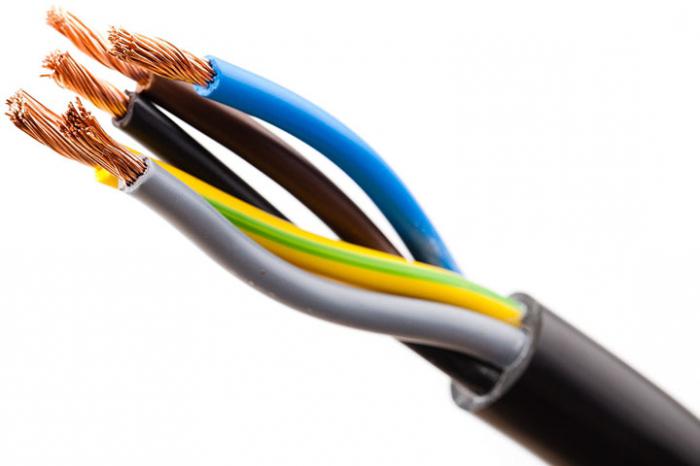
World manufacturers of household appliances when assembling their equipment use color marking of mounting wires. It is a designation in the electrician L and N. Due to the strictly defined color, the master can quickly determine which of the wires is phase, zero or grounding. This is important when connecting or disconnecting the equipment from the power supply.
Types of wires
When connecting electrical equipment, installing a variety of systems can not do without special conductors. They are made of aluminum or copper. These materials perfectly conduct electric current.
Important!Aluminum wires must be connected only with aluminum. They are chemically active. If they are connected to copper, the current transfer circuit will quickly collapse. Aluminum wires are usually connected with nuts and bolts. Copper - through the terminal. It should be noted that the latter type of conductors has a significant drawback - it is rapidly oxidized under the influence of air.

Advice in case the current ceases to pass at the site of oxidation:to restore the supply of electricity, the wire must be isolated from external influences using an electrical tape.
Classification of wires
A conductor is one uninsulated or one or more insulated conductors. The second type of conductors is covered with a special non-metallic sheath. This can be a winding with an insulating tape or a braid of fibrous raw materials. Non-insulated wires do not have any protective coatings. They are used in the construction of power lines.
Proceeding from the above, we conclude that the wires are:
- protected;
- unprotected;
- power;
- installation.
They should be used strictly for their intended purpose. The slightest deviation from the operating requirements leads to a breakdown in the power supply network. As a result of the closure, fires occur.
Designations for phase, neutral and grounding conductors
When installing electrical networks for domestic and industrial use, use insulated cables. They consist of many conductive veins. Each of them is painted in the corresponding color. The designation LO, L, N in the electric make it possible to shorten the time of installation, and if necessary, repair work.
The designation described below in the electrician L and N fully complies with the requirements of GOST R 50462 and is used in electrical installations in which the voltage reaches 1000 V. They have This group includes the electrical equipment of all residential, office buildings and economic facilities. What color designations of the phase L, zero, N and grounding must be observed when installing electrical networks? Let's figure it out.
Phase conductors
In the AC network, there are conductors that are live. They are called phase wires. Translated from English, the term "phase" means "line", "active wire", or "live wire".
The touch of a person to an insulated phase conductor can result in serious burns or even death. What does the designation in electrical L and N mean? On the electrical circuits, the phase wires are marked with the Latin letter "L", and in multi-core cables the insulation of the phase wire will be painted in one of the following colors:
- white;
- the black;
- brown;
- red.
Recommendations!If for any reason the electrician doubts the truthfulness of the information displaying the color marking of the cable wires, to determine the live wire, it is necessary to use the low-voltage

Zero conductors
These electric wires are divided into three categories:
- zero working conductors.
- zero protective (ground) conductors.
- zero conductors, combining a protective and operational function.
What is the designation of wires in an electrician L and N? The neutral of the network or the zero working conductor in the circuits of electrical circuits is denoted by the Latin letter "N". The zero conductors of the cables have the following color:
- blue color over the entire length without additional impregnations;
- blue color along the entire length of the veins without additional impregnations.
What does L, N and PE mean in an electrician? PE (N-RE) is a zero protective conductor that is colored along the entire length of the incoming wire in alternating lines of yellow and green.
The third category of zero conductors (REN-wires), which combine the working and protective functions, has a color designation in the electrician (L and N). The wires are painted blue, with ends and junctions with yellow-green stripes.
Necessity of verification of marking
The designation LO, L, N in an electrician for the installation of electrical networks is an important detail. How to check the correctness of the color marking? For this you need to use
To determine which of the conductors is phased and which is zero with the help of an indicator screwdriver, it is necessary to touch it with a sting to the bare part of the wire. If the LED lights up, then a contact has occurred with the phase conductor. After touching a screwdriver to the neutral wire there will be no glowing effect.
The importance of color marking of conductors and strict adherence to the rules for its use will significantly shorten the time of installation and troubleshooting of electrical equipment, while ignoring these elementary requirements will result in a health risk.
To date, imagine the installation of electrical wiring in an apartment or a private house with wires without color insulation is simply impossible. Wire color coding - this is not a pursuit of fashion and not a marketing move by the manufacturer, who wants to lure a potential buyer with his colorful electrical products.
The difference in the wires of wiring in color is an urgent necessity. First, according to the color scheme, we will be able to determine the purpose of each conductor that is in one or another group of wires. Secondly, the probability of making mistakes during connection and connection is reduced many times, and this will save the electrical wiring from a short circuit and a person's electric shock.
The color of the insulation of the wires is not chosen arbitrarily. There is a single standard of coloring, clearly spelled out in the PUE (rules for the installation of electrical installations). It says that all veins of wires and cables need to be identified by color or alphanumeric designations.
With the adoption of a single standard for the color designation of electrical conductors, their installation was greatly facilitated. Each vein has a specific purpose and is indicated by a unique color: black, white, yellow-green, blue, etc.
Most often, the insulation of the electrical wire is painted in color scheme along its entire length. But it is also possible to use color heat-shrinkable tubing (cambric) or colored insulating tape at the ends of the cores and at the connection points.
Let's consider, what color marking of wires is used in networks of single-phase, three-phase and direct current.
Wire colors in single-phase wiring
In electrical networks of alternating current, multicore wires with a different color insulation are used, which makes it much easier installation work and eliminates errors in connections.
We will find out what color the conductors have in the electrical installations of AC with a voltage of up to 1000V and with a deadly neutral (most administrative buildings and all residential buildings).
Color of zero protective and zero working conductors
The zero working conductor (N) must always be blue. The zero protective conductor (PE) is painted in yellow-green longitudinal or transverse bands. Wires with this color combination should only be used for their intended purpose!
The combined zero working and zero protective (PEN) wire has a blue color along the entire length of the conductor with yellow-green stripes at the ends. GOST allows and the opposite option - yellow-green stripes along the entire length with a blue color at the ends.

So, zero wires by color:
Zero work (N) - blue;
. zero protective (PE) - yellow-green color;
. combined (PEN) - yellow-green at the ends of blue marks (or vice versa).
Color of the phase wires
 Phase wires in the wiring, according to the recommendation of the UE, should have these colors: black, brown, red, gray, purple, pink, white, orange and turquoise.
Phase wires in the wiring, according to the recommendation of the UE, should have these colors: black, brown, red, gray, purple, pink, white, orange and turquoise.
We know that a single-phase is created by a branch from a three-phase one. At the same time, the phase conductor of a single-phase circuit must match the phase conductor with a three-phase conductor, with which it is connected.
The colors of the phase conductors must in no case coincide with the colors of the neutral and ground conductors (N, PE, PEN).
When using multicore wire (cable) with one-color marking, color marks are placed on the ends of the wires (after a dullness). For this, a color heat-shrinkable tube (cambric) or colored insulating tape is used.
Color of conductors in a three-phase network variable
In three-phase networks, buses and high-voltage transformers on substations and substations should have the following color: phase "A" - yellow, phase "B" - green, phase "C" - red.

Color of wires in the DC network (+ and -)
As we know, only two wires are used in the DC circuit. There is no phase or zero conductor, but there is only a positive (+) and negative (-) wire.
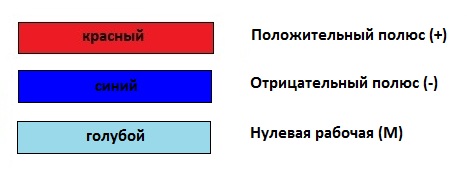
According to the specifications, the electrical conductors of the positive charge (+) are colored red, and the conductors of the negative charge (-) are blue. The middle conductor (M) is indicated in blue.
Recommended articles:
Winding electric wires
Conducting electrical work is quite a complicated matter, which is better to entrust to a specialist in this field. However, if you need to purchase cords, wires and various cables for installation, you need to understand their labeling. Indication of the isolation of products of alphanumeric cipher and there is a marking of wires.
At the moment, each manufacturer designates its products with codes, so that any consumer, having a look at it, could understand what the product is made of, what is the nominal withstand voltage, the type of cross-section, and also the features of its design and the type of insulation.
To comply with these parameters, all plants and enterprises engaged in the manufacture of electrical products are required to use the international standard - GOST. The marking of the wires also makes it possible to easily determine the location of the phase, zero, and in some cases also of the earth. Let's consider the basic electrotechnical products presented in the market.
Cables
Electrical cables come in several types depending on the purpose of use. They can also consist of copper or aluminum cores, which are assembled by bundles under one or different wrapping materials of plastic or PVC. Also sometimes there is an additional protective shell made of steel tape.
Depending on the application, the color coding of the wires can also be different. So, distinguish:
- Radio-frequency cables that transmit radio and video signals.
- Control signals for signal transmission to certain devices.
- Power cables are used in lighting devices for electricity transmission. Can be used in both internal and external electrical wiring.
- For the transfer of communication cables are used that can conduct a current of different frequencies.
- Automation systems use control cables, which are copper conductors located under a protective shield, which removes interference and prevents the application of mechanical damages.
Wires
An article made up of several wires or just one of them is called a wire. In most cases, the winding is plastic, less often wire, but is also found without insulation at all.
At the moment, the preference is given to wires whose veins are made of copper or aluminum. Such products are used not only in electrical work, but also as winding of electric motors.

Aluminum wires are of low cost, but a huge disadvantage is the impossibility of connecting them with others, for example, copper ones. Copper products can withstand loads well, but in the open air they are rapidly oxidized and are costly.
Marking of electrical wires also depends on their purpose. Installation and power are used both inside and outside the premises. Mounting, in turn, is used when collecting electrical circuits in panels or radio equipment.
Cords
The cord is a number of veins with a small cross section, which consist of many interwoven wires. Most often this electrotechnical product is represented by stranded cords, the winding of which is nonmetallic.
The main use of cords is connected to the network of industrial and household appliances.
Alphabet Marking
Any electrical product must be marked in accordance with GOST. The first letter means the material from which the vein is made. If it is copper, the letter is not assigned, if aluminum, it is marked with the letter "A".
The decoding and wires of the second letter characterize the kind or material of insulation. Depending on the type of wire, it can be written as "P", "M", "MH", "K", "U", which corresponds to flat, mounting, mounting with flexible wires, control and installation type of wire. Installation can also be marked as "P" or "W".
The next, third letter, means the material of the winding of the product:
- "K" - kapron;
- "C" - fiberglass;
- "BP" or "P" is polyvinyl chloride;
- "F" - metal;
- "E" - screened;
- "Р" - rubber;
- "ME" - enameled;
- "T" - winding with a bearing torso;
- "HP" or "H" is a nai- rithic;
- "L" - varnished;
- "G" - winding with a flexible core;
- "O" and "SH" - polyamide silk as a braid or insulation.

The marking of wires can also have a fourth letter that characterizes the design features of an electrical product:
- "K" - the wire is armored with round wire;
- "A" - asphalt wire;
- "T" - the product is used for conducting in pipes;
- "B" - armored with ribbons;
- "O" - the presence of a protective braid;
- "G" - for the wire - flexible, and for the cable - without protection.
Digital Marking
The marking of electric wires according to the first digit indicates the number of cores, in case it is absent, the conductor has only one core. The second and third digit means in millimeters square and the nominal withstand voltage of the network.

Grounding
For the most part, the color coding of wires is designed to facilitate the conduct of electrical work and the safety of its implementation.
According to the insulation of the land conductor must be green-yellow color. In some cases, the color may be exclusively green or only yellow.
For earthing, the color of the wires is applied either in the longitudinal direction or in the transverse direction. On electrical circuits "ground" is usually denoted by the letters "PE", which is also sometimes called zero protection.
Zero
The zero working contact does not carry a charge of voltage, but is only a conductor. Marking the wires according to the color should be bluish or blue. On the electrical circuit, zero is usually referred to as "N".
Phase
The phase wire is always energized if it is connected to the mains. The color identification of the phase wires can be made in many color shades - brown, black, turquoise, purple, gray and others. But most often the phase conductors are white or black.
PEN-conductor
In any residential building or building, it is always necessary to ground or neutralize the wiring. Currently, it is important to conduct a TN-C grounding system, which includes the interconnection of grounding and neutral wires. The marking of the color of the wires combined in such a system will change from yellow-green to blue.
First, you need to divide the conductor into two buses - PE and N, which are then connected together by a bridge in the middle or two along the edges. Then re-ground the PE bus and check the resistance.

How to determine the ground, neutral and phase?
Sometimes during the repair or renovation of the wiring it is necessary to determine which wire that means. But it happens that the marking of wires by color is not an ally in this, because it is impossible because of a long service life or in the case of a short circuit.
This task can be handled using an indicator screwdriver, popularly called "control". This method is suitable for a single-phase network, without a ground wire. First you need to turn off the electricity supply, divide both conductors to the sides and then turn it on again. Then bring it to one of the wires. If the lamp on the "control" is lit, respectively, this wire will be the phase, and the remaining core is zero.
If the wiring is three-wire, you can use a multimeter to determine each wire. This device has two wires. To begin with, it is necessary to install a rated voltage above 220 volts on it. Then one of the wires of the multimeter should be fixed on the contact with the phase, and the other to determine the ground or neutral. If the second wire detects an earth conductor, the readings on the device will drop slightly below 220, and if zero, the voltage will shift to 220 volts.
The third method of determining the wires can be used if there was not a screwdriver or a multimeter at hand. This can help marking wires, which in any situation to isolate zero will be marked in blue-blue. The other two contacts will be harder to determine.
If one of the contacts is colored, and the other one is white or black, then, most likely, the color will be the phase. According to the old standards, black and white color denoted a grounding conductor.
Also, according to the rules for the installation of electrical equipment, white color marks the ground wire.
Marking in a chain of a direct current
The marking of wires in the DC network has a red insulator for plus, and black for minus. If the network is three-phase, then each phase will have its own specific color: red, yellow and green. Zero and grounding, as usual, will be blue and yellow-green.
If a cable is inserted into the wires of the phases, black, white and red insulation will correspond, and the color of the neutral and ground will remain unchanged, as in the case of a 220 volt network.

Independent designation of wires
Sometimes, in the absence of a suitable color, you can change the color of the same wire used for zero, phase and ground. In this case, deciphering the marking of the wires will be very useful.
You can make small notes on the wires, which in the future can be very useful. You can also use colored electrical tape and wind wires according to the marking.
To date, great demand for cambric tubes, which are colored plastic tubes, capable of heat shrinkage. In the case of tires, it is also necessary to mark at the ends of the conductors.
Color insulation of conductors today is an essential attribute for conducting successful and correct installation of electrical wiring. Such a solution is by no means a way to make the wires beautiful and attractive to the consumer, it is a comfortable color marking standardized and regulated throughout the civilized world, which is, without exaggeration, a necessity.
The color coding of wires gives the exact designation for each conductor, the color of the insulation of the conductor marks its purpose in a group of several conductors, and facilitates the process of switching and mounting. This solution eliminates errors that may occur during installation, which can lead to a fatal electric shock or short circuit. Repair and maintenance of power grids also becomes safer if the wires are accurately labeled.
The standard set forth in the PUE strictly defines the colors of the marking, and thanks to this standard it becomes possible to easily identify each conductor, each cable core in the group by color or alphanumeric code.
As a rule, the conductor is entirely of a certain color, but only the ends of individual cores can be marked, at the switching points, where the use of colored insulating tape or colored cambriches is possible. In the following, we will discuss in more detail how exactly such marking is performed for single-phase, three-phase current and direct current networks.
Standard color code for buses and wires for three-phase AC networks:
In three-phase alternating current networks, the high-voltage inputs of transformers both at stations and substations, as well as buses, are painted in the following colors, according to the phases:
Phase "A" - colored yellow;
Phase "B" is colored green;
Phase "C" is colored red.

Standard color coding for wires and DC buses:
For DC circuits, only two tires are characteristic: positive and negative. Here, the positive wire (positive charge bus) is marked in red, and the negative wire (negative charge bus) is marked in blue, as there are essentially no zero and one phase wires. The middle wire (M) is marked in blue.
In the case where a DC network containing two conductors is created by branching from a three-wire DC circuit, the conductors are marked in the same way as the corresponding conductors of the original three-wire circuit.
Phase, zero and earth in the wiring:
AC electric networks are now always laid with stranded wire in the insulation of cores of different colors, this greatly facilitates the installation process. If the wiring is performed by one installer, and in the future, other people will carry out maintenance and repair of the network, they will no longer be forced to constantly identify, they just orient themselves in color.
But in the old days it was a real problem, for isolation used monochrome - or white, or black. Now the standard has been worked out, and in accordance with GOST R 50462 "Identification of conductors by colors or digital signs", the wires are separate and in cables have strictly regulated designations.
The function of marking - to create the ability to quickly and easily visualize the purpose of each specific conductor for any of its sections, this is one of the main requirements of the EEI.
What color should the conductors in electrical AC installations for voltages up to 1000 volts and with deadly neutral beams, to which almost all apartment houses and administrative buildings belong, have the same coloring according to GOST?
The zero working conductor (N) is marked blue. For the zero protective conductor (PE) - yellow-green marking in the form of strips along or across the vein. Such a marking in this color combination is only relevant for grounding conductors (for zero protective ones).
When the zero working conductor is made aligned, the marking is made along the entire length of the wire in blue, and at the connection points (at the ends of the conductor) - yellow-green stripes, or vice versa: a yellow-green conductor with blue ends.
Thus, zero wires are marked with the following colors:
Zero working wire (N) - marking in blue;
Zero protective conductor (PE) - marking in yellow-green color;
Zero combined wire (PEN) - marking with a yellow-green color with blue marks on the ends or vice versa (see above).
Phase wires, in accordance with the standard PUE, can be marked with one of these colors: red, black, purple, brown, gray, pink, orange, turquoise, or white.
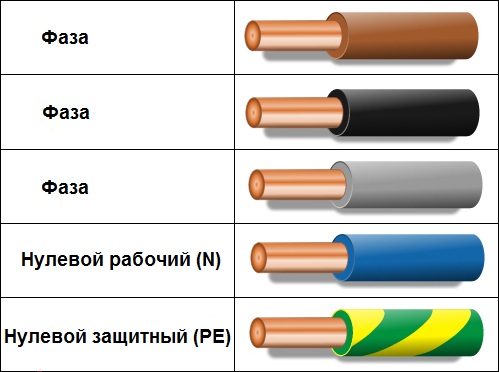
If a single-phase electrical circuit is obtained by branching from a three-phase network, the phase conductor of the resulting single-phase circuit must necessarily match the source wire of the three-phase network from which the branch is made.
The wires are marked so that the colors of the phase wires do not coincide in any way with the color of the zero conductor. And if an unmarked cable is used, the color marks are made at the ends of the cores, at the joints, with the help of heat-shrink tubing or colored insulating tape. But in order to prevent unnecessary work on making labels, it is enough to choose the right color of insulation from the very beginning, choosing a cable of sufficient length for your needs.
Sometimes electricians have to deal with not very pleasant situations when the wiring is already completed, and neither the connections in the shield nor the wires are marked, in this case the person has to waste time and to identify the "phase", "zero", and "grounding" .
However, it should always be remembered that even if it is not possible to purchase the wire of the desired color, you can of course use a wire of any color, but then it is necessary to mark the ends of the cores at least with colored heat shrinkage or colored electrical tape. And always remember that when laying electrical wiring it is necessary to be careful and always observe safety precautions.
Content:Material of conductors
Current-carrying veins are copper and aluminum. A significant lack of aluminum - high chemical activity. Directly aluminum conductors can be connected only with the same and then, basically, without the use of soldering. Direct contact of aluminum with copper leads to its rapid destruction, therefore, if necessary they are connected by means of terminals. If the high weight and cost are not critical, otherwise the copper wires are better. For proper use, it should be borne in mind that copper is oxidized in air, so open parts of copper wires are puddled.
Marking of wires in accordance with GOST
First there are the letters:
- Material: copper - no, aluminum "A";
For cables: sheath material, for wires: "P" - wire, "PP" - flat wire, there are two - or three-wire; - Insulation material: Р - rubber, П - polyethylene, Н - nayritic, В - polyvinylchloride;
- For cables - the design of the protective cover.
Then digital:
- Number of cores (if not, the product is solid);
- Cross-sectional area;
- The greatest voltage of the network;
There is a standard series of cross-sectional areas from which the desired value is selected according to the permissible current load, based on the conditions of its operation.
Wires
An article consisting of one, two, or more insulated or non-insulated cores in a common nonmetallic, metallic or fibrous shell. The solid wire is sometimes made bare - with air insulation. Stranded are only isolated. Isolated wire is sometimes made in a protected version - to resist mechanical influences. A conventional insulated wire is called unprotected.
Examples of marking of wire designations:
- APR 3 * 4 - 500 - three-core, aluminum, with rubber insulation, cross-section of veins - 4 square millimeters, maximum voltage - 500V;
- ППР 2 * 2,5 - 380 - flat wire two-core, copper, with rubber insulation, cross-section of veins - 2,5 square millimeters, maximum voltage - 380V;
- PVS - stranded copper with sheath and PVC insulation;
- PPPP - a rigid wire, with a copper core, with a sheath and PVC insulation;
- MGSHV - assembly, vein multiwire, insulation material - polyamide silk;
- MSW - mounting, single-wire conductor, insulation - fibrous and PVC.
- TRP - telephone wire lived copper, insulation - polyethylene.
Cable marking
Cable - a product consisting of one or more cores, necessarily isolated, in a common conductive or non-conductive shell, which can be reinforced or not reinforced with additional protection and metal armor.
Marking of cable designations according to GOST:
- AVRG 3х95-3000 - three-core, aluminum cable, 95 square millimeter conductor cross-section, rated for voltage up to 3 kV, insulation - rubber, sheath - PVC, protective cover - none.
- AVRG is the same, but the maximum voltage, the number of cores and the cross section are not indicated.
- VRG 5 * 2,5-380 - cable five-core, copper, cross section 2.5 square millimeters, rated for voltage up to 380 volts, insulation - rubber, sheath - PVC, protective cover - absent.
- 4 * 1.5 - copper four-core cable with a cross section of 1.5 square millimeters, with a sheath and PVC insulation.
- RC-50 is a radio-frequency coaxial single-wire cable with a wave resistance of 50 Ohm.
Marking cords
- Cord is a kind of wire, mainly two-core, with a cross-section up to 1.5 square millimeters, necessarily flexible and insulated, which serves for direct connection of household appliances to the network.
Marking of the designations of cords according to GOST:
- ШВВП 2 * 0,75 - a two-strand cord, veins multiwire, section 0,75 square millimeters, with PVC sheath and insulation;
- SHRT - heat-resistant cord with rubber sheath and insulation, stranded wires.
Permissible cross-section of wires and cables
In residential buildings, the smallest permissible and cables are: for the lines of group networks 1.5 square meters. mm, for the lines between floor and apartment flaps, to the apartment meter - 2.5 square meters. mm, for distribution lines of supply of apartments - 4 mm.
Selection of conductor cross-sections
The applied cross-section of the lines of electrocommunications should not be less than the value providing the current density limiting for these conditions of the gasket. On average, based on long-term operation, this value is 1 to 3 amps per square millimeter. The real current is found by dividing the voltage at the consumer by the total resistance of parallel loads. If the line is small, then the consumer's voltage can be taken equal to the source EMF. You can also select the current section according to the current table.