In the cold season, heating is the most important communication system, which is responsible for comfortable living in the house. Heating batteries are part of this system. The total temperature regime of the room will depend on their number and area. Therefore, the correct calculation of the number of radiator sections is the guarantee of effective operation of the entire system, plus the fuel economy used to heat the coolant.
In this article:
What you need for self-settlement
What you need to consider:
- the size of the rooms where they will be installed;
- the number of windows and entrance doors, their area;
- materials from which the house is erected (in this case walls, floor and ceiling are taken into account);
- location of the room with respect to the sides of the world
- technical parameters of the heating device.
If you are not an expert, it will be very difficult to calculate by yourself using all the listed criteria. Therefore, many private developers use a simplified methodology, which allows you to calculate only the approximate number of radiators for the room.
If you want to make accurate calculations, use the calculation calculations for SNiP.
The calculation procedure for SNiP
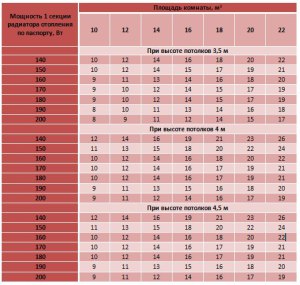
Table of approximate calculations
In SNiPe it is stipulated that the optimal variant of the required number of radiator sections depends on the indicator of the thermal energy that they allocate. It should be equal to 100 W per 1 m² of the room area.
For the calculation, the formula is used: N = Sx100 / P
- N is the number of battery sections;
- S is the area of the room;
- P is the capacity of the section (this figure can be seen in the product passport).
But since in the calculation additional parameters should be taken into account, new variables are added to the formula.
Amendments to the formula
- If the house is installed plastic windows, you can reduce the number of sections by 10%. That is, a coefficient of 0.9 is added for the calculation.
- If ceiling height is 2.5 meters, the coefficient is equal to 1.0. If the ceiling height is greater, the coefficient increases to 1.1-1.3
- The number and thickness of the outer walls also affects this parameter: the thicker the wall, the lower the coefficient.
- The number of windows also affects heat loss. Each window adds to the coefficient of 5%.
- If a heated attic or an attic is organized above the room, it is possible to reduce the number of sections in this room.
- Corner room or room with balcony add to the formula an additional 1.2 coefficients.
- Hidden in a niche and closed by a decorative screen, the batteries add to the final figure of 15%.
Using additional corrections, you will find out how many sections you need to put in each room. And already without difficulty you will be able to find out how many radiators you need per one square meter.
How to calculate the number of sections: an example on cast-iron batteries

We calculate how many radiator cast iron sections should be installed in a room with two double-chamber plastic windows with a ceiling height of 2.7 m, the area of which is 22 m².
The mathematical formula: (22х100 / 145) х1,05х1,1х0,9 = 15,77
We round the received number to the whole - we get 16 sections: two batteries for each window with 8 sections each.
Explanation of the coefficients:
- 1,05 is the 5% premium for the second window;
- 1.1 is an increase in the height of the ceiling;
- 0,9 - this is a reduction in the installation of plastic windows.
Let's put it bluntly - this option, as already mentioned above, is difficult for a simple consumer. But there are simplified ways, which will be discussed below.
The influence of the material on the number of sections

The developers often have a question, in the context of the material from which they are made. After all, steel, cast iron, copper, aluminum has its own heat transfer coefficient, and this must also be taken into account in the calculations.
As already mentioned above, this parameter can be found in the product passport.
For example:
- The cast iron radiator has a heat output of 145 W.
- Aluminum - 190 watts.
- Bimetallic - 185 watts.
From this list, we can conclude that the number of aluminum sections will be used less than, say, cast-iron ones. And more than bimetallic. And this is for all the same other parameters, as mentioned above.
Calculation of the area of the room
Here, the same formula is used - N = Sx100 / P, with one caveat: height of ceilings should not exceed 2.6 m.
We use the parameters that were taken into account in the example with a cast-iron battery, but we will make some changes regarding the number of windows.
- For the sake of simplicity, let's take just one window: 22x100 / 145 = 15,17
You can round down - up to 15 sections, but keep in mind that the missing section can lower the temperature by a couple of degrees, which will lead to a general decrease in the comfort of being in the room.
Calculation of the room volume
In this case the main indicator is thermal energy, equal to 41 W per 1 m³. This is also a standard value. However, in rooms with double-glazed windows a value equal to 34 W is used.
- 22х2,6х41 / 145 = 16,17 - round, we get 16 sections.
Pay attention to one very subtle nuance.
Producers, indicating in the product passport the value of heat transfer, take it into account by the maximum parameter. In other words, they believe that the temperature of the hot water in the system will be maximum. In life, this does not always correspond to reality. Therefore, we strongly recommend rounding the end result to a larger side.
And if the power of the section is determined by the manufacturer in a certain range (a plug between two indicators is installed), then choose a smaller indicator for making calculations.
Calculation by eye
Heat loss in an apartment building
This option is suitable for those who do not understand anything at all in mathematical calculations. Divide the area of the room by a standard figure - 1 section by 1.8 m².
- 22 / 1,8 = 12,22 - round, we get 13 sections.
Keep in mind: the height of the ceiling should not exceed 2.7 m. If the ceiling is higher, you will have to take it for a more complicated formula.
As you can see, it is possible to calculate the necessary number of sections for a room in different ways. Want to get the exact result - use the calculation of SNIP. You will not be able to determine the additional coefficients - choose any other simplified version.
There are several different ways to determine the required capacity of the heaters. Calculation of radiators in the apartment can be carried out by complex methods, which involve the use of fairly complex equipment (thermal imagers) and specialized software.
Calculation of the number of radiators can be done on their own, based on the required capacity of the heaters per unit area of the room, which is heated.
Conditional-schematic calculation of power
In the zone of moderate climate (the so-called average climatic zone), the adopted norms regulate the installation of heating radiators with a capacity of 60 - 100 W per square meter of the room. This calculation is also called area calculation.
In the northern latitudes (not the Far North, but the northern regions that lie above 60 ° N), power is assumed to be between 150 and 200 watts per square meter.
The capacity of the boiler is also determined from these values.
- Calculation of the power of heating radiators is carried out by this method. It is this capacity that heating radiators should have. The heat transfer values of the cast-iron batteries are in the range of 125-150 W per section. In other words, a room of fifteen square meters can be heated (15 x 100/125 = 12) by two six-section cast iron radiators;
- Bimetal radiators are calculated in this way, since their power corresponds to the power (in fact, it is slightly larger). The manufacturer must specify these parameters on the factory packaging (in extreme cases, these values are given in standard tables according to specifications);
- Calculation of aluminum radiators is carried out in the same way. The temperature of the heating devices themselves is largely related to the temperature of the coolant inside the system and the heat transfer values of each individual radiator. The overall price of the device is also connected with this.
There are simple algorithms, which are called the general term: a calculator for calculating radiators for heating, in which the above methods are used. The calculation by yourself with such algorithms is quite simple.
Additional factors
The above values of the power of the radiators are given for standard conditions, which are corrected with the help of correction factors depending on the presence or absence of additional factors:
- The height of the room is considered standard if it is 2.7 m. If the ceiling height is greater or less than this conventional standard power of 100 W / m2 multiplied by the correction factor, which is determined by dividing the height of the room by a standard (2.7 m).
For example, the coefficient for a 3.24-meter-high room is 3.24 / 2.70 = 1.2, and for a room with ceilings of 2.43 - 0.8.
- Number of two external walls in the room (corner room);
- Number of additional windows in the room;
- Presence of two-chamber energy-saving double-glazed windows.
Important!
Calculation of heating radiators in this way is better done with some margin, since such calculations are rather approximate.
Calculation of heat loss
The above calculation of the heat output of the radiators does not take into account many determining conditions. For more accurate, it is necessary to first determine the heat loss values of a building. They are calculated on the basis of data on each wall and ceiling of each room, the floor, the type of windows and their number, the construction of doors, the plaster material, the type of brick or insulation material.
Calculation of heat transfer from radiator radiators based on 1 kW per 10 m2 has significant drawbacks, which are primarily related to the inaccuracy of these indicators, since they do not take into account the type of the building (detached building or apartment), ceiling height, the size of windows and doors .
The formula for calculating heat loss:
TP total = V x 0.04 + TP about x n o + TP d x n d, where
- TP total - total heat loss in the room;
- V is the volume of the room;
- 0,04 - standard value of heat loss for 1 m3;
- ТП о - heat loss from one window (the value is assumed to be 0.1 kW);
- n o is the number of windows;
- TP d - heat losses from one door (the value of 0.2 kW is assumed)
- n д - number of doors.
Calculation of steel radiators
Pst = ТПобщ / 1,5 х k, where
- Рст - power of steel radiators;
- TPobshch - the value of the total heat loss in the room;
- 1,5 - factor for adjusting the length of the radiator taking into account work in the temperature range 70-50 ° C;
- k - safety factor (1,2 - for apartments in a multi-storey building, 1,3 - for a private house)

Example calculation of a steel radiator
We proceed from the conditions that the calculation is carried out for placement in a private house of 20 square meters with a ceiling height of 3.0 m, in which there are two windows and one door.
The calculation instruction prescribes the following:
- TPobshch = 20 x 3 x 0.04 + 0.1 x 2 + 0.2 x 1 = 2.8 kW;
- Рст = 2,8 kW / 1,5 х 1,3 = 2,43 m.
Calculation of steel radiators by this method leads to the result that the total length of radiators is 2.43 m. Given the presence of two windows in the room, it will be advisable to select two radiators of suitable standard length.
The scheme of connection and placement of radiators
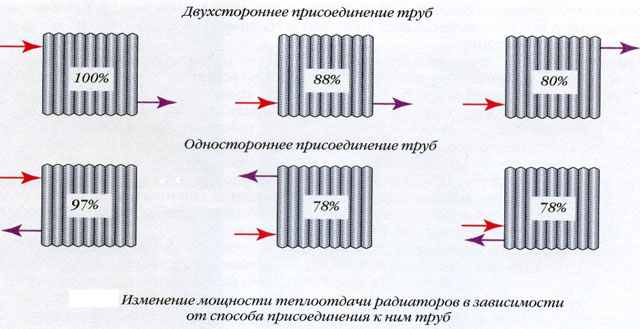
Heat transfer from the radiators depends on where the heater is located, as well as the type of connection to the main pipeline.
First of all, the radiators are placed under the windows. Even the use of energy-saving double-glazed windows does not make it possible to avoid the greatest heat loss through the light apertures. The radiator, which is installed under the window, heats the air in the room around it.

Heated air rises upward. In this case, a layer of warm air creates before the opening a thermal curtain, which prevents the movement of cold layers of air from the window.
In addition, cold air flows from the window, mixing with warm rising currents from the radiator, increase the overall convection throughout the room. This allows the air in the room to warm up more quickly.
In order to effectively create such a heat curtain, it is necessary to install a radiator, which would be at least 70% of the width of the window aperture.
The deviation of vertical axes of radiators and windows should not be more than 50 mm.
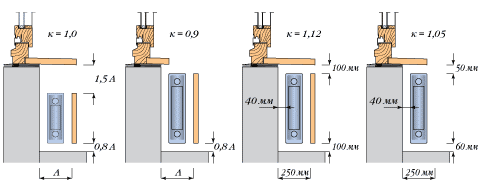
Important!
In the corner rooms, additional radiator panels must be placed along the outer walls, closer to the outer corner.
- When strapping radiators in which risers are used, they must be carried out in the corners of the room (especially in the outer corners of blind walls);
- With the trunk pipelines from opposite sides, the heat transfer of the instruments increases. From the constructive point of view, one-sided joining to the pipes is rational.
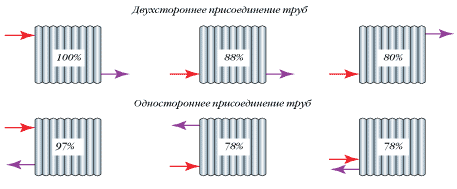
Important!
Radiators in which the number of sections is more than twenty should be connected from different sides. This is also true for such tying, when on one hitch there is more than one radiator.
The heat transfer depends also on the location of the places for supply and removal from the heaters of the coolant. More heat flow will be when the feed is connected to the top and the tap from the bottom of the radiator.
If the radiators are installed in several tiers, then in this case it is necessary to ensure a consistent movement of the coolant downwards in the direction of travel.
Video about calculating the power of heating devices:
Approximate calculation of bimetallic radiators
Almost all bimetal radiators are available in standard sizes. Non-standard should be ordered separately.
This somewhat facilitates the calculation of bimetal radiators.
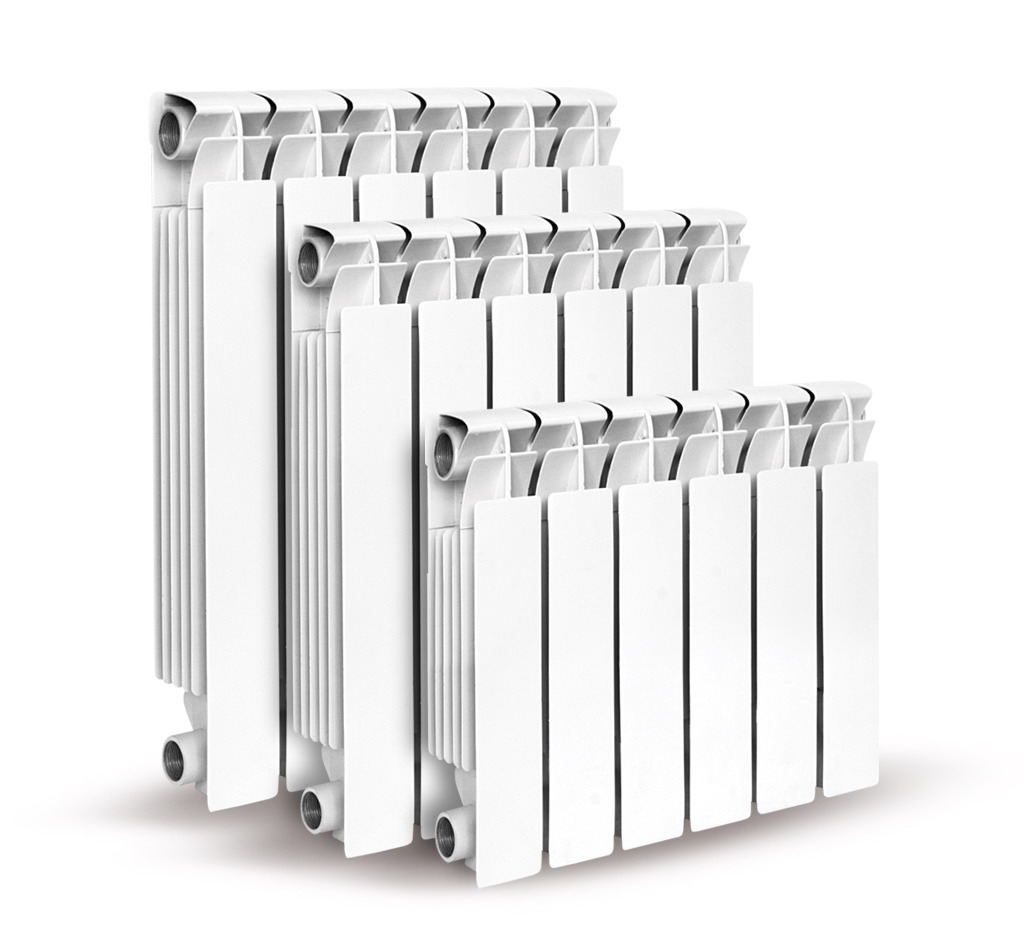

- At a standard height of ceilings (2,5 - 2,7 m) one section of a bimetallic radiator is taken at the rate of 1.8 m2 of a living room.
For example, for a room of 15 m2 the radiator must have 8 to 9 sections:
- For volumetric calculation of the bimetal radiator, the value 200 W of each section is taken for every 5 m3 of the room.
For example, for a room of 15 m2 and a height of 2.7 m, the number of sections for this calculation will be 8:
15 x 2.7 / 5 = 8.1
Important!
200 watts of standard power were adopted by default, as standard. Although in practice there are sections of different power from 120 W to 220 W.

Determination of heat loss using a thermal imager
Thermal imagers are now widely used for careful monitoring of the thermal characteristics of objects and determining the thermal insulation properties of structures. Using a thermal imager, a rapid survey of buildings is conducted to determine the exact value of heat losses, as well as hidden building defects and poor material quality.
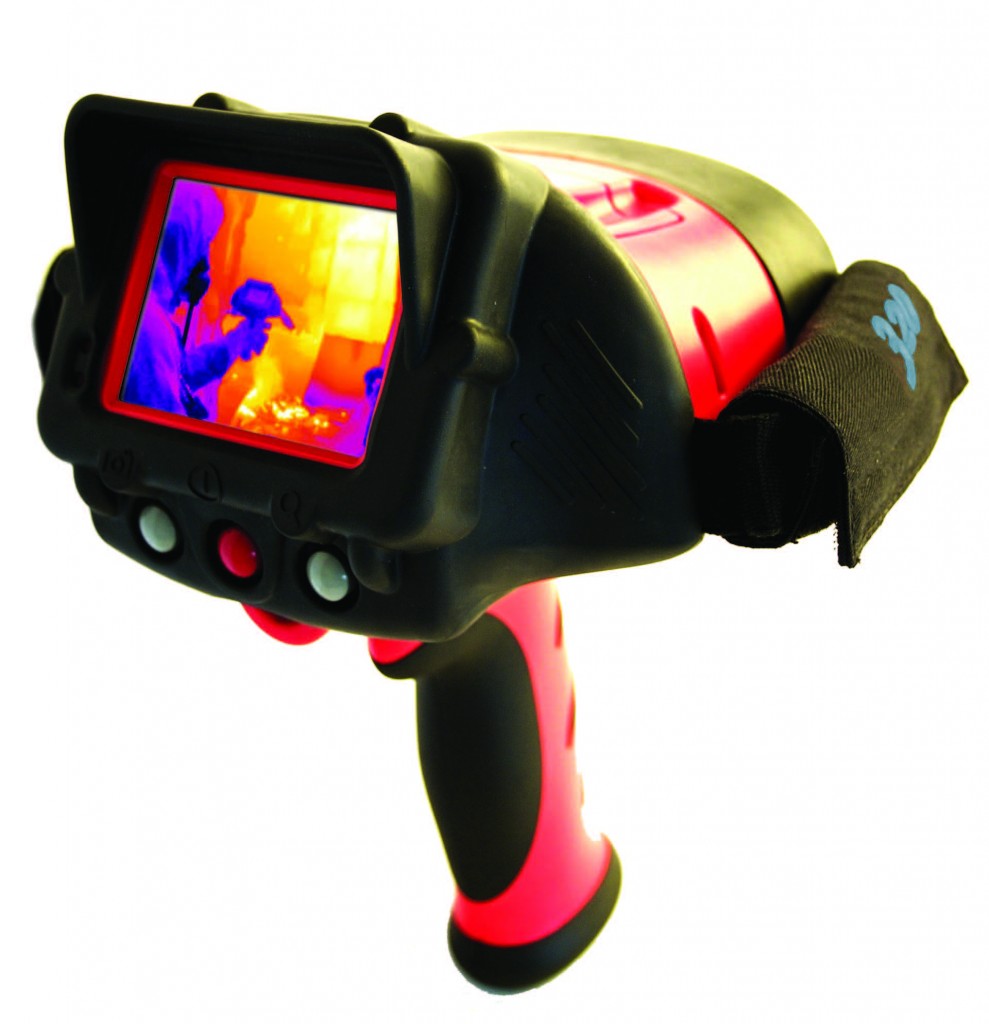

The use of these devices makes it possible to determine the exact values of the actual heat losses through the structural elements. Taking into account the given coefficient of heat transfer resistance, these values are compared with the standards. In the same way, the places of condensation of moisture and irrational piping of radiators in the heating system are determined.

conclusions
Calculation of the power of the radiator should be carried out, taking into account the many criteria on which the values of heat loss in the room depend.
The principle, which is adopted in calculating the power of heating devices, is suitable for all types of radiators. When calculating panel radiators, consideration is given to the method for recalculating the partition coefficient.
1.
2.
3.
When designing a heat supply system for a private house or apartment located in a new building, you need to know how to calculate the power of the radiators to determine the required number of sections for each room and utility rooms. The article presents several simple computational options.
Peculiarities of calculations
Calculating the power of the radiator is associated with a number of problems. The fact is that during the heating season the temperature outside the window is constantly changing, and accordingly the heat loss is different. So at 30 degrees of frost and a strong north wind, they will be much more than at -5 degrees, and even in windless weather.Many real estate owners are worried that the incorrectly calculated heat output of the heating radiators can lead to cold weather in the house, and in warm weather it will be necessary to keep open the window a whole day and thus heat the street (more in detail: "").
However, there is a concept called the temperature graph. Due to this the temperature of the coolant in the heating system varies depending on the weather in the street. As the temperature of the air on the street increases, the heat transfer of each of the battery sections increases. And if so, then with respect to any heating equipment, we can talk about the average value of heat transfer.
As for tenants of private households, after installing a modern electric or gas heating unit or heating using heat pumps, they do not have to worry about the temperature that the coolant circulates in the heating circuit contour.
The thermal equipment, created with the use of the latest technologies, allows to control it with the help of thermostats and adjust the capacity of the batteries in accordance with the needs. The presence of a modern boiler does not require control over the temperature of the coolant, but to install heat radiators the power calculation will still be required.
Procedure for calculating the power of radiators
All calculations related to the arrangement of the heating structure are inextricably linked with such a concept as thermal power. There are several options for calculating the power of the radiator. At the same time, it should be noted that this parameter is always indicated in the documents attached to them from the well-known and well-known manufacturers (read also: "").To calculate bimetal radiators or cast-iron batteries, based on the thermal power, it is necessary to divide the required amount of heat by 0.2 kW. As a result, the number of sections to be purchased will be obtained to provide room heating (in more detail: "").
If the cast iron radiators (see photo) do not have flushing valves, experts recommend taking 130-150 watts into account for each section, considering. Even when they initially give off more heat than is required, the contaminants that appear in them will reduce heat transfer.

As practice shows, it is desirable to mount batteries with a margin of about 20%. The fact is that in the event of extreme cold, excessive heat in the house will not be. Also, the choke on the piping will help to fight with increased heat output. The purchase of extra several sections and the regulator will not greatly affect the family budget, and the heat in the house will be provided in frosts.
The required value of the heat output of the radiator
When calculating a heating battery, you need to know the required heat output so that the house can live comfortably. How to calculate the power of a heating radiator or other heating appliances for the heat supply of an apartment or a house is of interest to many consumers.- The method according to SNIP assumes that one square of the area requires 100 watts.
But in this case it is necessary to take into account a number of nuances:
- Heat losses depend on the quality of thermal insulation. For example, to heat an energy-efficient house equipped with a heat recovery system with walls made of sip panels, the thermal power will need less than 2 times;
- the creators of sanitary norms and rules in their development were guided by a standard ceiling height of 2.5-2.7 meters, and this parameter can be 3 or 3.5 meters;
- this option, which allows calculating the power of the radiator and heat output, is correct only if the approximate temperature of 20 ° C in the apartment and on the street is 20 ° C. A similar picture is typical for the settlements located in the European part of Russia. If the house is located in Yakutia, much more heat will be required. - The calculation method, based on volume, is not considered difficult. For each cubic meter of the room, 40 watts of heat is required. If the size of the room is 3x5 meters, and the ceiling height is 3 meters, then 3х5х3х40 = 1800 watts of heat is required. And although the errors associated with the height of the premises in this version of calculations are eliminated, it is still not accurate.
- The specified method of calculation by volume, taking into account more variables, givesmore realistic result. The basic value is still the same 40 watts per cubic meter of volume.
When an accurate calculation of the heat output of the radiator and the required heat transfer value is made, it should be borne in mind that:
- one door to the outside takes away 200 watts, and each window - 100 watts;
- if the apartment is corner or face, the correction coefficient is 1.1 - 1.3, depending on the type of wall material and their thickness;
- for private households the coefficient is 1.5;
- for southern regions take a coefficient of 0.7 - 0.9, and for Yakutia and Chukotka apply an amendment from 1.5 to 2.
As an example for the calculation, a corner room with one window and a door in a private brick house measuring 3х5 meters with a three-meter ceiling in the north of Russia is taken. The average temperature outside the window in winter in January is -30.4 ° C.

- determine the volume of the room and the required power - 3х5х3х40 = 1800 watts;
- a window and a door increase the result by 300 watts, totaling 2100 watts;
- taking into account the angular location and the fact that the private house will be 2100x1.3x1.5 = 4095 watts;
- the former result is multiplied by a regional coefficient of 4095x1.7 and gets 6962 watts.
How to perform the calculation of radiators in an apartment? How many sections will be minimally necessary for a certain area of the room?
About simple and relatively complicated methods of calculation - this article.
Put aside the gas key and the Bulgarian. Today our tool is a calculator.
Disclaimer
This article is not aimed at heating engineers, but on the owners of an apartment or a private house, who are going to mount a heating system by their own hands. If so, the calculation instruction should be simple and understandable.
We will not use complex formulas and concepts such as "heat flow" and "thermal resistance of walls", trying to simplify the calculations as much as possible.
General Provisions
Any simple calculation method has a rather large error. However, from the practical point of view, it is important for us to ensure a guaranteed sufficient heat output. If it turns out to be more than necessary even in the peak of winter cold - so what?
In an apartment where heating is paid for by the area, the heat of bones does not break; and adjusting chokes and thermostatic temperature controllers are not something very rare and inaccessible.
In the case of a private house and own boiler, the price of a kilowatt of heat is well known to us, and it would seem that excessive heating will hit the pockets. However, in practice this is not so. All modern gas and are supplied with thermostats, which regulate the heat transfer depending on the temperature in the room.
Even if our calculation of the power of the radiators generates a significant error in the larger direction, we risk only the cost of a few additional sections.
By the way: apart from the average winter temperatures, extreme frosts occur every few years.
There is a suspicion that in connection with global climate change, they will happen more often, so that when calculating the radiators, do not be afraid to make a big mistake.
How to calculate the heat output of a heater
- For all electric heaters without exception, the effective thermal power is exactly equal to their electrical power rating.
Remember the school physics course: if no useful work is done (that is, moving an object with a non-zero mass against the gravity vector), all the energy spent goes to heating the environment.
- At the majority of radiators from decent manufacturers their thermal capacity is underlined in the accompanying documentation or on a site of the manufacturer.
Often, you can find even a calculator calculating the radiators for a certain volume of the room and the parameters of the heating system.
Here there is one subtlety: almost always the manufacturer calculates the heat transfer of the radiator - radiators, convector or fan coil - for a very specific temperature difference between the coolant and the room of 70C. For Russian realities, such parameters are often an unattainable ideal.
Finally, a simple, albeit approximate, calculation of the heat sink's power by the number of sections is possible.
Bimetal radiators
Calculation of bimetallic radiators of heating is repelled from the overall dimensions of the section.
Take the data from the site of the Bolshevik plant:
- For a section with an interaxial distance of the feeder of 500 millimeters, the heat transfer is 165 watts.
- For the 400 mm section, 143 watts.
- 300 mm - 120 watts.
- 250 mm - 102 watts.

Aluminum radiators
Calculation of aluminum radiators is based on the following values (data for Italian radiators Calidor and Solar):
- Section with an axis distance of 500 millimeters gives 178-182 watts of heat.
- With an interaxial distance of 350 millimeters, the heat transfer of the section decreases to 145-150 watts.
Steel plate radiators
And how to perform the calculation of steel radiators of plate type heating? They do not have sections, the number of which can be based on the calculation formula.
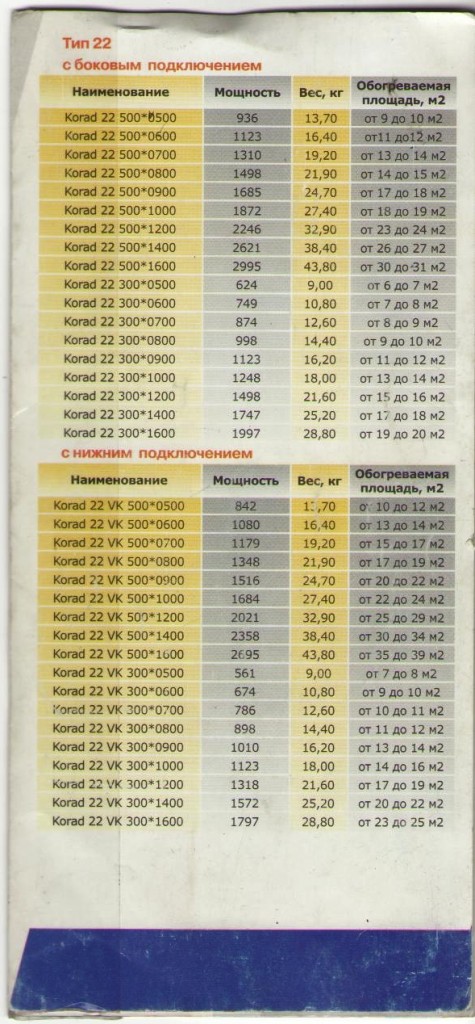
Here the key parameters are again the interaxial distance and the length of the radiator. In addition, manufacturers recommend taking into account the method of connecting the radiator: for different ways of tapping into the heating system, heating and, consequently, the thermal power can also differ.
In order not to bore the reader with an abundance of formulas in the text - we simply send it to the power table of the model row of radiators Korad.
Cast iron radiators
And only here everything is extremely simple: all the cast-iron radiators produced in Russia have the same interaxial distance of the feeds equal to 500 millimeters, and heat transfer at a standard temperature delta of 70C equal to 180 watts per section.
Half the work is done. Now we know how to calculate the number of sections or heaters at a known required heat output. But where do you get the very thermal power we need?
Calculation of heat output
We will consider several calculation methods that take into account a different number of variables.
By area
The calculation for the area is based on sanitary norms and rules, in which the Russian in white says: one kilowatt of heat output should fall on 10 m2 of the room area (100 watts per m2).
Clarification: when calculating a coefficient is applied, depending on the region of the country. For the southern regions it is 0.7-0.9, for the Far East 1.6, for Yakutia and Chukotka 2.0.
It is clear that the method gives a very significant error:
- Panoramic glazing in one thread will clearly give large heat loss in comparison with a solid wall.
- The location of the apartment inside the house is not taken into account, although it is clear that if nearby the warm walls of neighboring apartments - with the same number of radiators will be much warmer than in a corner room that has a common wall with a street.
- Finally, the main thing: the calculation is correct for the standard ceiling height in a Soviet-built house, equal to 2.5 - 2.7 meters. However, at the beginning of the 20th century, houses were built with a ceiling height of 4 - 4.5 meters, and stalks with three-meter ceilings also require an accurate calculation.
Let's still apply the method for a room measuring 3x4 meters located in the Krasnodar Territory.
The area is 3x4 = 12 m2.
The required heating power of heating is 12m2 x 100W x0.7 of the district coefficient = 840 watts.
At a power of one section of 180 watts, we need 840/180 = 4.66 sections. We figure, of course, rounded up to five.
Tip: in the Krasnodar Territory, the temperature delta between the room and the battery at 70C is unrealistic. It is better to install radiators with at least a 30% margin.

Simple calculation by volume

Calculation of the total volume of air in the room will clearly be more accurate because it takes into account the spread of ceiling heights. It is also very simple: for 1 m3 of volume you need 40 watts of power of the heating system.
Let's calculate the necessary power for our room near Krasnodar with a little refinement: it is in a stalinka in 1960 built with a ceiling height of 3.1 meters.
The volume of the room is 3х4х3,1 = 37.2 cubic meters.
Accordingly, the radiators should have a power of 37.2 × 40 = 1488 watts. Take into account the district coefficient 0.7: 1488x0.7 = 1041 watts, or six sections of cast iron horror under the window. Why horror? Appearance and constant leakage between sections after a few years of exploitation of delight do not cause.
If you recall that the price of a cast iron section is higher than that of an aluminum one, or - the idea of buying such a heating device really starts to cause a slight panic.
Refined calculation by volume
A more accurate calculation of heating systems takes into account more variables:
- Amount of doors and windows. The average loss of heat through a window of standard size is 100 watts, through the door - 200.
- The location of the room at the end or corner of the house will force us to use a factor of 1.1 - 1.3, depending on the material and the thickness of the walls of the building.
- Private houses use a coefficient of 1.5, since much more heat loss through the floor and roof. Above and below, it's not warm apartments, but a street ...
The base value is the same 40 watts per cubic meter and the same regional coefficients as in calculating the area of the room.
Let's perform the calculation of the heat output of the radiators for a room with the same dimensions as in the previous example, but we will mentally transfer it to the corner of the private house in Oymyakon (the average January temperature is -54C, the minimum during the observation period is 82). The situation is exacerbated by the door to the street and the window, from which cheerful reindeer herders are visible.
The base capacity, taking into account only the volume of the room, we have already fulfilled: 1488 watts.
The window and door will add 300 watts. 1488 + 300 = 1788.
A private house. Cold floor and heat leakage through the roof. 1788x1.5 = 2682.
The angle of the house will force us to apply a factor of 1.3. 2682x1.3 = 3486.6 watts.

Finally, the warm and affectionate climate of the Oymyakonsky ulus of Yakutia leads us to the idea that the result can be multiplied by a regional coefficient of 2.0. 6973.2 watts is required for heating a small room!
Calculation of the number of radiators is already familiar to us. The total number of cast iron or aluminum sections is 6973.2 / 180 = 39 sections with rounding. With a section length of 93 millimeters, the accordion under the window will have a length of 3.6 meters, that is, it will hardly fit along the longer of the walls ...

"Ten sections?" A good start! "- such a phrase resident of Yakutia will comment on this photo.
Conclusion
For more information on calculating heating systems, see the video at the end of this article. The author at last wants to make an official statement: in Oimyakon at will - not a foot. Warm winters!
