In the repair and construction of houses, many materials are used, but there are among them those that have covered themselves with unfading fame. Take, for example, fiberboard. What it is?
The name stands for "fibreboard". This sheet material, which is produced by pressing wood chips with the addition of various types of binding components.
As a rule, synthetic polymeric resins are used in the last incarnation. In addition, they include various substances that impart hydrophobicity properties to the finished material.
The most expensive (and therefore more often used) ceresin and paraffin. Often the composition is added antiseptic additives. Because of them, mold does not practically grow on fiberboard. What it is? Most often in the role of such an antiseptic additive are phenols, which successfully prevent the development of fungi and destroy their spores.
Produced in two ways: dry and wet. However, recently there were intermediate methods: wet-dry and semi-dry.
The cheapest method is dry, when the fiberboard (what it is, we have already said) is formed from wood chips in ordinary conditions and without wetting it with water. The board is pressed at high temperature and pressure.
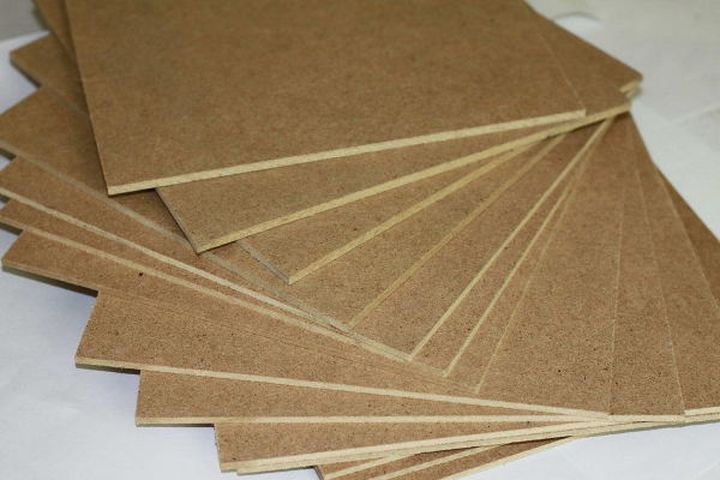 The resultant material is characterized by low cost, considerable porosity and lightness. Its moisture content is only 6-8%.
The resultant material is characterized by low cost, considerable porosity and lightness. Its moisture content is only 6-8%.
The wet method consists of the same steps, but the wood chips are sent to the pressing, being moistened with water. After leaving the press chamber, the material is cut into separate sheets and sent to the dryer. Such panels of fiberboard have humidity already within 70%. Because they are more powerful, but more durable.
The semi-dry method is similar to the first method, which is described above. The only difference is that before feeding to the compact, the chips are watered, so that the moisture content of the resulting material is 16-18%.
The wet-dry method differs from all of the above in that, first, a plate is formed from the water impregnated with water, then it is fed into the drying plant and only then sent to the hot pressing procedure. The result is a fiberboard plywood, which is actually 0%.
We note that we are not doing quite right when we speak of "chips". The fact is that this shaving, with the help of special machines, is first triturated into fibers, from which the fabric of finished panels is already formed.
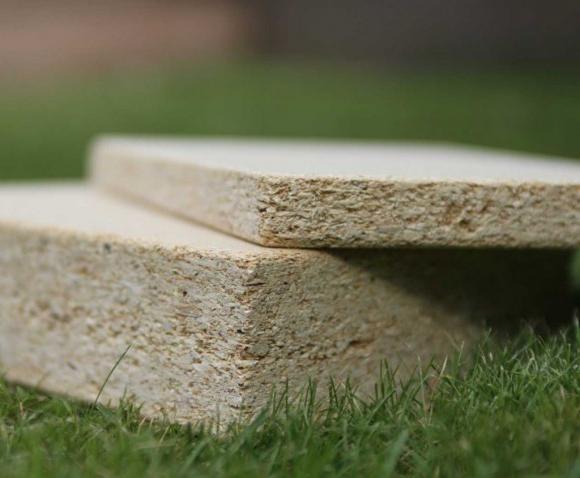 In recent years, a refined fiberboard has been used much more often. When manufacturing such panels, a multi-layer coating is applied to their surface. At the first stage the plate is covered with a special primer layer, which creates a reliable base. It prints a picture that simulates the usual surface of a tree.
In recent years, a refined fiberboard has been used much more often. When manufacturing such panels, a multi-layer coating is applied to their surface. At the first stage the plate is covered with a special primer layer, which creates a reliable base. It prints a picture that simulates the usual surface of a tree.
Such a plate is practically not afraid of moisture, and also abrasion. To harden the surface in this case, a special lacquer is used.
So we told you about DVP. What is it, you now know. Because of the cheapness and strength properties of this material, it is often used not only in the furniture industry, but also in the construction industry.
These sheet sawn goods are in great demand among buyers because of low cost and availability in processing by the simplest, household tool, that is, that the owner is always at hand. In the process of construction, restoration or repair, if everything is done on their own, they are really irreplaceable.
But the erroneous opinion of people who are not particularly versed in varieties of the same type of products, that the fiberboard and chipboard is almost the same, often leads to the fact that over time it becomes clear - the choice of the material was done incorrectly. So is there a difference between a fiberboard and a particle board, and if so, in what way and how much is it fundamentally?
The imaginary identity of particleboard and fiberboard is that wood fractions (or components based on it) are used as raw materials in the production of these boards. A difference, and very significant - especially the manufacture of plates, more precisely, in their structural composition. That's what determines the main performance characteristics of the samples.
Components
- Wood shavings, which follows from the name.
- Sawdust.
- Resin (mainly, formaldehyde), which serves as a binder for bonding individual fractions.

Technology
The production of plates is done by pressing the initial mass at elevated temperatures.
Features of chipboard
On strength these plates surpass the products under the abbreviation of fiberboard. This is due to the fact that they are produced in a larger thickness (up to 5 cm), so they are able to withstand a load such that the wood fiber samples are deformed or broken.

- Insufficient density. Simply put, chipboard - the material is somewhat loose.
- Increased hygroscopicity.
- Rigidity. The tight fastening of the chipboard on an uneven substrate leads to the formation of cracks in the plate.
Examples of using
- Arrangement of "dry" screed.
- Installation of decking.
- As a continuous crate.
- To strengthen the base, vertically oriented.
- Erection of canopies, partitions, fences, decking, barns, furniture items (and in a number of other cases.

Limitations in the use of particleboard
- In conditions of constant dampness or systematic changes in humidity, the service life of the chipboard is sharply reduced.
- It is not necessary to use it for the erection of demountable / prefabricated structures. Constant re-installation of fasteners leads to the fact that the material on this segment begins to scatter, and screws or screws (if it's not about through drilling with fixation on a harder basis) at this point no longer hold.
The most reliable, durable and versatile in the application of chipboard - with a three-layer structure.
Fiberboard
Components
- Wood dust.
- The fiber is synthetic.
- Polymer additives. The individual properties of the fiberboard depend on their type. For example, paraffin helps to reduce the level of moisture absorption of the material.
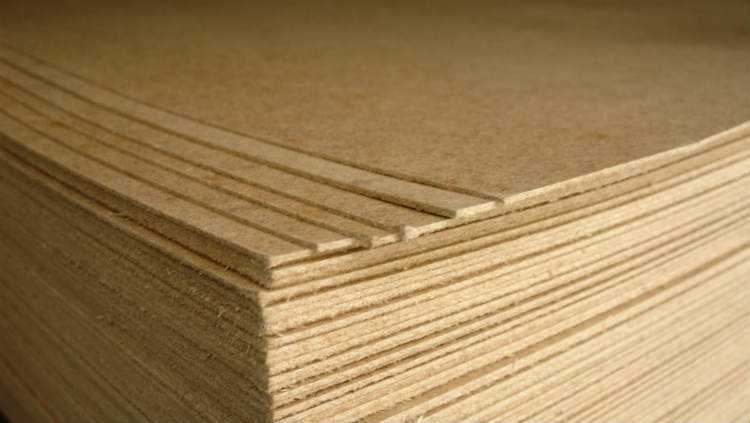

Technology
The same as for particleboard - "hot" pressing. But due to the fact that the finest fractions are used as raw material, the sheets are made thinner (from 2 to 10 mm).

Features of fiberboard
- Density is higher than that of chipboard.
- Flexibility to flex.
- Lower level of hygroscopicity.
- The price of the fiberboard sheet is lower than the chipboard with the same dimensions.
- High degree of heat and sound insulation. This DVP advantageously differs from chipboard.
- The assortment is more diverse, which can not be said about particle boards. Fibers are simple, colored or laminated. For each type of work, you can choose the best option.
Strength is inadequate. The fiberboard can not hold a significant load. This is understandable, given even the maximum sheet thickness (10 mm).
![]()
Examples of the use of hardboard
- Manufacture of various containers.
- Furniture manufacture - the bottom of drawers, rear walls.
- Installation of multi-level ceilings.
- "Spot" repair of withered wooden floors.
- Sheathing of frame structures.
- Additional insulation of surfaces. For example, metal garages.
There are no restrictions on the use of fiberboard for everyday life. The fiberboard is more protected from mechanical damage (scratches).
Particleboard and fiberboard differ in their specific properties, so their comparison by the principle better / worse is incorrect. A clear understanding of why the sheet material is purchased is the guarantee of the right choice.
Wood-based and fibreboard are very popular insulating materials. Formed by pressing wood waste, these sheets are an excellent protection against moisture and cold penetration and are actively used in construction.
In addition, chipboard and fiberboard is used in car building, furniture production, as well as in the manufacture of packaging and joinery. The high popularity of these materials explains the convenience of their use and low price.
Composition and characteristics of chipboard and fiberboard
A chipboard is a sheet material produced by the method of hot pressing of wood waste, preferably chips, mixed with a binder. As the latter, urea-formaldehyde resin is most often used.
Particleboard panels are divided into the following parameters:
- in accordance with the physical and mechanical properties, mark P-A, P-B;
- for the quality of the surface, varieties I and II are distinguished;
- by the type of surface, materials with an ordinary and fine-structured surface are isolated;
- by type of processing - polished and unpolished;
- on hydrophobic characteristics - simple and with increased water resistance;
- by the content of formaldehyde - in the classes E1 and E2.
Sheets of chipboard are available in several standard sizes, in accordance with GOST 27680.
The physical and mechanical characteristics of general purpose boards are as follows:
- density - 550-820 kg / m³;
- thickness swelling (24 hours) - 20% for P-A and 30% for PB;
- elasticity at a static bend - 1700-4000 MPa;
- impact strength - 4000-8000 J / m²;
- hardness - 20-40 MPa.

- Fibreboard is also a sheet material, but manufactured in a slightly different way: the fibers obtained by steaming and grinding wood raw materials are formed into a carpet and then subjected to compression. To improve performance, reinforcing agents such as synthetic resins, ceresin, paraffin, and antiseptics are added to the mass to form the sheets. Fibreboard is produced by wet and dry method: in the first case, a material with one-sided smoothness of the surface is obtained, in the second case, with a two-sided surface.
Depending on the type of face and strength, sheets of fiberboard are divided into the following brands:
- T - having an uninfected face;
- Т-С - with a face from fine-dispersed mass;
- Т-П - sheets with a tinted front surface;
- T-SP - with a tinted surface of finely divided mass;
- Т-В - having an ungraded surface and increased water resistance;
- T-CB - having a surface of finely dispersed mass and increased water resistance;
- HT - semi-solid sheets (with reduced density);
- CT - superhard sheets (with increased density);
- ST-C - superhard sheets with a surface of finely dispersed mass.
Fibreboard sheets are available in different sizes and depending on the brand can have different indicators of the basic physical and mechanical properties:
- density - 800-1100 kg / m³;
- ultimate strength at bending - 33-50 MPa;
- thickness swelling (24 h) - 13-23%;
- humidity - 3-10%
- water absorption by the front surface (24 h) - 6-11% - for plates with a surface of finely dispersed mass.
Sheet wood materials are actively produced all over the world.
A few words about the history of the production of chipboard and fiberboard
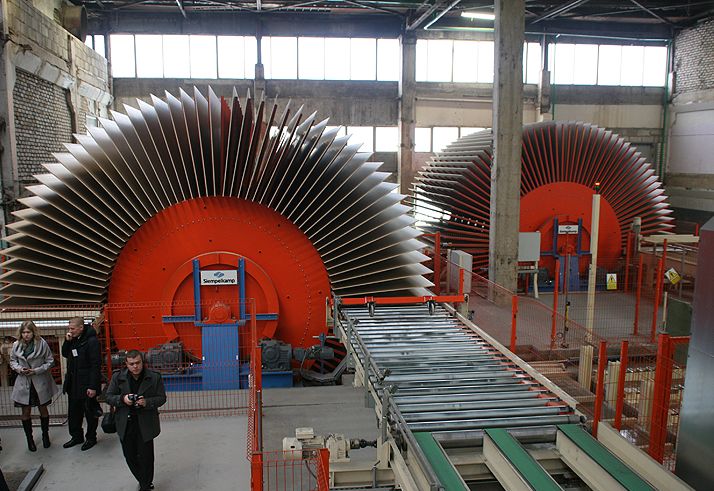

Produce DSP began in the 30s of the last century. The inventor of this material is the German Luftwaffe pilot Max Himmelheber, who offered him as an alternative to a more expensive plywood. Technology has become interested in Germany and Switzerland: in these countries, few forests and the opportunity to make the most of the waste from the woodworking industry looked very attractive. The first commercial sample was produced in the Bremen factory, and today the EAF is the most popular material, a worthy replacement for which is not yet expected. 
The annual output of particleboard in the world is about 55 million cubic meters, in Russia - about 5 million cubic meters.
There is a sharp competition in the market of particle board. The technology of their production is in continuous development. Manufacturers offer both unlined plates, and having a laminated surface. Many companies provide sawing and facing services for edges.
Fiberboard for the first time began to produce in the 20s in the United States. However, the first technological patent was registered in Sweden in 1931. Equipment for the production of sheets of fiberboard by Defibrator has become widespread in many countries around the world. Domestic production of this material started in Moscow in 1936. Now the production of fiberboard is one of the most actively developing and successful branches of the national economy.
Using wood-based panels for house insulation

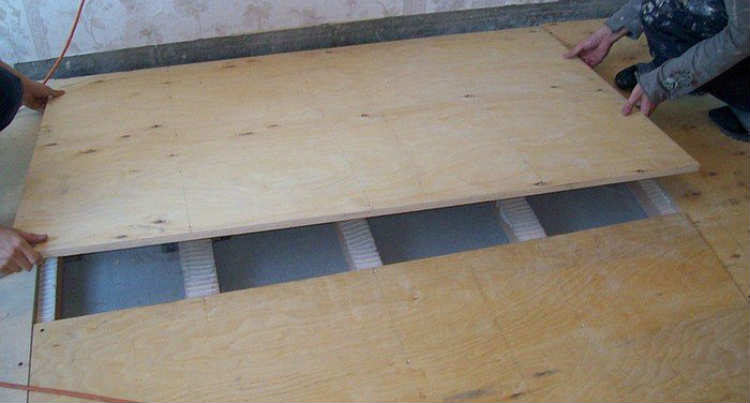
One of the most popular areas of use of sheets of chipboard and fiberboard is the warming and leveling of the floor.
Concrete floor - cold and uncomfortable. This is particularly noticeable in the winter time on the first floor of the house. In this situation, even warm slippers are not saved. On a concrete floor you can not lie down and play with children and pets. That's why before laying the finish flooring, whether it's linoleum, laminate or parquet, the floors are leveled and at the same time insulated by chipboard flooring. This simple procedure allows you to achieve a perfectly flat surface and provides warmth and comfort. 
Sheet wood materials are also actively used for warming the walls and roof of houses from the inside. You can use both soft and hard boards. Preliminarily, a frame of wooden slats is stuffed onto the walls, then soft plates, which act as a heater, are beaten, followed by hard ones, which will protect the layer of insulation from penetration of steam.
Particleboard and fiberboard are universal materials used for roofing, walls and flooring, making partitions and all kinds of structures. Construction and decoration of a private house is difficult to imagine without the use of wood sheets. Working with them is convenient and easy, but the result is never disappointing.
In this article: what is DVP, the history of creation; types of fiberboard, characteristics, field of application; the dignity of fiberboard; disadvantages of fiberboard.
Wood is the most popular and demanded material in construction and furniture production. History still remembers those times when for the construction of wooden houses or for the manufacture of wooden furniture hectares of forests were cut down.
Trees disappeared faster than they managed to grow new ones. And this is not surprising. After all, earlier only part of the tree trunk was used for building purposes. The rest simply rotted. In the hope of preserving the endangered forests, scientists began to think out how to use previously unsuitable wood - waste after wood processing. As a result of some efforts, a fiberboard appeared.
What is fiberboard?
Fibreboard is a material in the form of a rectangular sheet, obtained by the method of hot pressing or drying of a fibrous mass formed in the form of a carpet.

History of the DVP
For the first time the fiberboard was patented in 1858 by the resourceful scientist Lyman. A few years later (in 1864) the technology for the production of fiberboard was improved by the scientist Munch. He developed equipment with the possibility of hot pressing. Plates have not yet been produced without the use of a binder.
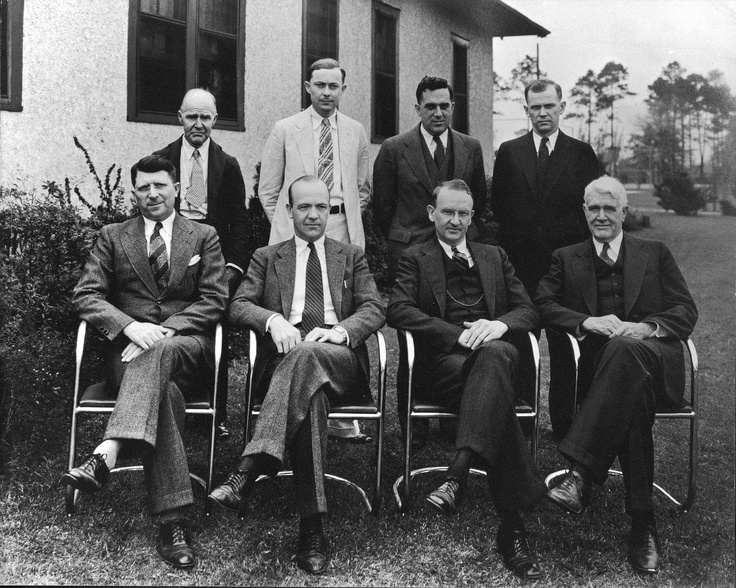
The "wet" method of obtaining fiberboard was opened in 1924 by an American Mason (pictured right in the front row). In his technology for creating fiberboard, he used a blowtorch, a printing press and an old car boiler. Thus, a high density fibreboard was produced, which Mason named in his honor - "Maysonite". The discovery of Mason marked the beginning of the industrial manufacture of fibrous plates.

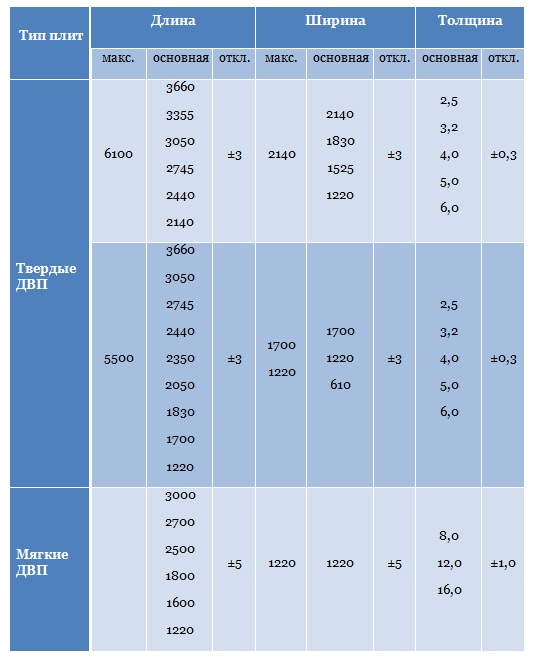
Types of fiberboard, characteristics, scope
Depending on the hardness, hardboard, super hard, solid, semi-solid, soft and medium density (MDF) are distinguished.
Super hard fiberboard
The density of superhard fiberboard varies from 950 to 1100 kg / m 3. They have good flexural and tensile strengths. Fibreboard with these characteristics is used as an electrical insulation material for the manufacture of panels and flaps. They are also used in the installation of floors as a heat and sound insulation material and the cladding of external doors.

Hardboard
The density of solid fiberboard is approximately 850 kg / m 3. Such fiberboard also has sufficient strength in bending and stretching. They are used mainly in the production of furniture - they go to the back walls of cabinets, drawers, etc. In construction, solid fiberboard is used as a covering material for interior walls with their subsequent painting.
In addition to finishing with paint and varnish materials, the slabs can be ennobled with synthetic PVC-based films and melamine films (synthetic veneer). As a result, the surface of the fiberboard can be matte, glossy, pigmented or imitate the texture of wood.

Semi-solid fiberboard
The density of semi-solid fiberboard is 400-800 kg / m 3. The strength of bending and stretching is about 2 times lower than that of hard and super hard fiberboard. Semi-solid fiberboards have found their application in furniture production as the back walls of cabinets, as well as in the construction sphere - the substrate for the installation of floors. In addition, semi-solid fiberboard is used as a packaging material.

Soft Fibreboard
The density of soft fiberboard depending on the brand varies from 100 to 400 kg / m 3. They are made from wood waste without adding a synthetic binder, which makes the material environmentally safe, including for people with allergies.
Soft hardboard mainly serve for heat and sound insulation of walls, ceilings and ceilings. They are used for covering walls and ceilings. Soft Fiberboard is the main competitor of drywall. But unlike gypsum cardboard it is more lightweight, flexible and convenient in mounting material.
Also, a soft fiberboard is used as a backing layer in the installation of floors, leveling significant defects in the base. Plates are used as a substrate for a laminate, parquet or linoleum.

MDF (medium density plates)
MDF is a kind of semi-solid fiberboard, but occupies a special place among its species. MDF panels are a relatively new material. But, despite this, he won the respect of builders and furniture makers. And this is understandable why. The density of MDF is 700-800 kg / m 3, and the bending strength is almost the same as that of a solid fiberboard, and approximately 2 times higher than that of a traditional chipboard!

MDF is easy to handle - sawing, milling and drilling.

The field of application of MDF is very wide. Plates are made of molded products - skirting boards, fillets, platbands, etc. MDF is used in the laying of rough floors, as wall and ceiling panels. Plates are used in the manufacture of interior doors. A high-density MDF (HDF) produces a laminate.

In addition, MDF produces: perforated decorative plates, T-beams, lathing for roofs, window sills, facades of cabinet furniture and much more.

Advantages of fiberboard
- Water resistance. Hard wood fiber boards are produced with increased water resistance, which makes it possible to use them in exterior and balcony doors.
- Durability. Fibers have a long service life.
- Low cost. The price for the slab, depending on the type of fiberboard, thickness and dimensions starts from 150 rubles per sheet.
- high heat and sound insulation properties;
- light weight and ease of handling.
Disadvantages of fiberboard
- a narrow area of application of a separate type of fiberboard (except for MDF);
- toxicity of some types of fiberboard in connection with the content of formaldehyde. Therefore, when processing the fiberboard, personal protective equipment should be used - a dust mask and goggles. Also, work should be carried out in a well-ventilated area.
Fibreboard is a building material consisting of pressed wood fiber under high pressure. It is successfully used in furniture production, in construction, and in repair work. Let us consider in more detail the varieties and properties of all types of fiberboard.
Main properties and technical characteristics of fiberboard
The properties of fiberboard can be attributed to the following:
- This material is not subject to deformation and does not warp from time to time;
- High moisture resistance;
- High strength and durability;
- Ecological compatibility. The fiberboard does not emit harmful substances.
According to GOST standards, the main technical properties of fiberboard are as follows:
- Density from 100 to 1100 kg / m3;
- The limiting operational humidity is 3-12%;
- Thermal conductivity 0.046 - 0.093 W / mK.
It is worth noting that the fiberboard does not swell for a long time at an air humidity of over 50%, as well as during a long immersion in water.
Varieties of fiberboard
In total, there are five types of fiberboard, differing in technical characteristics and scope.
Soft porous plate of fiberboard
In most cases, it is used as a heater and soundproof material. In this case, the slab is used as a substrate for floor or wall materials. The maximum thickness of fiberboard is not more than 25 mm, and density is 350 kg / m3. The main drawback is the low strength of the building material. The soft fiberboard is divided into three brands: M1, M2 and M3.
Semi-solid fiberboard. Widely used in furniture production: from it the back walls of cabinets and the bottom of kitchen boxes are made. Density - up to 850 kg / m3, thickness - up to 12 mm. Brand - NT.
Hardboard
Used for the manufacture of panel doors. The main feature is the low porosity of the building material. Density - up to 800 - 1100 kg / m3, thickness - up to 6 mm. Brands - Т, Т-В, Т-П, Т-С, Т-СП.
Super hard fiberboard of increased strength. It is used for the manufacture of interroom doors, partitions, arches. Density - from 950 kg / m3, thickness - up to 5 mm. Brand - ST.
Noble fiberboard
Officially it is not described in GOST, companies independently develop its standards. This building material combines the best properties of all four varieties. Plates can be painted or laminated and used as furniture lining or decorative panel.
In conclusion, it is worth noting the basic rules of storage Fiberboard . The main of them - the plates should lie on a flat surface in order to avoid deformation. If the fiberboard is stored on the street, it must be covered with a protective moisture-proof material.
Find out more about moisture-resistant chipboard in our next article.
