Sometimes it is very important to accurately calculate the volume of water passing through the pipe. For example, when you need to design a new heating system. Hence the question arises: how to calculate the volume of a pipe? This figure helps to choose the right equipment, for example, the size of the expansion tank. In addition, this indicator is very important when using antifreeze. Usually it is sold in several forms:
- Diluted;
- Undiluted.
The first type can withstand a temperature of 65 degrees. The second will freeze already at -30 degrees. To buy the right amount of antifreeze, you need to know the volume of the coolant. In other words, if the volume of liquid is 70 liters, then you can buy 35 liters of undiluted liquid. It is enough to dissolve them, keeping the proportion of 50-50 and get the same 70 liters.
In order to obtain accurate data, it is necessary to prepare:
- Calculator;
- Calipers;
- Ruler.
First, the radius indicated by the letter R is measured. It can be:
- Internal;
- Outdoor.
The outer radius is needed to determine the size of the space it will occupy.
For calculation, it is necessary to know the data of the pipe diameter. It is denoted by the letter D and calculated by the formula R x 2. The circumference is also determined. Denoted by the letter L.
To calculate the volume of the pipe, measured by cubic meters (m3), you must first calculate its area.
To obtain the exact value, you must first calculate the cross-sectional area.
To do this, apply the formula:
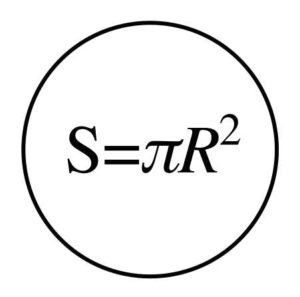
- S = R x Pi.
- The required area is S;
- The radius of the pipe is R;
- The number of Pi is 3.14159265.
The resulting value must be multiplied by the length of the pipeline.
How to find the volume of a pipe by the formula? You only need to know 2 values. The formula for calculation is as follows:
- V = S x L
- The volume of the pipe is V;
- The cross-sectional area is S;
- Length - L
For example, we have a metal pipe with a diameter of 0.5 meters and a length of two meters. To carry out the calculation in the formula calculating the area of the circle, the size of the outer cross member of the stainless steel is inserted. The pipe area will be equal to;
S = (D / 2) = 3.14 x (0.5 / 2) = 0.0625 square meters. meter.
The final calculation formula will take the following form:
V = HS = 2 x 0.0625 = 0.125 cu. meter.
This formula calculates the volume of any pipe. And it does not matter what material it is. If the pipeline has many components, applying this formula, you can calculate separately the volume of each section.
When performing the calculation, it is very important that the dimensions are expressed in the same units of measurement. The easiest way to do the calculation is if all the values are converted to square centimeters.
If you use different units of measurement, you can get very questionable results. They will be very far from the real values. When you perform constant daily calculations, you can use the calculator's memory to set a constant value. For example, the number Pi, multiplied by two. This will help to make a much faster calculation of the volume of pipes of different diameters.
Today, you can use ready-made computer programs for calculating, in which standard parameters are pre-specified. To perform the calculation, you will only need to enter additional variable values.
Download the program https://yadi.sk/d/_1ZA9Mmf3AJKXy
How to calculate the cross-sectional area
If the pipe is round, the cross-section area should be taken from the formula of the area of the circle: S = π * R2. Where R is the radius (internal), π - 3,14. In total, we need to build the radius in a square and multiply it by 3.14.
For example, the cross-sectional area of a pipe of 90 mm diameter. We find the radius - 90 mm / 2 = 45 mm. In centimeters it is 4.5 cm. Squared: 4.5 * 4.5 = 2.025 cm2, substitute S = 2 * 20.25 cm2 = 40.5 cm2 in the formula.
The sectional area of the profiled product is calculated by the formula of the area of the rectangle: S = a * b, where a and b are the lengths of the sides of the rectangle. If we assume that the cross section of the profile is 40 x 50 mm, we obtain S = 40 mm * 50 mm = 2000 mm2 or 20 cm2 or 0.002 m2.
Calculation of the volume of water in the whole system
To determine such a parameter, it is necessary to substitute the value of the inner radius in the formula. However, the problem immediately appears. And how to calculate the total volume of water in the pipe of the entire heating system, which includes:
- Radiators;
- Expansion tank;
- Boiler heating.
First, the volume of the radiator is calculated. To do this, open his technical passport and write out the value of the volume of one section. This parameter is multiplied by the number of sections in a particular battery. For example, one is 1.5 liters.
When the bimetal radiator is installed, this value is much smaller. The amount of water in the boiler can be found from the device's passport.
To determine the volume of the expansion vessel, it is filled with the quantity of liquid measured beforehand.
It is very easy to determine the volume of pipes. The available data for one meter, a certain diameter, you just need to multiply by the length of the entire pipeline.
Note that in the global network and reference literature, you can see special tables. They show the approximate data of the product. The error of the given data is sufficiently small, therefore the values given in the table can be used to calculate the volume of water.
I must say that when calculating the values, you need to take into account some of the characteristic differences. Metal pipes having a large diameter, let in a quantity of water, much less than the same polypropylene pipes.
The reason lies in the smoothness of the surface of the pipes. At steel products it is executed with the big roughness. PPR pipes do not have a roughness on the inner walls. However, steel products have a greater volume of water than in other pipes of the same cross section. Therefore, to make sure that the calculation of the water volume in the pipes is made correctly, you need to double-check all the data and back up the result with an online calculator.
Internal volume of running meter of pipe in liters - table
The table shows the internal volume of the running meter of the pipe in liters. That is, how much water, antifreeze or other liquid (coolant) is required to fill the pipeline. The internal diameter of the pipes is taken from 4 to 1000 mm.
| Inside diameter, mm | Internal volume of 1 m of the chimney, liters | Internal volume of 10 m running pipes, liters |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0.0126 | 0.1257 |
| 5 | 0.0196 | 0.1963 |
| 6 | 0.0283 | 0.2827 |
| 7 | 0.0385 | 0.3848 |
| 8 | 0.0503 | 0.5027 |
| 9 | 0.0636 | 0.6362 |
| 10 | 0.0785 | 0.7854 |
| 11 | 0.095 | 0.9503 |
| 12 | 0.1131 | 1.131 |
| 13 | 0.1327 | 1.3273 |
| 14 | 0.1539 | 1.5394 |
| 15 | 0.1767 | 1.7671 |
| 16 | 0.2011 | 2.0106 |
| 17 | 0.227 | 2.2698 |
| 18 | 0.2545 | 2.5447 |
| 19 | 0.2835 | 2.8353 |
| 20 | 0.3142 | 3.1416 |
| 21 | 0.3464 | 3.4636 |
| 22 | 0.3801 | 3.8013 |
| 23 | 0.4155 | 4.1548 |
| 24 | 0.4524 | 4.5239 |
| 26 | 0.5309 | 5.3093 |
| 28 | 0.6158 | 6.1575 |
| 30 | 0.7069 | 7.0686 |
| 32 | 0.8042 | 8.0425 |
| 34 | 0.9079 | 9.0792 |
| 36 | 1.0179 | 10.1788 |
| 38 | 1.1341 | 11.3411 |
| 40 | 1.2566 | 12.5664 |
| 42 | 1.3854 | 13.8544 |
| 44 | 1.5205 | 15.2053 |
| 46 | 1.6619 | 16.619 |
| 48 | 1.8096 | 18.0956 |
| 50 | 1.9635 | 19.635 |
| 52 | 2.1237 | 21.2372 |
| 54 | 2.2902 | 22.9022 |
| 56 | 2.463 | 24.6301 |
| 58 | 2.6421 | 26.4208 |
| 60 | 2.8274 | 28.2743 |
| 62 | 3.0191 | 30.1907 |
| 64 | 3.217 | 32.1699 |
| 66 | 3.4212 | 34.2119 |
| 68 | 3.6317 | 36.3168 |
| 70 | 3.8485 | 38.4845 |
| 72 | 4.0715 | 40.715 |
| 74 | 4.3008 | 43.0084 |
| 76 | 4.5365 | 45.3646 |
| 78 | 4.7784 | 47.7836 |
| 80 | 5.0265 | 50.2655 |
| 82 | 5.281 | 52.8102 |
| 84 | 5.5418 | 55.4177 |
| 86 | 5.8088 | 58.088 |
| 88 | 6.0821 | 60.8212 |
| 90 | 6.3617 | 63.6173 |
| 92 | 6.6476 | 66.4761 |
| 94 | 6.9398 | 69.3978 |
| 96 | 7.2382 | 72.3823 |
| 98 | 7.543 | 75.4296 |
| 100 | 7.854 | 78.5398 |
| 105 | 8.659 | 86.5901 |
| 110 | 9.5033 | 95.0332 |
| 115 | 10.3869 | 103.8689 |
| 120 | 11.3097 | 113.0973 |
| 125 | 12.2718 | 122.7185 |
| 130 | 13.2732 | 132.7323 |
| 135 | 14.3139 | 143.1388 |
| 140 | 15.3938 | 153.938 |
| 145 | 16.513 | 165.13 |
| 150 | 17.6715 | 176.7146 |
| 160 | 20.1062 | 201.0619 |
| 170 | 22.698 | 226.9801 |
| 180 | 25.4469 | 254.469 |
| 190 | 28.3529 | 283.5287 |
| 200 | 31.4159 | 314.1593 |
| 210 | 34.6361 | 346.3606 |
| 220 | 38.0133 | 380.1327 |
| 230 | 41.5476 | 415.4756 |
| 240 | 45.2389 | 452.3893 |
| 250 | 49.0874 | 490.8739 |
| 260 | 53.0929 | 530.9292 |
| 270 | 57.2555 | 572.5553 |
| 280 | 61.5752 | 615.7522 |
| 290 | 66.052 | 660.5199 |
| 300 | 70.6858 | 706.8583 |
| 320 | 80.4248 | 804.2477 |
| 340 | 90.792 | 907.9203 |
| 360 | 101.7876 | 1017.876 |
| 380 | 113.4115 | 1134.1149 |
| 400 | 125.6637 | 1256.6371 |
| 420 | 138.5442 | 1385.4424 |
| 440 | 152.0531 | 1520.5308 |
| 460 | 166.1903 | 1661.9025 |
| 480 | 180.9557 | 1809.5574 |
| 500 | 196.3495 | 1963.4954 |
| 520 | 212.3717 | 2123.7166 |
| 540 | 229.0221 | 2290.221 |
| 560 | 246.3009 | 2463.0086 |
| 580 | 264.2079 | 2642.0794 |
| 600 | 282.7433 | 2827.4334 |
| 620 | 301.9071 | 3019.0705 |
| 640 | 321.6991 | 3216.9909 |
| 660 | 342.1194 | 3421.1944 |
| 680 | 363.1681 | 3631.6811 |
| 700 | 384.8451 | 3848.451 |
| 720 | 407.1504 | 4071.5041 |
| 740 | 430.084 | 4300.8403 |
| 760 | 453.646 | 4536.4598 |
| 780 | 477.8362 | 4778.3624 |
| 800 | 502.6548 | 5026.5482 |
| 820 | 528.1017 | 5281.0173 |
| 840 | 554.1769 | 5541.7694 |
| 860 | 580.8805 | 5808.8048 |
| 880 | 608.2123 | 6082.1234 |
| 900 | 636.1725 | 6361.7251 |
| 920 | 664.761 | 6647.6101 |
| 940 | 693.9778 | 6939.7782 |
| 960 | 723.8229 | 7238.2295 |
| 980 | 754.2964 | 7542.964 |
| 1000 | 785.3982 | 7853.9816 |
If you have a specific design or pipe, the formula above shows how to calculate the exact data for the correct flow of water or other coolant.
Calculation online
http://mozgan.ru/Geometry/VolumeCylinder
Conclusion
To find the exact figure of the coolant consumption of your system, you will have to sit for a while. Either search on the Internet, or use a calculator, which we advise. Perhaps he can save you time.
Do you have a water-type system, then do not bother and make an accurate selection of the volume. It is enough to estimate approximately. Exact calculation is needed more in order not to buy excess and minimize costs. Since many stop at choosing an expensive coolant.
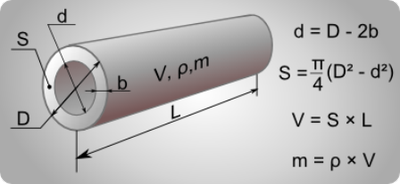
All parameters are specified in mm
L - Pipe length.
D1 - The diameter of the inside.
D2 - The diameter of the outside of the pipe.
With this program, you can calculate the volume of water or any other liquid in the pipe.
For the exact calculation of the volume of the heating system, the volume of the boiler and radiators must be added to the result obtained. As a rule, these parameters are indicated in the passport on the product.
Based on the results of calculations, you will know the volume of the pipeline common, per running meter, surface area of the pipe. Typically, the surface area is used to calculate the required amount of paint and varnish material.
When calculating, you must specify the outer and inner diameter of the pipeline and its length.
The program calculates the surface of pipes using the following formula P = 2 * π * R2 * L.
Calculation of the volume of the pipe is carried out according to the formula V = π * R1 ^ 2 * L.
L - length of the pipeline.
R1 Is the inner radius.
R2 Is the outer radius.
How the body volume calculations are performed correctly
Calculating the volume of a cylinder, pipes and other physical bodies is a classic task from applied science and engineering. As a rule, this task is not trivial. According to the analytical formulas for calculating the volume of liquids in different bodies and containers it can be very difficult and cumbersome. But, basically the volume of simple bodies can be calculated quite simply. For example, with the help of several mathematical formulas you can determine the volume of the pipeline. Typically, the amount of liquid in the pipes is determined by the value of m3 or cubic meters. However, in our program, you get all the calculations in liters, and the surface area is determined in m2 - square meters.
Helpful information
The dimensions of steel pipelines for gas supply, heating or water supply are indicated in whole inches (1 ", 2") or its fractions (1/2 ", 3/4"). For 1 "according to generally accepted standards take 25.4 millimeters. To date, steel pipes can be found in reinforced (with a double wall) or in the usual design.
For the reinforced and conventional pipeline, the internal diameters differ from the standard ones - 25.4 millimeters: so in the reinforced, this parameter is 25.5 millimeters, and in the standard or usual - 27.1 millimeters. It follows that this is insignificant, but these parameters are different, which should also be taken into account when choosing pipes for heating or water supply. As a rule, specialists do not particularly understand these details, since for them an important condition is - Do (Dn) or conditional pass. This value is dimensionless. This parameter can be defined using special tables. But we do not need to delve into these details.
Docking of various steel pipes, the size of which is presented in inches with aluminum, copper, plastic and others, the data of which are presented in millimeters, are provided with special adapters.
Typically, this type of pipe calculation is necessary in the process of calculating the size of the expansion tank for the heating system. The volume of water in the room or house heating system is calculated using our program in online mode. However, often, these data inexperienced professionals are simply neglected, which is not worth doing. Since, for the effective functioning of the heating system, all parameters must be taken into account in order to correctly select the boiler, pump and radiators. Also important is the volume of liquid in the pipeline will be in the case when instead of water will use antifreeze in the heating system, which is quite expensive and overpayments in this case will be superfluous.
To determine the volume of the liquid, it is necessary to correctly measure the outer and inner diameter of the pipeline.
Important! Do not neglect the calculation results when designing a heating system. Otherwise, you risk not choosing the boiler correctly in terms of capacity, which will be inefficient and uneconomical in the process of operation, and as a consequence the premises will be poorly heated.
An approximate calculation can be made based on the proportion of 15 liters of liquid per 1 kW of boiler output
For example, you have a 4 kW boiler, hence the total system volume is 60 liters (4 × 15)
We have given exact values of the volume of liquid for different radiators in the heating system.
Water volume:
- the old cast-iron battery in 1 section - 1.7 liters;
- a new cast-iron battery in 1 section - 1 liter;
- bimetal radiator in 1 section - 0,25 liters;
- aluminum radiator in 1 section - 0.45 liters.
Conclusion
Now you know how to calculate the volume of a pipe for a water supply or a heating system correctly and quickly.
Bookmark this site
If the design is available end, then in the absence of a caliper, we can measure the diameter of the tape measure or ruler, just by attaching it to the end in the middle so that the ruler passes through the center of the circle and displays the largest value of the diameter. At the same time, the accuracy of the measurement will be lower, than when using a caliper, but it will not become critically low and will remain sufficient, as in the case with the above-described measurement of the thread. The error will be less if the cut is level.
Consider another interesting non-standard way that will help you out when the pipe is in a hard-to-reach place and you do not have the opportunity to grab it with the legs of a caliper or wrap it with a thread. Here, modern technologies come to the rescue. Almost everyone is available today a digital camera, and if not in the form of a separate device, then certainly it is present in the mobile phone. We apply a ruler or any object to the pipe, the dimensions of which are known to us in advance (for example, matchbox), and take a photo. Further we make measurements on a photo and on a proportional relation of this size to the known (ruler or object), considering the scale of the image. These actions are called the copy method.
What you should know about the dimensions

And in conclusion - some useful information. Typically, the pipes have standard dimensions that are expressed in inches. To translate the value from inches to inches and back, use the following relationships: 1 inch = 2.54 cm; 1 cm = 0.398 inches. But in order not to be mistaken in choosing pipes, one important thing must be considered. For example, when it comes to water pipe in 1 inch (denoted - 1 "), then there is in view of not its outer diameter, but the so-called conditional pass of the tube, which is closer in its meaning to the inner diameter. The conditional pass should be understood as the mean internal diameter, rounded to the values of the standard series: 6, 8, 10, 15, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 65, 80, 100, 125, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350 , 400, 500, 600, 800, 1000, 1200, 1400, 1600, 2000, 2400, 3000 mm. For a better understanding of this nuance and for the convenience of size conversion, you can use the following table.
The table shows sizes up to 6 ", because big you hardly need. The values of the outer diameter may differ slightly from the table diameters, depending on the different types of products.
When building and arranging a house, pipes are not always used to transport liquids or gases. They often act as construction material - to create a framework of various structures, supports for canopies, etc. When determining the parameters of systems and structures, it is necessary to calculate different characteristics of its components. In this case, the process itself is called the calculation of a pipe, and it includes both measurements and calculations.
What is the calculation of pipe parameters?
In modern construction not only steel or galvanized pipes are used. The choice is already quite wide - PVC, polyethylene (HDPE and PVD), polypropylene, metal, corrugated stainless steel. They are good because they do not have as much mass as steel analogs. Nevertheless, when transporting polymer products in large volumes, it is desirable to know their mass - in order to understand which machine is needed. Weight of metal pipes is even more important - the delivery is considered by tonnage. So this parameter is desirable to control.
Know the area of the outer surface of the pipe is necessary for the purchase of paint and heat insulation materials. Only steel products are painted, because they are susceptible to corrosion, unlike polymer ones. So we have to protect the surface from the effects of aggressive media. They are used more often for construction, frames for hozpostroek (, sheds, etc.), so operating conditions are heavy, protection is necessary, therefore all skeletons require painting. This is where the area of the surface to be painted is required - the outer area of the pipe.
When constructing a water supply system for a private house or dacha, pipes are laid from the source of water (or well) to the house - underground. And anyway, so that they do not freeze, warming is required. Calculate the amount of insulation can be knowing the area of the outer surface of the pipeline. Only in this case it is necessary to take the material with a solid stock - joints should overlap with a solid margin.
The cross-section of the pipe is necessary to determine the throughput - whether this product can hold the required amount of liquid or gas. The same parameter is often needed when choosing the diameter of pipes for heating and running water, calculating the pump's output, etc.
Inner and outer diameter, wall thickness, radius
Pipes are a specific product. They have an inner and outer diameter, since the wall is thick, their thickness depends on the type of pipe and the material of which it is made. AT technical characteristics more often indicate the outer diameter and wall thickness.
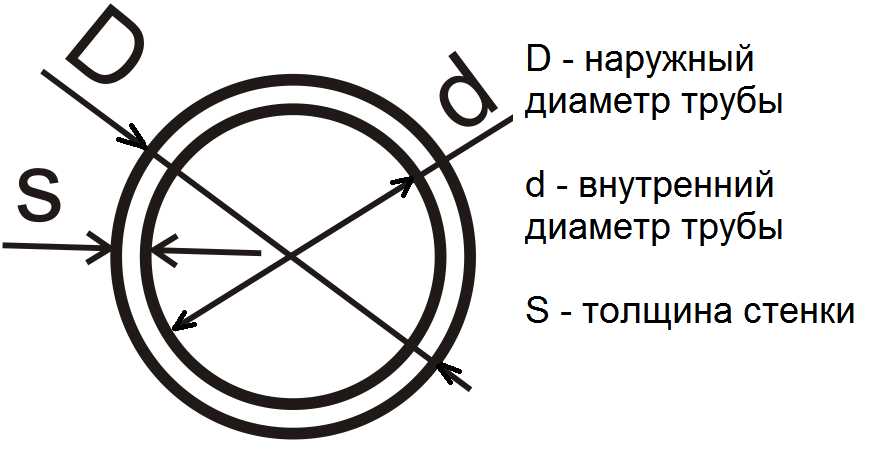
If on the contrary, there is an internal diameter and wall thickness, but an external one is needed - to the existing value we add twice the thickness of the stack.
With radii (denoted by the letter R) it is even easier: half of the diameter: R = 1/2 D. For example, we find the radius of a pipe with a diameter of 32 mm. Just 32 divide by two, we get 16 mm.
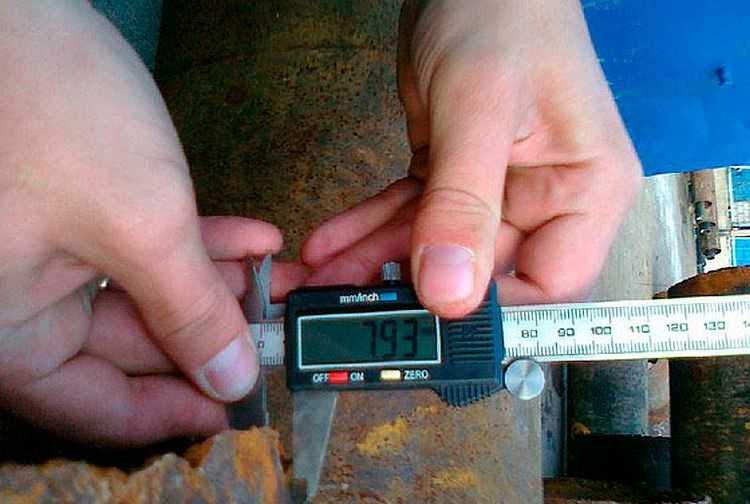

What if there is no technical data for the pipe? To measure. If you do not need special accuracy, the usual ruler is also suitable, for better measurements it is better to use a caliper.
Calculation of the pipe surface area
The pipe is a very long cylinder, and the surface area of the pipe is calculated as the area of the cylinder. For calculations, you need a radius (internal or external - depends on what surface you need to calculate) and the length of the segment that you need.
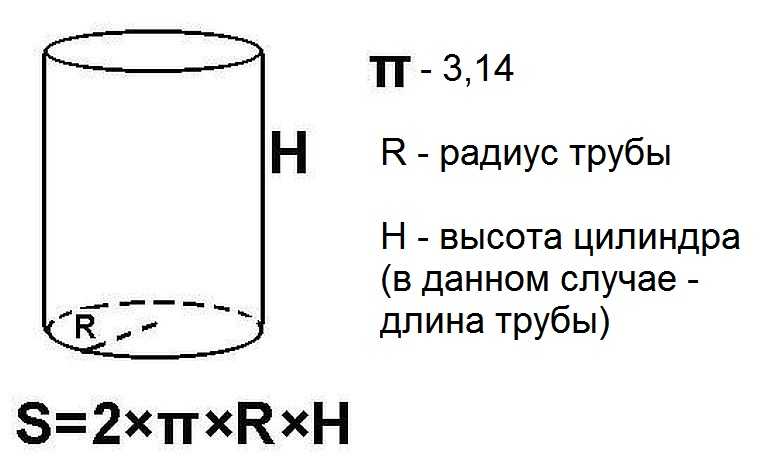
To find the lateral area of the cylinder, multiply the radius and length, multiply the resulting value by two, and then - by the number "Pi", we obtain the required value. If desired, you can calculate the surface of one meter, then you can multiply it by the desired length.
For example, calculate the outer surface of a piece of pipe length of 5 meters, with a diameter of 12 cm. First, we calculate the diameter: divide the diameter by 2, we get 6 cm. Now we need to bring all the values to one unit of measurement. Since the area is considered square meters, then centimeters are translated into meters. 6 cm = 0,06 m. Further we substitute everything in the formula: S = 2 * 3,14 * 0,06 * 5 = 1,884 m2. If you round, it will be 1.9 m2.
Calculation of weight
With the calculation of the weight of the pipe, everything is simple: you need to know how much the running meter weighs, then multiply this by the length in meters. The weight of round steel pipes is in the reference books, since this type of rolled metal is standardized. The weight of one running meter depends on the diameter and thickness of the wall. One thing: the standard weight is given for steel with a density of 7.85 g / cm2 - this is the kind that is recommended by GOST.
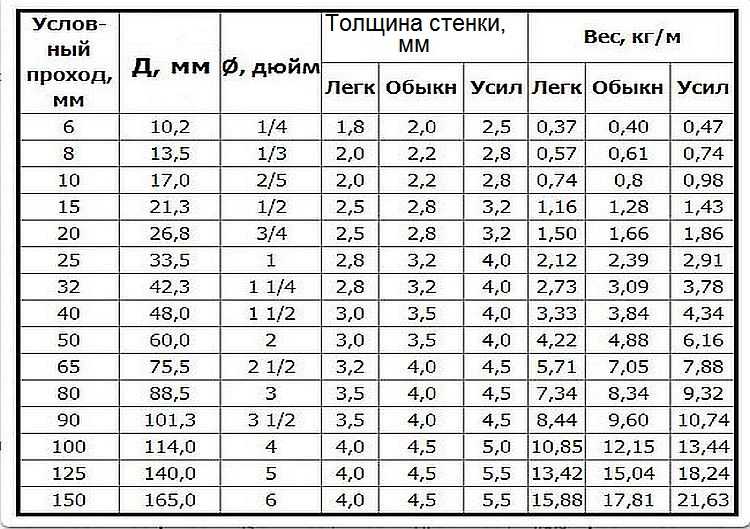
In the table D - the outer diameter, the conditional pass - the inner diameter, And one more important point: the mass of ordinary rolled steel is indicated, galvanized by 3% heavier.
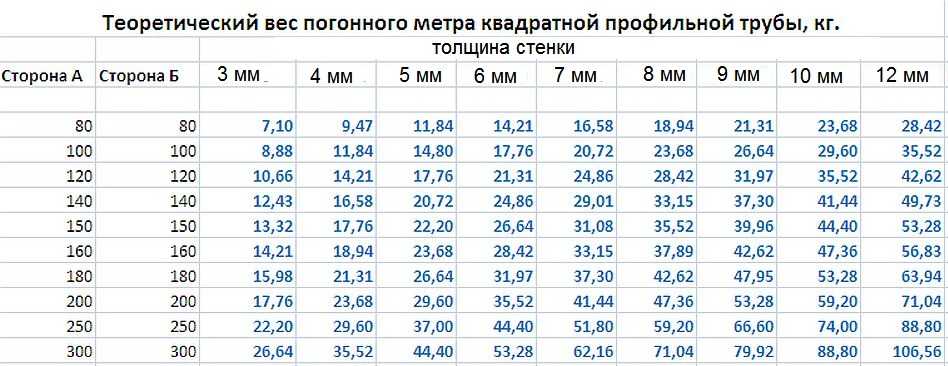
How to calculate the cross-sectional area
For example, the cross-sectional area of a pipe of 90 mm diameter. We find the radius - 90 mm / 2 = 45 mm. In centimeters it is 4.5 cm. We squeeze into a square: 4.5 * 4.5 = 2.025 cm 2, substitute S = 2 * 20.25 cm 2 = 40.5 cm 2 in the formula.
The sectional area of the profiled pipe is calculated by the formula of the area of the rectangle: S = a * b, where a and b are the lengths of the sides of the rectangle. If the cross section of the profile is assumed to be 40 x 50 mm, we obtain S = 40 mm * 50 mm = 2000 mm 2 or 20 cm 2 or 0.002 m 2.
How to calculate the volume of water in the pipeline
When organizing a heating system, you may need a parameter such as the amount of water that will fit in the pipe. This is necessary when calculating the amount of coolant in the system. For this case, a cylinder volume formula is needed.
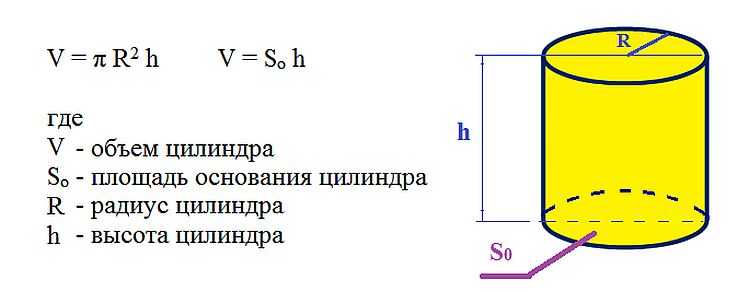
There are two ways: first calculate the cross-sectional area (described above) and multiply it by the length of the pipeline. If we count everything according to the formula, we need the inner radius and the total length of the pipeline. Calculate how much water will fit in the system of 32 millimeters long pipes of 30 meters.
First we translate millimeters into meters: 32 mm = 0.032 m, find the radius (divide in half) - 0.016 m. Substitute in the formula V = 3,14 * 0,016 2 * 30 m = 0,0241 m 3. It turned out = slightly more than two hundredths of a cubic meter. But we are accustomed to measuring the volume of the system in liters. To convert cubic meters into liters, we must multiply the figure by 1000. This yields 24.1 liters.
Occurrence of malfunctions in a water, gas or sewage system often involves installing pipes - replacing a fragment of an old pipe or installing a new one. When performing such work, you will need the skills to determine the diameter of the pipes of your system with improvised tools. When installing a new water supply system, it is also necessary to accurately determine the dimensions of old pipes in order to determine the choice of new plastic or metal-plastic pipes.
Of course, there are special tools for performing such measurements, for example, a laser meter, ruler-zircom meter and others. But what if you are not a professional professional, and there are no such precision instruments in your home tool set? How to measure the diameter of the pipe in another way?
Before answering this question, it is useful to know in which units these indicators are measured. The value of the pipe diameter is usually measured in inches. One inch is equal to 2.54 centimeters.
When working with a pipe, the measurement will be subject to both internal and external diameter. The outside diameter of the pipe is important due to the fact that its value is taken into account when threading and creating threaded connections. The outer diameter is in direct proportion to the thickness of the pipe walls. The size of the wall thickness is the difference between the outer and inner diameter of the pipe.
From words to deeds
There are several ways of measuring pipe diameters, which differ in their characteristics, depending on the conditions that are important to take into account in order to avoid mistakes. The choice of a particular metering method often depends on the accessibility to the metering object. Let's consider some of them.
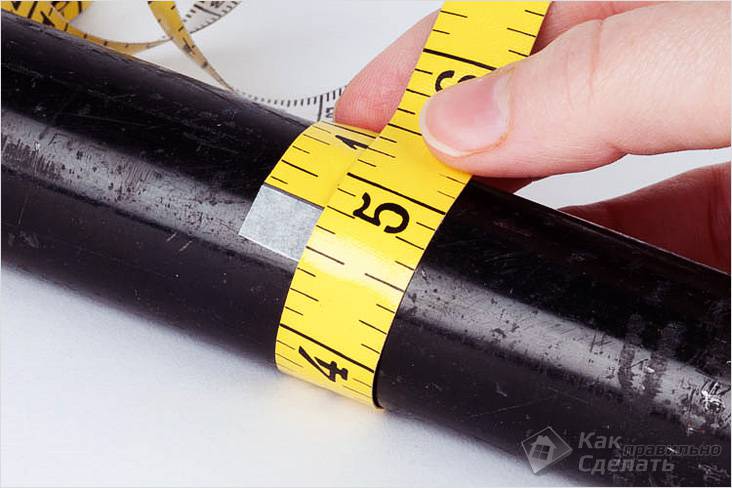

Most commonly, a well-known caliper is used to measure the diameter of a pipe. But you may not have it or if you have a large pipe diameter to measure with its help is not possible. In this case, the simplest set of tools and knowledge is used:
- flexible ruler (according to the type of measuring tape used in the sewing business);
- roulette;
- school knowledge of the Pi number (it is 3.14).
With a similar set of tools, it is possible to measure the diameter of not only the pipe, but also of any other round object - rod, column or garden bed.
We need to do only one measurement - to determine the length of the circumference of the pipe using a tape measure or a flexible ruler. To do this, centimeter tape or roulette is placed on the surface of the pipe in its widest part. The resulting value of the circle should be divided by 3.14. For more accurate dimensions, a value of 3.1416 is used.
It should be noted that the import of pipes is accompanied by documentation, in which the pipe diameters in inches are already indicated. To translate these values into centimeters, multiply them by 2.54. Similarly, for the reverse translation of centimeters per inch - multiply by 0.398.

The measurements are carried out using a caliper with no mathematical calculations. The condition is full accessibility to the pipe. This method is suitable for measuring accessible pipes of small diameter (not more than 15 cm). To measure the legs of the caliper, they are applied to the end of the tube and tightly clamped on the outer walls. The obtained value on the scale of the caliper is accurate to the tenth of a millimeter and will be the outer diameter of the tube.

If the end part of the pipe is not available for measuring, that is, when the pipe is a mounted element of an already operating water or gas supply scheme, then the calipers are applied to the side surface of the pipe for gauging. In this case, an important condition for the measurement: the length of the legs of the caliper should exceed half the diameter of the pipe.
Measurement of a large diameter pipe

We have already mentioned the formula with the value above. Measurements of the circumference of a large pipe can be done with a cord or a tape measure, and then its diameter is determined by the formula D = L: 3.14, where: D - pipe diameter;
L is the circumference of the pipe.
For example, if the length of the circumference of the pipe measured by you is 31.4 cm, the pipe diameter will be D = 31.4: 3.14 = 10 cm (or 100 mm).
Measuring pipes using photography (copy method)

This non-standard method is used when completely unavailable to a pipe of any size. A ruler or any other object is applied to the pipe to be measured, the dimensions of which are known to any master beforehand (often in this case a matchbox with a length of 5 cm or a coin is used). Then this section of the pipe with the attached subject is photographed (except for the camera, in modern conditions, the use of a mobile phone is also available). The following calculations of the sizes are made from photographs: in the picture, the visual thickness in mm is measured, and then it is translated into real values, taking into account the scale of the photographs.
Determination of the inner diameter of an accessible pipe

With the help of a conventional ruler or caliper, the thickness of the pipe wall at its cut is measured. This value, multiplied by 2, is subtracted from the values of the outer diameter. The value obtained will be equal to the inner diameter of the tube.
Monitoring of the parameters of pipes in production conditions

Outer diameter of tap water or sewer pipes in the conditions of large-scale production are controlled and verified using a more complicated formula: D = L: 3.14 - 2Δp - 0.2 mm.
In this formula, in addition to the already known values, the Δp symbols represent the thickness of the roulette web in mm, which you use to measure the diameter, and "0.2 mm" from the formula are the allowable deviations taking into account the fitting of the tape measure to the pipe. The allowable deviation value for pipes with a cross section of 200 mm is ± 1.5 mm.
When measuring large diameter pipes, the permissible deviations are measured in percent. Example, for products measuring from 820 to 1020 mm, the tolerance is 0.7%. Such measurements use a measuring unit based on ultrasound.
The thickness of the pipe walls in large production facilities is measured with a caliper with a scale division of 0.01 mm. The permissible deviation from nominal thickness in the direction of reduction should not exceed 5%.
The values of the curvature of the pipe, which must not exceed 1.5 mm per running meter of pipe length, are also subject to control. The total curvature of the products in relation to its length should not be more than 0.15%. The ovality of the pipe ends is determined by the ratio of the difference between the largest and smallest diameter to the nominal diameter of the pipe.
The value of this parameter should not exceed 1% for pipes with a wall thickness of up to 20 mm and not more than 0.8% for walls above 20 mm.
The ovality of the pipe can be determined by measuring the diameter of the pipe end with the help of an indicator bracket or caliper in two mutually perpendicular planes.
Simple school knowledge and careful use of simple tools will greatly simplify your task - how to measure the diameter of the pipe with improvised means.
Video
We suggest watching a video about working with measuring instruments.
