thickness should be 1 mm. For the wire VVGng 3x2 5 mm square. at a voltage of 0.66 kV it does not exceed 0.60 mm. For operation at 1 kV, the nominal insulation thickness is 0.70 mm.
Voltage
Before use, the wire must undergo electrical testing. The product, which is intended for operation at a voltage of 66 kV, is first checked for 10 minutes at a voltage of 3 kV. The wire, designed for 1 kV, must withstand 3.5 kV.
Ability to bend
According to GOST, each wire, depending on the type, has certain mechanical characteristics. Those products that use stranded conductors can be bent to a radius of 7.5 of the diameter of the cable. Single-wire products easily bend at a radius of 10 diameters.
Temperature
The nominal cable temperature ranges from -50 to +50 degrees. The optimum temperature regime for wire installation is: - 15 degrees. At a lower temperature, it is not recommended to work with a cable. Otherwise, as the electricians claim, the product will crumble and even break.
Description of the wire ВВГнг 3х2,5
The product consists of three conductive copper cores. As an insulator, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is used. This material It is also used as a winding. The wire is not flammable in case of a group gasket. There is no protective cover for the product.
Technical specifications at voltage 0,66 kV
This conductive product with the indicated voltage value is characterized by the following parameters:
- The nominal cross-section of the core is 2.5 mm2.
- A wire of one thousand meters in length weighs 135 kg.
- In the cross-section, the diameter is 9.3 cm.
- The insulation coating of the cores has a thickness of 0.60 mm.
- A multiwire product has a minimum bending radius of 7 cm. If the core contains one wire, then the bending radius is 93 mm.
- The wire is designed for an admissible current load of 37 A (in the ground) and 28 A (in air).
- In case of a short circuit, 0.27 kA is considered acceptable for the wire.
- The electrical resistance of the insulation layer does not exceed 10 megohms.
Characteristics of a wire with a voltage of 1 kV
At the indicated voltage value BBGng 3x2.5 has the following parameters:
- Cross-section of a vein: 2,5 mm sq. M.
- The wire of length of thousand meters weighs 144 kg.
- The multiwire product is characterized by a minimum bending radius of 0.73 cm, and a single-wire core is designed for bending with a radius of 0.97 cm.
- The thickness of the insulating layer is 0.70 mm.
- The insulation resistance per thousand meters is 10 megohms.
The wires are sold in a twisted form, in drums. Their length varies from 500 to 7,200 meters.

Application
Place for laying wires VVGng can be:
- Dry and damp rooms: tunnels, canals, galleries, mines, sewers, industrial premises.
- Partially flooded structures in which a weak, medium or strong corrosive activity is noted.
- Special cable trestle blocks and bridges.
- Premises in residential and public buildings.
- Fire-hazardous premises.
- Explosive areas.
Conclusion
The operational warranty period of the wire is at least five years. According to consumers, it is possible to use VVGng for much longer. The demand for this conductive product is explained by the ratio of its high technical characteristics and relatively low cost.